在C++ STL中的unordered_map
unordered_map是一种关联容器,它存储由键值和映射值组合形成的元素。键值用于唯一识别元素,映射值是与键相关联的内容。键和值都可以是任何类型预定义或用户定义的。简单来说,一个 unordered_map就像一个字典类型的数据结构,它将元素存储在自身中。它包含连续的对 (key, value),这允许基于其唯一键快速检索单个元素。
内部实现 unordered_map 使用哈希表,提供给 map 的键被哈希成哈希表的索引,这就是为什么数据结构的性能很大程度上取决于哈希函数,但平均来说,来自哈希表的搜索、插入和删除的成本是O(1)。
注意: 在最坏情况下,它的时间复杂度可能会从O(1)变成O(n),特别是对于大素数。在这种情况下,强烈建议使用 map 代替,以避免出现超时错误(TLE)。
语法:
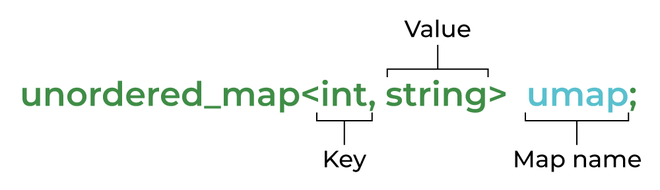
unordered_map 语法
以下是演示无序映射的C++程序:
// C++ program to demonstrate
// functionality of unordered_map
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Declaring umap to be of
// <string, int> type key
// will be of STRING type
// and mapped VALUE will
// be of int type
unordered_map<string, int> umap;
// inserting values by using [] operator
umap["GeeksforGeeks"] = 10;
umap["Practice"] = 20;
umap["Contribute"] = 30;
// Traversing an unordered map
for (auto x : umap)
cout << x.first << " " <<
x.second << endl;
}
输出:
Contribute 30
Practice 20
GeeksforGeeks 10
unordered_map 输出
解释: 这个输出证明的具体事情是,unordered_map 的输出值是以随机键值对为基础产生的,而map则以有序方式显示值和键。
unordered_map vs unordered_set
| unordered_map | unordered_set |
|---|---|
| unordered_map 仅包含 (键-值) 对形式的元素。 | unordered_set 不一定包含以键-值对的形式的元素,主要用于查看集合的存在/不存在。 |
| 使用运算符 ‘[]’ 提取地图中存在的键的相应值。 | 查找元素是使用 find() 函数进行的,因此不需要运算符”[]” |
注意: 例如,考虑计算单词频率的问题。我们不能使用unordered_set(或set),因为我们不能存储计数,而我们可以使用 unordered_map。
unordered_map vs map
| unordered_map | Map |
|---|---|
| unordered_map键可以以任何方式存储。 | Map是一系列唯一键的有序序列。 |
| 由于unordered_map实现了不平衡的树结构,因此不可能在元素之间保持顺序。 | Map实现了平衡的树结构,因此可以通过特定的树遍历来保持元素之间的顺序。 |
| unordered_map操作的时间复杂度平均为O(1)。 | Map操作的时间复杂度为O(log n)。 |
unordered_map的方法
有很多可用于unordered_map的函数。其中最有用的是:
- operator =
- operator []
- empty
- size for capacity
- begin和end,用于迭代器。
- 查找和计数。
- 插入和删除。
下表显示了unordered_map的所有方法的完整列表:
| 方法/函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| at() | 此C++ unordered_map函数返回与元素作为键的k相对应的值的引用。 |
| begin() | 返回指向unordered_map容器中第一个元素的迭代器。 |
| end() | 返回指向unordered_map容器中最后一个元素后面的位置的迭代器。 |
| bucket() | 返回元素与键k相对应的存储桶编号。 |
| bucket_count | 用于计算unordered_map中桶的总数。不需要传递参数。 |
| bucket_size | 返回unordered_map中每个桶中的元素数量。 |
| count() | 计算包含给定键的元素数量。 |
| equal_range | 返回一个范围,包括序列中所有与键k相等的元素。 |
| find() | 返回元素的迭代器。 |
| empty() | 检查unordered_map容器是否为空。 |
| erase() | 在unordered_map容器中删除元素。 |
C++11库还提供了函数,以查看内部使用的桶计数、桶大小以及使用的哈希函数和各种哈希策略,但在实际应用中它们并不是很有用。我们可以使用迭代器遍历unordered_map的所有元素。
//C++程序演示
//初始化、索引、迭代
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
//主函数
int main()
{
//声明umap为
//<string,double>类型key
//将是字符串类型的键部分,
//映射值将是double类型
unordered_map<string, double> umap = { //直接在映射中插入元素
{"One", 1},
{"Two", 2},
{"Three", 3}
};
//通过[]运算符插入值
umap["PI"] = 3.14;
umap["root2"] = 1.414;
umap["root3"] = 1.732;
umap["log10"] = 2.302;
umap["loge"] = 1.0;
//通过insert函数插入值
umap.insert(make_pair("e", 2.718));
string key = "PI";
//如果在map中未找到键,则迭代器将返回“end”
if (umap.find(key) == umap.end())
cout << key << " not found\n\n";
//如果找到了键,则返回到该键的迭代器
else
cout << "Found " << key << "\n\n";
key = "lambda";
if (umap.find(key) == umap.end())
cout << key << " not found\n";
else
cout << "Found " << key << endl;
//遍历umap中的所有值
unordered_map<string, double> :: iterator itr;
cout << "\nAll Elements : \n";
for (itr = umap.begin();
itr != umap.end(); itr++)
{
//itr作为pair<string,double>类型的指针工作,指向键 和 值
//itr->first 存储键和 itr->second 存储值
cout << itr->first << " " <<
itr->second << endl;
}
}
输出
Found PI
lambda not found
All Elements :
e 2.718
loge 1
log10 2.302
Two 2
One 1
Three 3
PI 3.14
root2 1.414
root3 1.732
查找单词的词频
给定一串单词,任务是找出单独单词的出现频率:
输入: str = “geeks for geeks geeks quiz practice qa for”;
输出: 各单词的频率为
(practice,1)
(for,2)
(qa,1)
(quiz,1)
(geeks,3)
下面是实现上述方法的C++程序:
// C++程序使用unordered_map查找每个单词的出现频率
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//以str为参数打印单个单词的频率
void printFrequencies(const string &str)
{
//声明map为类型,
//每个单词都映射到其频率
unordered_map<string, int> wordFreq;
//使用stringstream将输入拆分成单个单词
stringstream ss(str);
//用于拆分单词
string word;
while (ss >>word;)
wordFreq[word]++;
//现在迭代word, freq键值对并以<,>格式打印它们
unordered_map<string, int> :: iterator p;
for (p = wordFreq.begin();
p != wordFreq.end(); p++)
cout << "(" << p->first << ", " <<
p->second << ")\n";
}
//主函数
int main()
{
string str = "geeks for geeks geeks quiz "
"practice qa for";
printFrequencies(str);
return 0;
}
输出
(practice, 1)
(for, 2)
(qa, 1)
(quiz, 1)
(geeks, 3)
 极客教程
极客教程