Python for循环中的else语句
Python支持在”for”循环语句中使用”else”语句。如果在”for”循环中使用”else”语句,在序列耗尽之前,”else”语句会被执行,然后控制转移到主执行流程。
以下流程图说明了如何在 for 循环中使用 else 语句 –
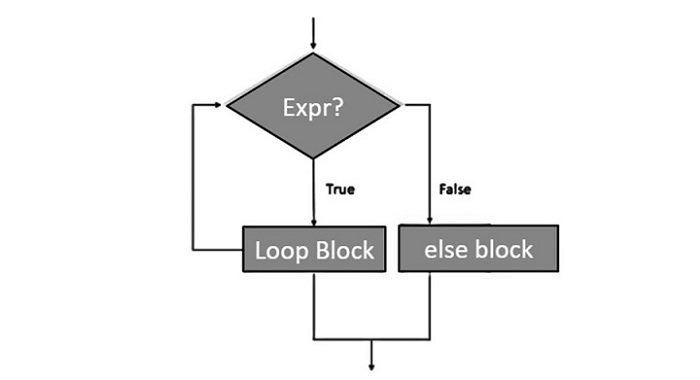
示例
下面的示例演示了else语句与for语句的结合使用。在计数小于5之前,会打印出迭代计数值。当计数变为5时,在else块中的打印语句会被执行,在控制权传递给主程序中的下一条语句之前。
for count in range(6):
print ("Iteration no. {}".format(count))
else:
print ("for loop over. Now in else block")
print ("End of for loop")
执行此代码后将产生以下 输出 −
Iteration no. 1
Iteration no. 2
Iteration no. 3
Iteration no. 4
Iteration no. 5
for loop over. Now in else block
End of for loop
嵌套循环
Python编程语言允许在一个循环内使用另一个循环。下面的部分展示了一些例子来说明这个概念。
语法
for iterating_var in sequence:
for iterating_var in sequence:
statements(s)
statements(s)
Python编程语言中嵌套 while 循环语句的语法如下:
while expression:
while expression:
statement(s)
statement(s)
关于循环嵌套的最后一点是,您可以将任何类型的循环放在任何其他类型的循环内。例如,一个for循环可以放在一个while循环内,反之亦然。
示例
以下程序使用嵌套的for循环显示1-10的乘法表。
#!/usr/bin/python3
for i in range(1,11):
for j in range(1,11):
k=i*j
print ("{:3d}".format(k), end=' ')
print()
print()函数的内部循环中有一个end=’ ‘,它会添加一个空格而不是默认的换行符。因此,数字会在一行中显示。
最后一个print()将在内部for循环结束时执行。
当执行以上代码时,会产生以下输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30
4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60
7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 72 80
9 18 27 36 45 54 63 72 81 90
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
 极客教程
极客教程