R语言 实现Hexabin图的可视化
在这篇文章中,我们将看到如何在R编程语言中实现六边形图的可视化。
Hexabin图采用六边形将区域划分为多个部分,并为每个部分分配一种颜色。图形区域(可以是一个地理位置)被划分为一连串的六边形,每个六边形中的数据点的数量被计算出来,并通过颜色梯度显示。
这个图是用来显示密度的,六边形的形状允许轻松创建连续的区域,同时将空间分成不连续的部分。
使用此链接下载数据。该数据存储了美国各州的多边形数据
基本六边形地图
为了用us_states_hexgrid数据集绘制hexabin,我们将从这个数据集中创建数据框架,然后我们将绘制空间数据。
# R library
library(tidyverse) # handle the data
library(geojsonio) # handle the geojson data
library(RColorBrewer) # for color palette
library(rgdal) # handling the spatial data
# load the geospatial data
us_data <- geojson_read("us_states_hexgrid.geojson", what = "sp")
# polygon spatial data
us_data@data = us_data@data %>%
mutate(google_name = gsub(" \\(United States\\)", "", google_name))
# plot the basic Hexabin Map
plot(us_data)
输出
将数据与正方形地图合并
Hexabin用于绘制高密度数据的散点图,这里我们将把数据与来自geojson文件的空间特征合并起来,然后用ggplot绘制hexabin。
# R library
library(tidyverse) # handle the data
library(geojsonio) # handle the geojson data
library(RColorBrewer) # for color palette
library(rgdal) # handling the spatial data
# load the geospatial data
us_data <- geojson_read("us_states_hexgrid.geojson",
what = "sp")
# polygon spatial data
us_data@data = us_data@data %>%
mutate(google_name = gsub(" \\(United States\\)",
"", google_name))
# library to convert data to a tidy data
library(broom)
us_data@data = us_data@data %>% mutate(
google_name = gsub(" \\(United States\\)",
"", google_name))
us_data_fortified <- tidy(us_data,
region = "google_name")
# getting the US state Marriage data
data <- read.table("https://raw.githubusercontent.com\
/holtzy/R-graph-gallery/master/DATA/State_mariage_rate.csv",
sep = ",", na.strings="---", header = T)
# extracting the data sequence
data %>%
# getting the data for year 2015
ggplot( aes(x = y_2015)) +
# preparing the histogram
geom_histogram(bins = 10, fill='#69b3a2', color='white')
# merging the data with the spatial features from geojson file
us_data_fortified <- us_data_fortified %>%
left_join(. , data, by=c("id"="state"))
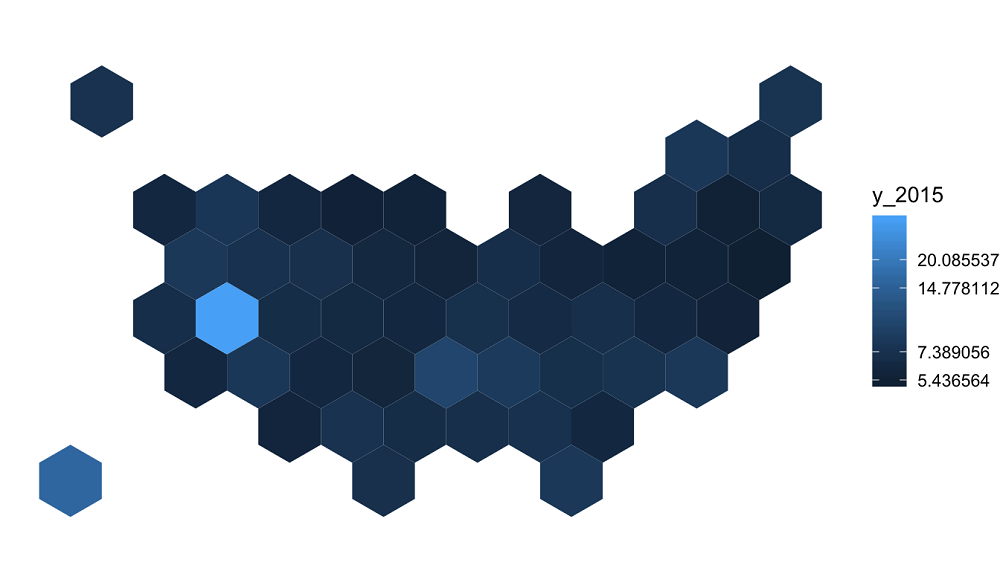
# preparing a choropleth map
ggplot() +
geom_polygon(data = us_data_fortified, aes(
fill = y_2015, x = long, y = lat, group = group)) +
scale_fill_gradient(trans = "log") +
coord_map()
输出
 极客教程
极客教程