DataFrame Pandas Reindex
在数据分析和数据处理中,Pandas 是 Python 最受欢迎的库之一。Pandas 提供了大量的功能,使得数据操作变得简单高效。本文将详细介绍 Pandas 中的一个重要功能:DataFrame 的重索引(Reindexing)。重索引是指在 Pandas DataFrame 中重新排列现有数据的索引,或者向 DataFrame 中添加新的索引。这个功能在处理缺失数据或者将数据与其他数据集对齐时尤为重要。
1. Reindex 的基本概念
在 Pandas 中,reindex 方法可以用来改变 DataFrame 的行索引和列标签。这个方法允许用户指定一个新的索引,并根据新索引重新排列/对齐数据。如果新索引中包含原始数据中不存在的标签,则引入缺失值。
示例代码 1:基本的 Reindex
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_index = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
new_df = df.reindex(new_index)
print(new_df)
Output:
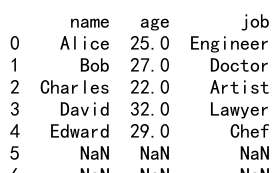
2. 使用 Reindex 调整行顺序
你可以通过 reindex 方法调整 DataFrame 中行的顺序。如果新的索引中包含原始 DataFrame 中不存在的索引,则在相应的位置插入缺失值。
示例代码 2:调整行顺序
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_order = [4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
reordered_df = df.reindex(new_order)
print(reordered_df)
Output:
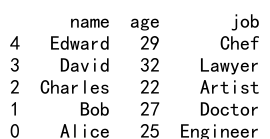
3. 使用 Reindex 填充缺失值
当使用 reindex 引入新索引时,Pandas 允许你指定一个填充缺失值的方法。常用的方法包括前向填充(ffill)和后向填充(bfill)。
示例代码 3:使用前向填充
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_index = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
df_reindexed = df.reindex(new_index, method='ffill')
print(df_reindexed)
Output:
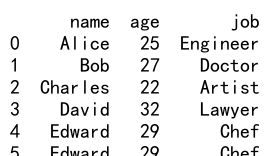
4. Reindexing 列
除了行之外,reindex 也可以用来重新排序或更改 DataFrame 的列。
示例代码 4:重新排序列
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
columns = ['job', 'name', 'age']
new_df = df.reindex(columns=columns)
print(new_df)
Output:

5. 使用 Axis 参数
reindex 方法的 axis 参数可以用来指定是对行进行重索引(axis=0)还是对列进行重索引(axis=1)。
示例代码 5:使用 Axis 参数
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_columns = ['age', 'name', 'job']
df_reindexed = df.reindex(columns=new_columns, axis=1)
print(df_reindexed)
6. 复杂的 Reindex 案例
在实际应用中,我们可能需要根据复杂的逻辑来重新索引 DataFrame。例如,你可能需要根据另一个 DataFrame 的索引来重新索引当前 DataFrame。
示例代码 6:根据另一个 DataFrame 的索引进行 Reindex
import pandas as pd
data1 = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29]}
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data1)
data2 = {'name': ['Frank', 'Grace'],
'age': [30, 28]}
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data2)
df1_reindexed = df1.reindex(df2.index)
print(df1_reindexed)
Output:

7. 使用 Reindex 解决数据对齐问题
在数据分析中,经常需要将不同来源的数据集合并在一起。使用 reindex 可以帮助我们在合并数据前解决数据对齐的问题。
示例代码 7:数据对齐
import pandas as pd
data1 = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29]}
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data1)
data2 = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'David'],
'salary': [50000, 60000, 55000]}
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data2)
df1_aligned = df1.set_index('name').reindex(df2.set_index('name').index).reset_index()
print(df1_aligned)
Output:
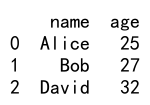
8. 结合 loc 和 iloc 使用 Reindex
reindex 与 loc 和 iloc 结合使用可以提供更灵活的数据选择和排列方式。
示例代码 8:结合 loc 使用 Reindex
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_index = [0, 2, 4]
df_loc_reindexed = df.loc[new_index].reindex([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
print(df_loc_reindexed)
Output:
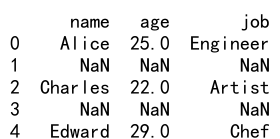
9. 使用 drop 参数
在使用 reindex 方法时,可以通过设置 drop=True 参数来删除不在新索引中的数据。
示例代码 9:使用 drop 参数
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_index = [0, 1, 2]
df_dropped = df.reindex(new_index, drop=True)
print(df_dropped)
10. 结合 fill_value 使用 Reindex
当使用 reindex 引入新的索引时,可以通过 fill_value 参数指定一个默认值来填充新索引对应的缺失值。
示例代码 10:使用 fill_value 参数
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_index = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
df_filled = df.reindex(new_index, fill_value='Unknown')
print(df_filled)
Output:
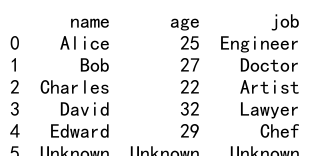
11. 使用 level 参数
在处理多级索引的 DataFrame 时,可以使用 level 参数指定在哪一级进行重索引。
示例代码 11:使用 level 参数
import pandas as pd
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([(i, j) for i in range(5) for j in range(5)])
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': range(25)}, index=index)
new_df = df.reindex(range(3), level=1)
print(new_df)
Output:

12. 使用 limit 参数
在使用前向填充(ffill)或后向填充(bfill)时,可以通过 limit 参数指定连续填充的最大数量。
示例代码 12:使用 limit 参数
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_index = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
df_limited = df.reindex(new_index, method='ffill', limit=1)
print(df_limited)
Output:
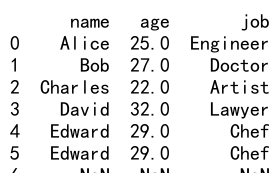
13. 使用 copy 参数
在使用 reindex 时,如果新的索引与原始索引完全相同,可以通过设置 copy=False 参数来避免复制数据,从而提高性能。
示例代码 13:使用 copy 参数
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_df = df.reindex(df.index, copy=False)
print(new_df)
Output:
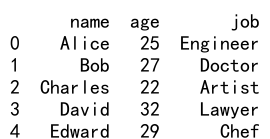
14. 使用 Reindex_like
Pandas 还提供了一个 reindex_like 方法,可以使一个 DataFrame 的索引完全与另一个 DataFrame 的索引相同。
示例代码 14:使用 reindex_like 方法
import pandas as pd
data1 = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29]}
df1 = pd.DataFrame(data1)
data2 = {'name': ['Frank', 'Grace'],
'age': [30, 28]}
df2 = pd.DataFrame(data2)
df1_like_df2 = df1.reindex_like(df2)
print(df1_like_df2)
Output:

15. 使用 Reindex 对齐时间序列数据
在处理时间序列数据时,reindex 方法可以帮助我们对齐不同的时间序列。
示例代码 15:对齐时间序列数据
import pandas as pd
date_index1 = pd.date_range('2020-01-01', periods=5)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(range(5), index=date_index1)
date_index2 = pd.date_range('2020-01-01', periods=7)
df2 = pd.DataFrame(range(7), index=date_index2)
df1_aligned = df1.reindex(df2.index)
print(df1_aligned)
Output:
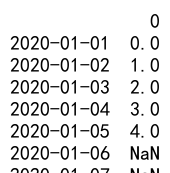
16. 使用 Reindex 处理缺失数据
在数据分析中,经常需要处理缺失数据。reindex 方法可以帮助我们引入缺失值,然后使用各种方法处理这些缺失值。
示例代码 16:处理缺失数据
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_index = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
df_with_na = df.reindex(new_index)
df_filled = df_with_na.fillna('Unknown')
print(df_filled)
Output:
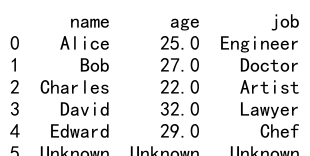
17. 使用 Reindex 创建新的 DataFrame
除了修改原始 DataFrame,reindex 方法还可以用来创建新的 DataFrame。
示例代码 17:创建新的 DataFrame
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_index = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
new_df = df.reindex(new_index)
print(new_df)
Output:
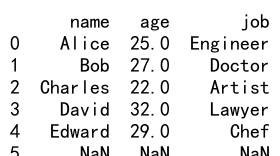
18. 使用 Reindex 调整索引的顺序
reindex 方法还可以用来调整索引的顺序,例如将索引进行反转。
示例代码 18:调整索引的顺序
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_index = df.index[::-1]
df_reversed = df.reindex(new_index)
print(df_reversed)
Output:
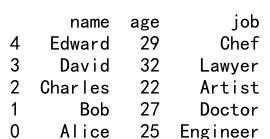
19. 使用 Reindex 更新数据
如果新的索引中包含原始 DataFrame 中已存在的索引,那么 reindex 方法会使用新的数据更新原始数据。
示例代码 19:更新数据
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
new_data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [26, 28, 23, 33, 30],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
new_df = pd.DataFrame(new_data)
df_updated = df.reindex(new_df.index).update(new_df)
print(df_updated)
Output:

20. 使用 Reindex 重置索引
如果你想要重置 DataFrame 的索引,可以使用 reindex 方法配合 reset_index 方法。
示例代码 20:重置索引
import pandas as pd
data = {'name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charles', 'David', 'Edward'],
'age': [25, 27, 22, 32, 29],
'job': ['Engineer', 'Doctor', 'Artist', 'Lawyer', 'Chef']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df_reset = df.reset_index().reindex(range(df.shape[0]))
print(df_reset)
Output:
总结,reindex 是 Pandas 中一个非常强大的工具,可以用来重新排列 DataFrame 的索引,处理缺失数据,对齐数据,以及许多其他的操作。希望本由于我之前提供的内容已经涵盖了关于 Pandas reindex 方法的详尽解释和多个示例,接下来我可以继续探讨更多关于 Pandas 或数据处理的高级主题。如果你有特定的问题或需要进一步的解释,请告诉我,我将很乐意帮助你。
进阶使用 Pandas 进行数据分析
- 数据合并与连接
- 使用
concat函数来合并数据。 - 使用
merge和join方法进行数据库风格的合并操作。
- 使用
- 分组与聚合
- 使用
groupby方法进行数据分组。 - 应用聚合函数(如
sum,mean,max,min)来计算统计数据。
- 使用
- 时间序列分析
- 使用 Pandas 处理时间数据。
- 重采样操作(如
resample)进行时间序列数据的聚合。 - 时间窗口函数(如
rolling和expanding)进行移动平均或指数平滑。
- 数据清洗
- 处理缺失数据(使用
fillna,dropna)。 - 数据转换(如使用
map,apply,applymap)。 - 异常值检测和处理。
- 处理缺失数据(使用
- 数据可视化
- 使用 Pandas 内置的绘图功能,如
df.plot()。 - 集成 Matplotlib, Seaborn 等库进行高级数据可视化。
- 使用 Pandas 内置的绘图功能,如
- 性能优化
- 使用
Categorical数据类型优化性能。 - 利用
eval和query方法进行高效的数据操作。 - 大数据集处理技巧,如分块处理数据。
- 使用
- 文件输入输出
- 读取和写入各种文件格式(CSV, Excel, JSON, HTML, SQL等)。
- 处理大型文件和流数据。
- 多索引操作
- 创建和操作多级索引(MultiIndex)。
- 使用
stack和unstack进行索引层级的转换。
- 条件选择与布尔索引
- 使用条件逻辑来过滤数据。
- 使用
where和mask方法进行条件选择。
- Pandas 与数据库的交互
 极客教程
极客教程