R语言 if-else 语句
编程语言中的if语句只告诉我们,如果一个条件为真,它将执行一个语句块,如果条件为假,则不执行。但是,如果我们想在条件为假的情况下做其他事情,该怎么办呢?这时就需要R else语句。 我们可以将else语句与if语句一起使用,在条件为假时执行一个代码块。
R语言 if-else语句的语法
if (condition)
{
// Executes this block if
// condition is true
} else
{
// Executes this block if
// condition is false
}
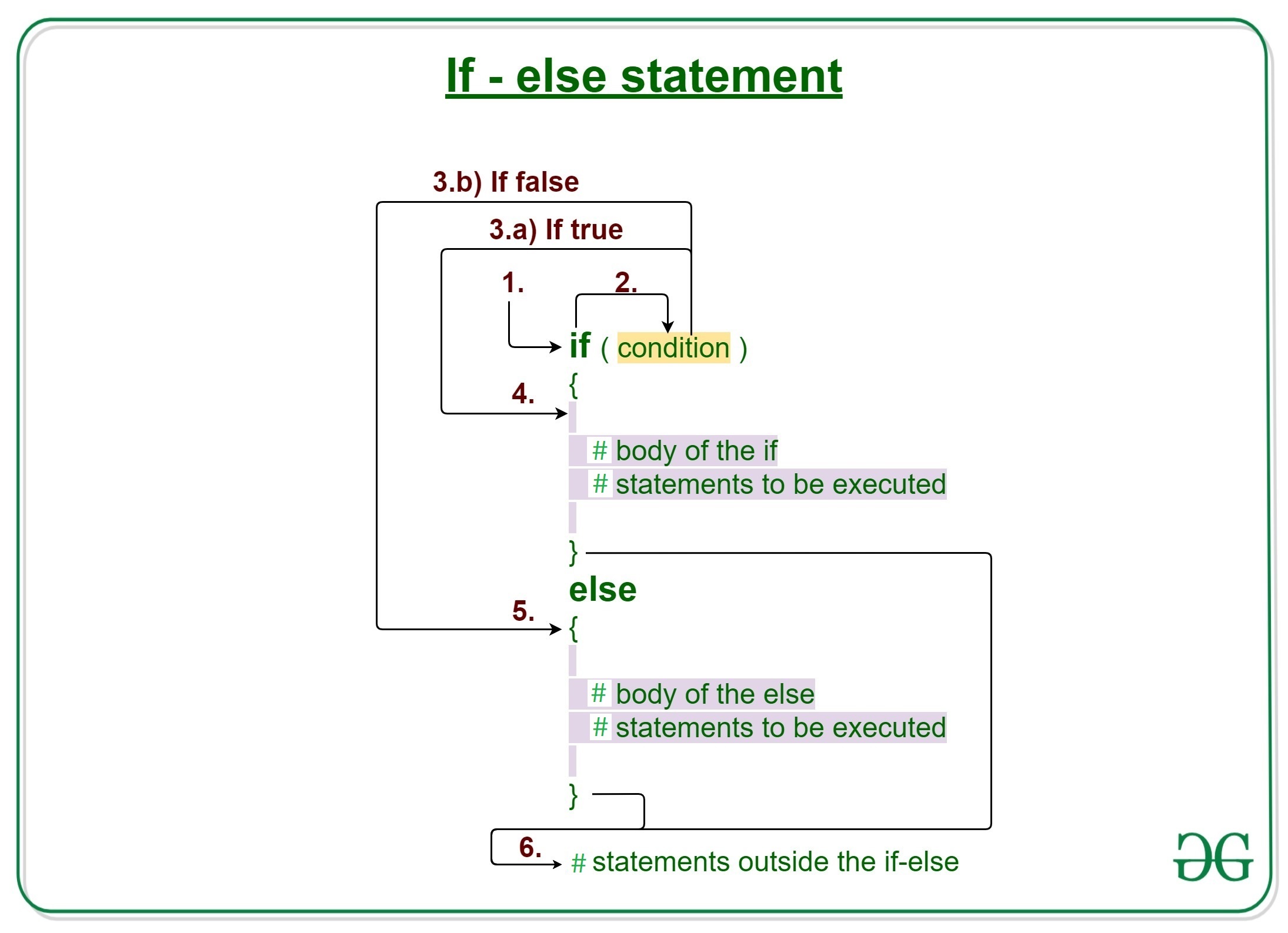
R编程中if-else语句的工作原理
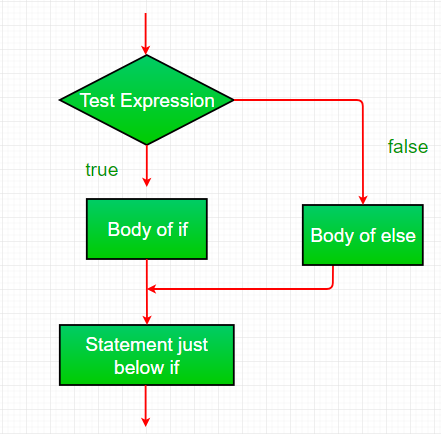
- 控制落入if块。
- 流程跳转到Condition。
- 对Condition进行测试。
- 如果Condition为真,转到第4步。
- 如果Condition为假,转到第5步。
- 执行if块或if中的主体。
- 执行else块或else块中的主体。
- 流程退出if-else块。
R语言 if-else语句的流程图
R语言 if-else 语句示例
例1 :
x <- 5
# Check value is less than or greater than 10
if(x > 10)
{
print(paste(x, "is greater than 10"))
} else
{
print(paste(x, "is less than 10"))
}
输出
[1] "5 is less than 10"
在上述代码中,首先,x被初始化为5,然后检查if条件(x>10),结果为false。流进入else块,并打印出 “5小于10 “的语句。
例2 :
x <- 5
# Check if value is equal to 10
if(x == 10)
{
print(paste(x, "is equal to 10"))
} else
{
print(paste(x, "is not equal to 10"))
}
输出
[1] "5 is not equal to 10"
R中的嵌套if-else语句
if-else语句可以嵌套在一起,形成一组语句,并根据条件逐一评估表达式,分别从外部条件开始到内部逐一评估。一个if-else语句在另一个if-else语句中,能更好地证明其定义。
语法
if(condition1){
# execute only if condition 1 satisfies
if(condition 2){
# execute if both condition 1 and 2 satisfy
}
}else{
}
例子
# creating values
var1 <- 6
var2 <- 5
var3 <- -4
# checking if-else if ladder
if(var1 > 10 || var2 < 5){
print("condition1")
}else{
if(var1 <4 ){
print("condition2")
}else{
if(var2>10){
print("condition3")
}
else{
print("condition4")
}
}
}
输出
[1] "condition4"
 极客教程
极客教程