如何用Python检查时间序列数据是否是静止的
时间序列数据通常具有时间性的特点。这种时间性给数据增加了一种趋势或季节性,使其符合时间序列分析和预测的要求。如果时间序列数据不随时间变化或没有时间结构,则被称为静止的。因此,非常有必要检查数据是否是静止的。在时间序列预测中,如果数据是静止的,我们就不能从数据中获得有价值的见解。
静止数据的示例图:
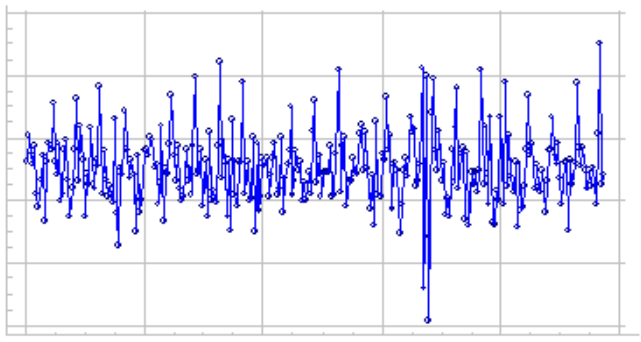
静止性的类型:
当涉及到识别数据是否静止时,意味着要识别数据中细微的静止性概念。在时间序列数据中观察到的静止性类型包括
1.趋势静止 – 不显示趋势的时间序列。
2.季节性静止 – 一个不显示季节性变化的时间序列。
3.严格静止 – 观察值的联合分布不受时间转移的影响。
分步实现
下面的步骤将让用户容易理解检查给定时间序列数据是否静止的方法。
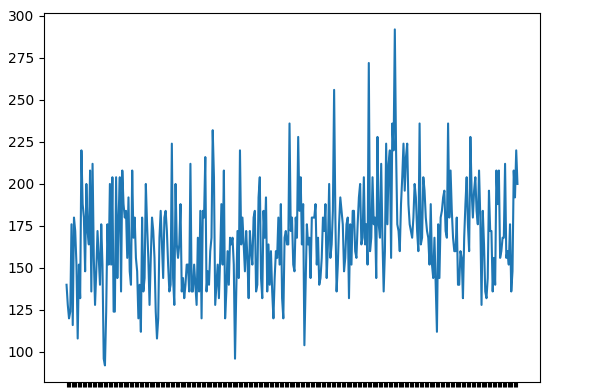
第1步:绘制时间序列数据
点击这里下载实践数据集daily-female-births-IN.csv。
# import python pandas library
import pandas as pd
# import python matplotlib library for plotting
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# read the dataset using pandas read_csv()
# function
data = pd.read_csv("daily-total-female-births-IN.csv",
header=0, index_col=0)
# use simple line plot to see the distribution
# of the data
plt.plot(data)
输出:
第2步:评估描述性统计数字
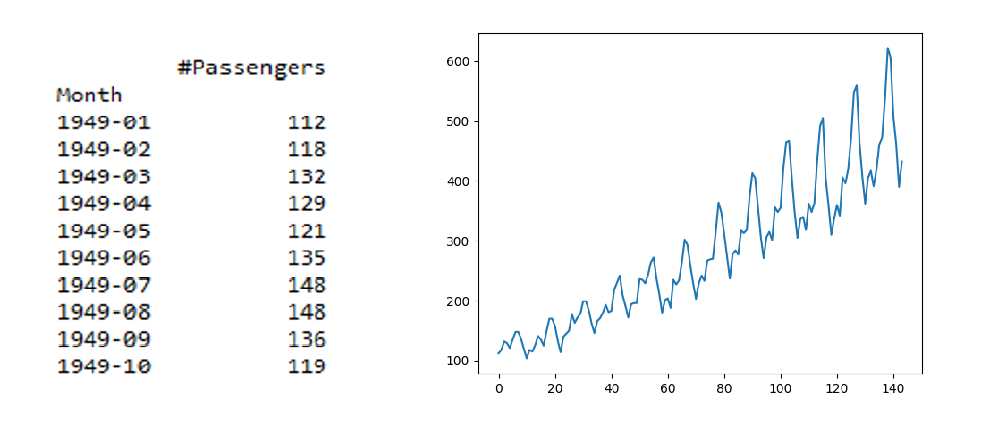
这通常是通过将数据分成两个或更多的分区并计算每组的平均数和方差来实现的。如果这些一阶矩在这些分区中是一致的,那么我们可以假设数据是静止的。让我们使用1949-1960年间的航空公司乘客数量数据集。
# import python pandas library
import pandas as pd
# import python matplotlib library for
# plotting
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# read the dataset using pandas read_csv()
# function
data = pd.read_csv("AirPassengers.csv",
header=0, index_col=0)
# print the first 6 rows of data
print(data.head(10))
# use simple line plot to understand the
# data distribution
plt.plot(data)
输出:
现在,让我们把这些数据划分为不同的组,并计算不同组的平均数和方差,检查其一致性。
# import the python pandas library
import pandas as pd
# use pandas read_csv() function to read the dataset.
data = pd.read_csv("AirPassengers.csv", header=0, index_col=0)
# extracting only the air passengers count from
# the dataset using values function
values = data.values
# getting the count to split the dataset into 3
parts = int(len(values)/3)
# splitting the data into three parts
part_1, part_2, part_3 = values[0:parts], values[parts:(
parts*2)], values[(parts*2):(parts*3)]
# calculating the mean of the separated three
# parts of data individually.
mean_1, mean_2, mean_3 = part_1.mean(), part_2.mean(), part_3.mean()
# calculating the variance of the separated
# three parts of data individually.
var_1, var_2, var_3 = part_1.var(), part_2.var(), part_3.var()
# printing the mean of three groups
print('mean1=%f, mean2=%f, mean2=%f' % (mean_1, mean_2, mean_3))
# printing the variance of three groups
print('variance1=%f, variance2=%f, variance2=%f' % (var_1, var_2, var_3))
输出:

输出结果清楚地表明,三组的平均数和方差相差很大,说明数据是非平稳的。例如,如果均值1=150,均值2=160,均值3=155,方差1=33,方差2=35,方差3=37,那么我们可以得出结论,数据是静止的。有时这种方法对某些分布会失效,如对数正态分布。
让我们试试上面的例子,但用NumPy的log()函数对乘客人数进行记录,并检查结果。
# import python pandas library
import pandas as pd
# import python matplotlib library for plotting
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# import python numpy library
import numpy as np
# read the dataset using pandas read_csv()
# function
data = pd.read_csv("AirPassengers.csv", header=0, index_col=0)
# extracting only the air passengers count
# from the dataset using values function
values = log(data.values)
# printing the first 15 passenger count values
print(values[0:15])
# using simple line plot to understand the
# data distribution
plt.plot(values)
输出:
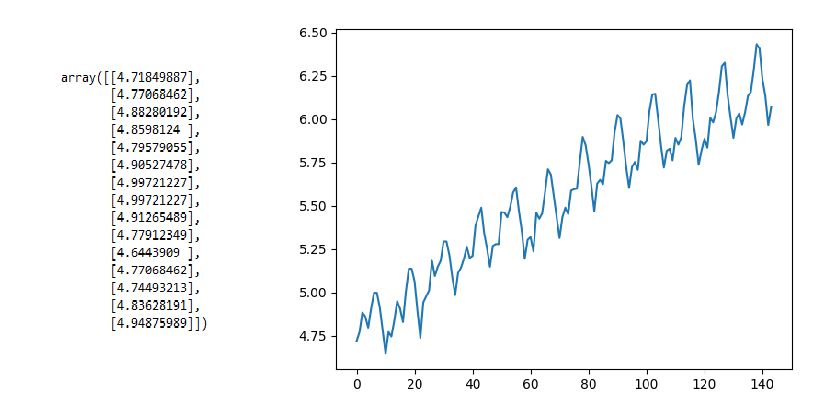
输出表明有一些趋势,但不像前面的情况那样非常陡峭,现在我们来计算分区的平均值和方差。
# getting the count to split the dataset
# into 3 parts
parts = int(len(values)/3)
# splitting the data into three parts.
part_1, part_2, part_3 = values[0:parts], values[parts:(parts*2)], values[(parts*2):(parts*3)]
# calculating the mean of the separated three
# parts of data individually.
mean_1, mean_2, mean_3 = part_1.mean(), part_2.mean(), part_3.mean()
# calculating the variance of the separated three
# parts of data individually.
var_1, var_2, var_3 = part_1.var(), part_2.var(), part_3.var()
# printing the mean of three groups
print('mean1=%f, mean2=%f, mean2=%f' % (mean_1, mean_2, mean_3))
# printing the variance of three groups
print('variance1=%f, variance2=%f, variance2=%f' % (var_1, var_2, var_3))
输出:
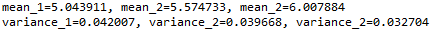
理想情况下,我们会预期平均数和方差会有很大的不同,但它们是一样的,在这种情况下,这种方法会非常失败。为了避免这种情况,我们有另一种统计测试,下面将讨论。
第3步:增强的迪克-富勒检验
这是一个专门用来测试单变量时间序列数据是否静止的统计测试。这个测试是基于一个假设,可以告诉我们它被接受的概率程度。它通常被归类为单位根检验之一,它决定了单变量时间序列数据遵循趋势的程度。让我们定义一下无效假设和备用假设。
- 何(无假设):时间序列数据是非平稳的
- H1(备用假设):时间序列数据是静止的
假设α=0.05,意味着(95%的置信度)。如果p>0.05不能拒绝无效假设,则用p值来解释测试结果,否则如果p<=0.05则拒绝无效假设。现在,让我们使用同样的航空乘客数据集,用stats模型包提供的adfuller()统计函数进行检验,以检查数据是否静止。
# import python pandas package
import pandas as pd
# import the adfuller function from statsmodel
# package to perform ADF test
from statsmodels.tsa.stattools import adfuller
# read the dataset using pandas read_csv() function
data = pd.read_csv("AirPassengers.csv", header=0, index_col=0)
# extracting only the passengers count using values function
values = data.values
# passing the extracted passengers count to adfuller function.
# result of adfuller function is stored in a res variable
res = adfuller(values)
# Printing the statistical result of the adfuller test
print('Augmneted Dickey_fuller Statistic: %f' % res[0])
print('p-value: %f' % res[1])
# printing the critical values at different alpha levels.
print('critical values at different levels:')
for k, v in res[4].items():
print('\t%s: %.3f' % (k, v))
输出:
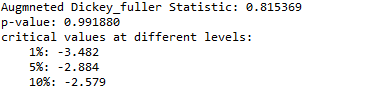
根据我们的假设,ADF统计量在不同的水平上都远远大于临界值,而且P值也大于0.05,这意味着,我们在90%、95%和99%的置信度下都无法拒绝无效假设,这意味着时间序列数据是强烈的非平稳的。
现在,让我们试着对对数规范化的数值进行ADF检验,并交叉检查我们的结果。
# import python pandas package
import pandas as pd
# import the adfuller function from statsmodel
# package to perform ADF test
from statsmodels.tsa.stattools import adfuller
# import python numpy package
import numpy as np
# read the dataset using pandas read_csv() function
data = pd.read_csv("AirPassengers.csv", header=0, index_col=0)
# extracting only the passengers count using
# values function and applying log transform on it.
values = log(data.values)
# passing the extracted passengers count to adfuller function.
# result of adfuller function is stored in a res variable
res = adfuller(values)
# Printing the statistical result of the adfuller test
print('Augmneted Dickey_fuller Statistic: %f' % res[0])
print('p-value: %f' % res[1])
# printing the critical values at different alpha levels.
print('critical values at different levels:')
for k, v in res[4].items():
print('\t%s: %.3f' % (k, v))
输出:

正如你所看到的,ADF检验再一次表明,ADF统计量在不同的水平上都远远大于临界值,而且P值也远远大于0.05,这标志着,我们可以在90%、95%和99%的置信水平下拒绝无效假设,这意味着时间序列数据是强烈的非平稳的。
因此,ADF单位根检验是检查时间序列数据是否静止的一种稳健检验。
 极客教程
极客教程