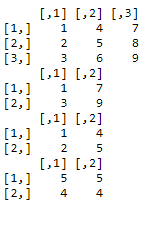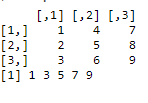R语言 从矩阵中获取特定位置的元素
在任何时候,都可能需要遍历一个矩阵的某个特定位置的元素。在这篇文章中,我们将使用整数向量、逻辑向量作为索引,从R编程语言的矩阵中获取元素。
方法1:使用整数向量访问元素
整数向量是一个向量,它包括所有整数类型的元素。
语法
matrix_name[row_vector_with_values,column_vector_with_values,]
例子
选择矩阵a的第1、3行和第1、3列。
print(a )
程序
# create a vector named data with 9 elements
data=c(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)
# pass this vector to matrix input
a=matrix(data, nrow = 3, ncol = 3)
print(a)
# select rows 1 & 3 and columns 1 & 3
print(a[c(1,3),c(1,3)] )
# select rows 1 & 2 and columns 1 & 2
print(a[c(1,2),c(1,2)] )
# select rows 2 & 1 and columns 2 & 2
print(a[c(2,1),c(2,2)] )
输出
方法2:使用逻辑向量访问矩阵元素
逻辑向量包括一个包含布尔值的向量,即TRUE或FALSE。
语法:
matrix_name[logical_vector]
如果该位置为TRUE,则访问矩阵元素。
如果该位置为FALSE,则不访问矩阵元素。
例子
data=c(TRUE,TRUE,FALSE)
程序1 :
# create a vector named data with 9 elements
data=c(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)
# pass this vector to matrix input
a=matrix(data, nrow = 3, ncol = 3)
print(a)
a[c(TRUE, FALSE,TRUE, FALSE,TRUE, FALSE,TRUE, FALSE,TRUE)]
# accessing elements
输出
程序2
# create a vector named data with 9 elements
data=c(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)
# pass this vector to matrix input
a=matrix(data, nrow = 3, ncol = 3)
print(a)
print(a[c(TRUE)])
# accessing elements by placing all TRUE
print(a[c(FALSE)])
# accessing elements by placing all FALSE
输出
 极客教程
极客教程