Python深度学习 实现
在这个深度学习的实现中,我们的目标是预测某家银行的客户流失率,即哪些客户可能会离开这家银行的服务。使用的数据集相对较小,包含10000行,14列。我们使用Anaconda分布,以及Theano、TensorFlow和Keras等框架。Keras是建立在Tensorflow和Theano之上的,TensorFlow和Theano是其后端。
# Artificial Neural Network
# Installing Theano
pip install --upgrade theano
# Installing Tensorflow
pip install –upgrade tensorflow
# Installing Keras
pip install --upgrade keras
第1步:数据预处理
In[]:
# Importing the libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# Importing the database
dataset = pd.read_csv('Churn_Modelling.csv')
第2步
我们将数据集的特征和目标变量建立矩阵,即第14列,标记为 “退出”。
数据的初始外观如下图所示
In[]:
X = dataset.iloc[:, 3:13].values
Y = dataset.iloc[:, 13].values
X
输出
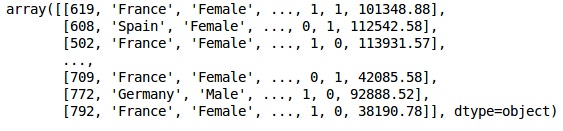
第3步
Y
输出
array([1, 0, 1, ..., 1, 1, 0], dtype = int64)
第4步
我们通过对字符串变量进行编码,使分析更加简单。我们使用ScikitLearn函数’LabelEncoder’来自动编码列中不同的标签,其值在0到n_classes-1之间。
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder, OneHotEncoder
labelencoder_X_1 = LabelEncoder()
X[:,1] = labelencoder_X_1.fit_transform(X[:,1])
labelencoder_X_2 = LabelEncoder()
X[:, 2] = labelencoder_X_2.fit_transform(X[:, 2])
X
输出
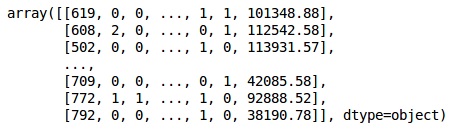
在上述输出中,国名被替换为0、1和2;而男性和女性被替换为0和1。
第5步
给编码数据贴标签
我们使用相同的 ScikitLearn 库和另一个名为 OneHotEncoder 的函数,只是传递列号创建一个虚拟变量。
onehotencoder = OneHotEncoder(categorical features = [1])
X = onehotencoder.fit_transform(X).toarray()
X = X[:, 1:]
X
现在,前两栏代表国家,第四栏代表性别。
输出
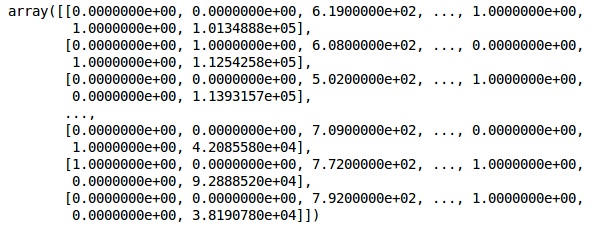
我们总是将数据分为训练和测试部分;我们在训练数据上训练我们的模型,然后我们在测试数据上检查模型的准确性,这有助于评估模型的效率。
第6步
我们使用ScikitLearn的 train_test_split 函数将我们的数据分成训练集和测试集。我们保持训练–测试分割的比例为80:20。
#Splitting the dataset into the Training set and the Test Set
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.2)
有些变量的值是以千为单位的,而有些变量的值是以十或一为单位的。我们对数据进行缩放,使其更具代表性。
第7步
在这段代码中,我们使用 StandardScaler 函数对训练数据进行拟合和转换。我们将我们的缩放比例标准化,这样我们就可以使用相同的拟合方法来转换/缩放测试数据。
# Feature Scaling
fromsklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
sc = StandardScaler()
X_train = sc.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
输出
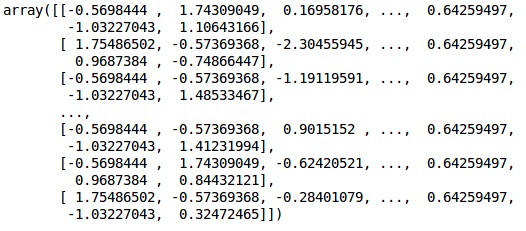
数据现在被正确地缩放了。最后,我们完成了数据的预处理。现在,我们将开始建立我们的模型。
第8步
我们在这里导入所需的模块。我们需要顺序模块来初始化神经网络,密集模块来添加隐藏层。
# Importing the Keras libraries and packages
import keras
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
第9步
我们将模型命名为分类器,因为我们的目的是对客户流失率进行分类。然后我们使用顺序模块进行初始化。
#Initializing Neural Network
classifier = Sequential()
第10步
我们使用密集函数逐一添加隐藏层。在下面的代码中,我们会看到许多参数。
我们的第一个参数是 output_dim 。 init 是随机梯度衰减器的初始化。在一个神经网络中,我们给每个节点分配权重。在初始化时,权重应该接近于零,我们使用均匀函数随机地初始化权重。 input_dim 参数只在第一层需要,因为模型不知道我们输入变量的数量。这里的输入变量总数为11。在第二层中,模型会自动知道第一隐藏层的输入变量的数量。
执行下面这行代码,添加输入层和第一隐藏层
classifier.add(Dense(units = 6, kernel_initializer = 'uniform',
activation = 'relu', input_dim = 11))
Execute the following line of code to add the second hidden layer −
classifier.add(Dense(units = 6, kernel_initializer = 'uniform',
activation = 'relu'))
Execute the following line of code to add the output layer −
classifier.add(Dense(units = 1, kernel_initializer = 'uniform',
activation = 'sigmoid'))
第11步
编译ANN
到目前为止,我们已经向我们的分类器添加了多个层。现在我们将使用 编译 方法对它们进行编译。在最后的编译控制中添加的参数完成了神经网络。因此,我们需要在这一步中小心谨慎。
下面是对这些参数的简要解释。
第一个参数是 优化器 ,这是一个用来寻找最佳权重集的算法。这种算法被称为 随机梯度下降(SGD)。 这里我们使用的是几种类型中的一种,称为 “亚当优化器”。SGD取决于损失,所以我们的第二个参数是损失。如果我们的因变量是二进制,我们使用对数损失函数,称为 “二进制_交叉熵 “,如果我们的因变量在输出中有两个以上的类别,那么我们使用 “分类_交叉熵 “。我们想根据 准确性 来提高我们的神经网络的性能,所以我们增加了准确性的 指标 。
# Compiling Neural Network
classifier.compile(optimizer = 'adam', loss = 'binary_crossentropy', metrics = ['accuracy'])
第12步
在这一步中需要执行一些代码。
拟合ANN到训练集
我们现在在训练数据上训练我们的模型。我们使用 拟合 方法来拟合我们的模型。我们还优化权重以提高模型效率。为此,我们必须更新权重。 批量大小 是我们更新权重后的观测值的数量。 Epoch 是迭代的总次数。批量大小和历时的值是通过试验和错误的方法选择的。
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train, batch_size = 10, epochs = 50)
进行预测和评估模型
# Predicting the Test set results
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
y_pred = (y_pred > 0.5)
预测一个新的观察结果
# Predicting a single new observation
"""Our goal is to predict if the customer with the following data will leave the bank:
Geography: Spain
Credit Score: 500
Gender: Female
Age: 40
Tenure: 3
Balance: 50000
Number of Products: 2
Has Credit Card: Yes
Is Active Member: Yes
第13步
预测测试集的结果
预测结果将给你客户离开公司的概率。我们将把这个概率转换为二进制的0和1。
# Predicting the Test set results
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
y_pred = (y_pred > 0.5)
new_prediction = classifier.predict(sc.transform
(np.array([[0.0, 0, 500, 1, 40, 3, 50000, 2, 1, 1, 40000]])))
new_prediction = (new_prediction > 0.5)
第14步
这是最后一步,我们评估我们的模型性能。我们已经有了原始结果,因此我们可以建立混淆矩阵来检查我们模型的准确性。
制作混淆矩阵
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
print (cm)
输出
loss: 0.3384 acc: 0.8605
[ [1541 54]
[230 175] ]
根据混淆矩阵,我们模型的准确率可以计算为 −
Accuracy = 1541+175/2000=0.858
我们取得了85.8%的准确率 ,这很好。
前向传播算法
在本节中,我们将学习如何编写代码来对一个简单的神经网络进行前向传播(预测) −
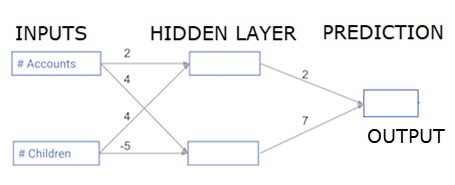
每个数据点都是一个客户。第一个输入是他们有多少个账户,第二个输入是他们有多少个孩子。该模型将预测该用户在下一年的交易量。
输入数据被预装为输入数据,而权重则在一个叫做权重的字典中。隐蔽层中第一个节点的权重数组分别在weights[‘node_0’],隐蔽层中第二个节点的权重数组在weights[‘node_1’]。
送入输出节点的权重在weights中可用。
整理过的线性激活函数
一个 “激活函数 “是一个在每个节点上工作的函数。它将节点的输入转化为某种输出。
整流线性激活函数(称为 ReLU )被广泛用于高性能网络中。这个函数将一个单一的数字作为输入,如果输入为负数,则返回0,如果输入为正数,则返回输入作为输出。
这里有一些例子–
- relu(4) = 4
- relu(-2) = 0
我们填入relu()函数的定义–
- 我们使用max()函数来计算relu()的输出值。
- 我们将relu()函数应用于node_0_input来计算node_0_output。
- 我们将relu()函数应用于node_1_input来计算node_1_output。
import numpy as np
input_data = np.array([-1, 2])
weights = {
'node_0': np.array([3, 3]),
'node_1': np.array([1, 5]),
'output': np.array([2, -1])
}
node_0_input = (input_data * weights['node_0']).sum()
node_0_output = np.tanh(node_0_input)
node_1_input = (input_data * weights['node_1']).sum()
node_1_output = np.tanh(node_1_input)
hidden_layer_output = np.array(node_0_output, node_1_output)
output =(hidden_layer_output * weights['output']).sum()
print(output)
def relu(input):
'''Define your relu activation function here'''
# Calculate the value for the output of the relu function: output
output = max(input,0)
# Return the value just calculated
return(output)
# Calculate node 0 value: node_0_output
node_0_input = (input_data * weights['node_0']).sum()
node_0_output = relu(node_0_input)
# Calculate node 1 value: node_1_output
node_1_input = (input_data * weights['node_1']).sum()
node_1_output = relu(node_1_input)
# Put node values into array: hidden_layer_outputs
hidden_layer_outputs = np.array([node_0_output, node_1_output])
# Calculate model output (do not apply relu)
odel_output = (hidden_layer_outputs * weights['output']).sum()
print(model_output)# Print model output
输出
0.9950547536867305
-3
将网络应用于许多观察值/数据行中
在本节中,我们将学习如何定义一个名为predict_with_network()的函数。这个函数将为多个数据观测值生成预测结果,这些数据来自上述网络,作为输入数据。上述网络中给出的权重正在被使用。relu()函数的定义也正在被使用。
让我们定义一个名为predict_with_network()的函数,它接受两个参数–input_data_row和weights–并将网络的预测值作为输出返回。
我们计算每个节点的输入和输出值,将它们存储为:node_0_input、node_0_output、node_1_input和node_1_output。
为了计算一个节点的输入值,我们将相关数组相乘并计算它们的总和。
为了计算一个节点的输出值,我们对节点的输入值应用relu()函数。我们使用一个 “for循环 “来迭代input_data —
我们还使用predict_with_network()为输入数据的每一行生成预测值–input_data_row。我们还将每个预测结果附加到结果中。
# Define predict_with_network()
def predict_with_network(input_data_row, weights):
# Calculate node 0 value
node_0_input = (input_data_row * weights['node_0']).sum()
node_0_output = relu(node_0_input)
# Calculate node 1 value
node_1_input = (input_data_row * weights['node_1']).sum()
node_1_output = relu(node_1_input)
# Put node values into array: hidden_layer_outputs
hidden_layer_outputs = np.array([node_0_output, node_1_output])
# Calculate model output
input_to_final_layer = (hidden_layer_outputs*weights['output']).sum()
model_output = relu(input_to_final_layer)
# Return model output
return(model_output)
# Create empty list to store prediction results
results = []
for input_data_row in input_data:
# Append prediction to results
results.append(predict_with_network(input_data_row, weights))
print(results)# Print results
输出
[0, 12]
这里我们使用了relu函数,其中relu(26)=26,relu(-13)=0,以此类推。
深度多层神经网络
在这里,我们正在编写代码,为一个有两个隐藏层的神经网络做前向传播。每个隐藏层有两个节点。输入数据已经被预装为 input_data 第一个隐藏层的节点被称为node_0_0和node_0_1。
它们的权重分别被预装为weights[‘node_0_0’]和weights[‘node_0_1’]。
第二个隐藏层的节点被称为 node_1_0和node_1。 它们的权重分别被预装为 weights[‘node_1_0’] 和 weights[‘node_1_1’ ]。
然后,我们使用预先加载的权重作为 weights[‘output’] 从隐藏节点创建一个模型输出。
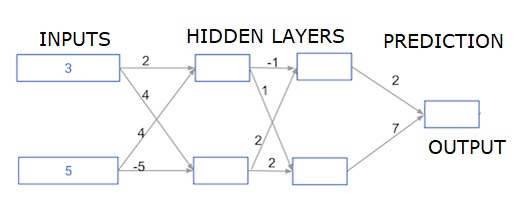
我们使用其权重weights[‘node_0_0’]和给定的输入数据来计算node_0_input。然后应用relu()函数来获得node_0_0_output。
我们对node_0_1_input进行上述同样的操作,得到node_0_1_output。
我们使用其权重weights[‘node_1_0’]和第一个隐藏层的输出–hidden_0_outputs,计算node_1_0_input。然后我们应用relu()函数来得到node_1_0_output。
我们对node_1_1_input进行上述同样的操作,得到node_1_1_output。
我们使用weights[‘output’]和第二个隐藏层hidden_1_outputs数组的输出来计算model_output。我们不对这个输出应用relu()函数。
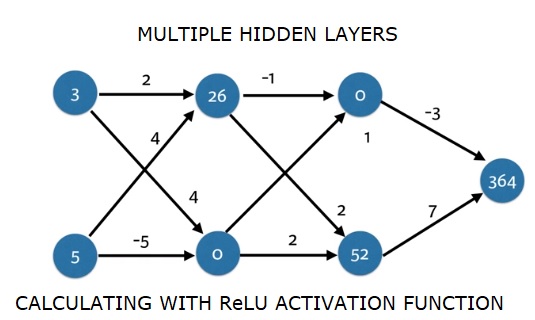
import numpy as np
input_data = np.array([3, 5])
weights = {
'node_0_0': np.array([2, 4]),
'node_0_1': np.array([4, -5]),
'node_1_0': np.array([-1, 1]),
'node_1_1': np.array([2, 2]),
'output': np.array([2, 7])
}
def predict_with_network(input_data):
# Calculate node 0 in the first hidden layer
node_0_0_input = (input_data * weights['node_0_0']).sum()
node_0_0_output = relu(node_0_0_input)
# Calculate node 1 in the first hidden layer
node_0_1_input = (input_data*weights['node_0_1']).sum()
node_0_1_output = relu(node_0_1_input)
# Put node values into array: hidden_0_outputs
hidden_0_outputs = np.array([node_0_0_output, node_0_1_output])
# Calculate node 0 in the second hidden layer
node_1_0_input = (hidden_0_outputs*weights['node_1_0']).sum()
node_1_0_output = relu(node_1_0_input)
# Calculate node 1 in the second hidden layer
node_1_1_input = (hidden_0_outputs*weights['node_1_1']).sum()
node_1_1_output = relu(node_1_1_input)
# Put node values into array: hidden_1_outputs
hidden_1_outputs = np.array([node_1_0_output, node_1_1_output])
# Calculate model output: model_output
model_output = (hidden_1_outputs*weights['output']).sum()
# Return model_output
return(model_output)
output = predict_with_network(input_data)
print(output)
输出
364
 极客教程
极客教程