R语言 非线性最小二乘法
在非线性函数中,绘制在图形上的点不是线性的,因此,在图形上没有给出一条曲线或直线。因此,非线性回归分析是用来改变函数的参数,以获得一条与你的数据闭合的曲线或回归线。
,为了执行这一点, 非线性最小 平方法被用来最小化残差值或误差值的总和,即图上垂直点与回归线之间的差异,并将相应地拟合非线性函数。
数学公式 。
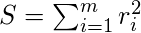
其中
r是2点之间的残差或误差值。
上述寻找最小残差函数的数学函数可以在R语言中使用 resid() 函数进行。
回归分析被广泛用于所有类型的商业问题,通过改变其业务的某个因素来执行明智的决策或预测未来。
在R语言中,非线性最小平方函数被表示为 –
语法
nls(formula, start)
其中
formula 表示模型公式,即非线性函数
start 是一个起始估计值的列表
注意: 要了解nls()的更多可选参数,请在R控制台使用以下命令 –
> help("nls")
>
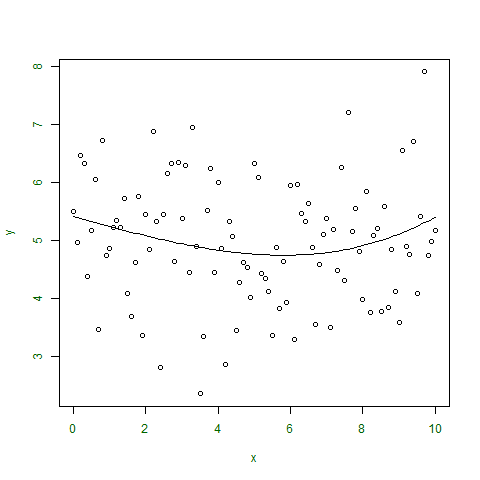
例1:
在这个例子中,取一个非线性函数,并在图上绘制成点。
# defining x and y coordinates
x <- seq(0, 10, 0.1)
y <- rnorm(101, 5, 1)
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file ="nls.png")
# Taking the model to get fitted
m <- nls(y~a * x ^ 3 + b * x + c,
start = list(a = 1, b = 2, c = 1))
# plot the graph
plot(x, y, col.lab ="darkgreen",
col.axis ="darkgreen")
# plot the graph with new fitting line
# or regression line
lines(x, predict(m))
# saving the file
dev.off()
# print minimum residual or error value
print(sum(resid(m)^2))
输出:
[1] 106.4507
例2:
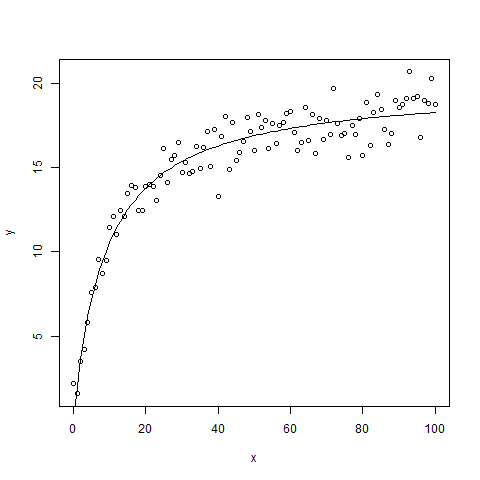
在这个例子中,下面的代码是接受一个非线性函数,如图所示。
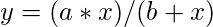
进一步绘制点和回归线,同时,通过使用 cor() 方法找出适合度。
# creating sequence of 101 values from 0 to 100
x <- seq(0, 100, 1)
y<-((runif(1, 10, 20)*x)/(runif(1, 0, 10) + x)) +
rnorm(101, 0, 1)
# output to be present as PNG file
png(file ="nls2.png")
# using starting values in nls() function
# to not get a warning
m<-nls(y~a * x/(b + x), start = list(a = 1, b = 2))
# goodness of fit
cor(y, predict(m))
# minimized residual value
sum(resid(m)^2)
# plotting points on graph
plot(x, y)
# finding regression line
lines(x, predict(m))
# saving the file
dev.off()
输出:
[1] 0.9622681
[1] 108.1481
 极客教程
极客教程