R语言 dictionaRy包
在这篇文章中,我们将讨论如何使用R编程语言的dictionaRy包。
dictionaRy 是R语言对 “免费字典API “的一个接口。它可以用来获取有关英语单词的数据,如定义、语篇、起源、发音等。我们将使用这个包来获得定义、语篇和函数的例子,同时也讨论其他的方法。
安装
install.packages(“dictionaRy”)
获取一个词的定义
- define() 将返回JSON数据
- select() 将只从括号内声明的JSON数据中获得选定的数据。
注意: 我们还将使用tidyverse包来使用 select() 以方便语法。这并不是强制性的。
要开始工作,首先我们需要导入dictionaRy和tidyverse包。现在我们需要一个词来进一步处理,并将其存储在一个变量中,在这个例子中,我们将使用 ” greetings “作为我们的输入,变量名称为 word。
在所有这些之后,我们将在define()中传递word变量,并将JSON响应存储在一个名为 “data “的变量中。为了使语法简单明了,我们将使用 select() 从JSON中获取值。这里 select() 需要一个参数,它将搜索匹配的键并返回其值。
# installing package
install.packages("dictionaRy")
# importing packages
library(tidyverse)
library(dictionaRy)
# storing word in a variable
word <- "greetings"
# requesting data of the word
data <- define(word)
# getting definition of the word
# note: select() belongs to dplyr
# package
data %>% select(definition)
输出
# A tibble: 3 x 1
definition
<chr>
1 A conventional phrase used to start a letter or conversation or otherw~
2 The action of the verb to greet.
3 (sometimes formal, sometimes humorous) hello
刮出更多关于这个词的信息
为此,我们将再次导入dictionaRy和tidyverse软件包。现在我们将为这个例子抽取另一个词,并将其存储在一个变量中,对于这个例子,我们将使用 “hello “作为我们的输入和变量名称词。在所有这些之后,我们将在 define() 中传递单词变量,并将JSON响应存储在一个名为 “data “的变量中。
由于 define() 返回JSON,所以它也有几个键,如语音部分,例如,语音和音频,所以我们将在 select() 中逐一传递所有这些值,以获得JSON中的完整响应。
例子
# installing package
install.packages("dictionaRy")
# importing packages
library(tidyverse)
library(dictionaRy)
# storing word in a variable
word <- "hello"
# requesting data of the word
data <- define(word)
print(data)
# getting definition of the word
# note: select() belongs to dplyr package
data %>% select(definition)
# getting part of speech of the word
data %>% select(part_of_speech)
# getting example of the word
data %>% select(example)
# getting phonetics of the word
data %>% select(phonetic)
# gets url of audio on how to spell the word
data %>% select(audio)
输出
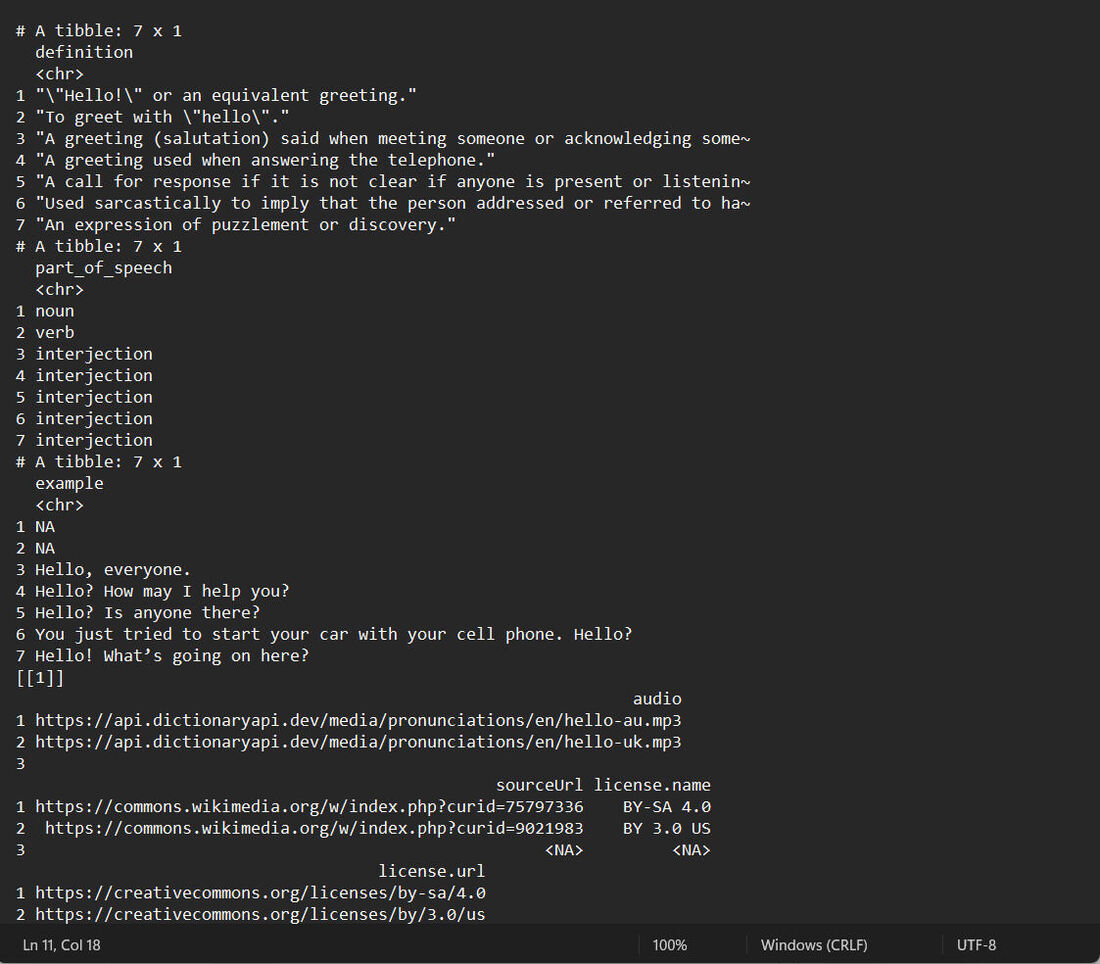
 极客教程
极客教程