如何在Python中向图表添加图例?
介绍…
图表的主要目的是使数据易于理解。 “一张图片胜过千言万语”意味着不能用语言表达的复杂想法可以通过一张图表传达。
在绘制具有大量信息的图形时,图例可能很有用,以显示相关信息以改善对所呈现数据的理解。
如何实现它..
在matplotlib中,图例可以以多种方式呈现。注释可用于吸引读者注意特定点,以帮助读者理解图表上显示的信息。
1.通过在python命令提示符中打开pip install matplotlib来安装matplotlib。
2.准备要显示的数据。
示例
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 数据准备
mobile = ['Iphone','Galaxy','Pixel']
# 每个手机单位出售的数据,单位:百万
units_sold = (('2016',12,8,6),
('2017',14,10,7),
('2018',16,12,8),
('2019',18,14,10),
('2020',20,16,5),)
3.将数据拆分为每家公司的移动单位的数组。
示例
# 数据准备-拆分数据
IPhone_Sales = [Iphones for Year, Iphones, Galaxy, Pixel in units_sold]
Galaxy_Sales = [Galaxy for Year, Iphones, Galaxy, Pixel in units_sold]
Pixel_Sales = [Pixel for Year, Iphones, Galaxy, Pixel in units_sold]
# 数据准备 - 标签
Years = [Year for Year, Iphones, Galaxy,Pixel in units_sold]
# 设置位置
Position = list(range(len(units_sold)))
# 设置宽度
Width = 0.2
4.使用准备好的数据创建柱形图。每个产品的销售都会调用.bar,指定其位置和销售额。
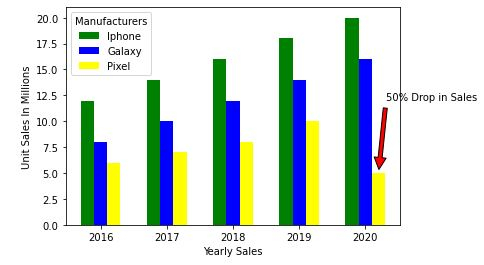
使用xy和xytext属性添加注释。查看数据,谷歌Pixel手机的销售额下降了50%,即从2019年销售1000万台到2022年的销售额只有500万。因此,我们将把文本和注释设置为最后一个条形。
最后,我们将使用legend参数添加图例。默认情况下,matplotlib将在数据最不重叠的区域绘制图例。
示例
plt.bar([p - Width for p in Position], IPhone_Sales, width=Width,color='green')
plt.bar([p for p in Position], Galaxy_Sales , width=Width,color='blue')
plt.bar([p + Width for p in Position], Pixel_Sales, width=Width,color='yellow')
# 将X轴设置为年份
plt.xticks(Position, Years)
# 设置Y轴标签
plt.xlabel('Yearly Sales')
plt.ylabel('Unit Sales In Millions')
# 设置注释使用xy和xytext更改箭头
plt.annotate('50%销售下降', xy=(4.2, 5), xytext=(5.0, 12),
horizontalalignment='center',
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='red', shrink=0.05))
# 设置图例
plt.legend(mobile, title='制造商')
输出
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x19826618400>
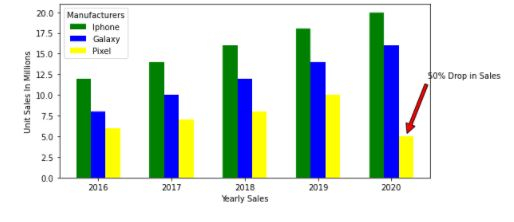
- 如果您觉得在图表中添加图例太吵闹,可以使用bbox_to_anchor选项将图例绘制在外面。bbox_to_anchor有(X,Y)位置,其中0是图形的左下角,1是右上角。
注意: -使用.subplots_adjust调整图例开始和结束的位置。
例如,right = 0.50的值意味着它在绘图的右侧留下50%的屏幕。 left的默认值是0.125,这意味着它在左侧留下12.5%的空间。
输出
“`python plt.legend(mobile, title=’制造商’, bbox_to_anchor=(1, 0.8))
plt.subplots_adjust(right=1.2)
<pre><code class="line-numbers">
## 示例
6\. 最后让我们保存这个图像。
“`python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 数据预处理(我捏造了这些数据,没有准确性)
mobile = [‘苹果’,’Galaxy’,’Pixel’]
# 数据为以百万为单位的4个季度中售出的移动设备数
units_sold = ((‘2016’,12,8,6),
(‘2017’,14,10,7),
(‘2018’,16,12,8),
(‘2019’,18,14,10),
(‘2020′,20,16,5),)
# 数据准备 – 分割数据
IPhone_Sales = [Iphones for Year, Iphones, Galaxy, Pixel in units_sold]
Galaxy_Sales = [Galaxy for Year, Iphones, Galaxy, Pixel in units_sold]
Pixel_Sales = [Pixel for Year, Iphones, Galaxy, Pixel in units_sold]
# 数据准备 – 标签
Years = [Year for Year, Iphones, Galaxy,Pixel in units_sold]
# 设置位置
Position = list(range(len(units_sold)))
# 设置宽度
Width = 0.2
plt.bar([p – Width for p in Position], IPhone_Sales, width=Width,color=’green’)
plt.bar([p for p in Position], Galaxy_Sales , width=Width,color=’blue’)
plt.bar([p + Width for p in Position], Pixel_Sales, width=Width,color=’yellow’)
# 将X轴设置为年份
plt.xticks(Position, Years)
# 设置Y轴标签
plt.xlabel(‘年度销量’)
plt.ylabel(‘百万部件销售量’)
# 设置注释,使用xy和xytext更改箭头
plt.annotate(‘销售降幅50%’, xy=(4.2, 5), xytext=(5.0, 12),
horizontalalignment=’center’,
arrowprops=dict(facecolor=’red’, shrink=0.05))
# 设置图例
plt.legend(mobile, title=’制造商’)
plt.legend(mobile, title=’制造商’)
plt.subplots_adjust(right=1.2)
# plt.show()
plt.savefig(‘MobileSales.png’)
 极客教程
极客教程