Python Pandas dataframe.resample()
Python是一种进行数据分析的伟大语言,主要是因为以数据为中心的Python包的奇妙生态系统。Pandas就是这些包中的一个,它使导入和分析数据变得更加容易。
Pandas dataframe.resample()函数主要用于时间序列数据。
时间序列是按时间顺序索引(或列出或绘制)的一系列数据点。最常见的是,一个时间序列是在连续的等距的时间点上采取的序列。它是一种方便的方法,用于时间序列的频率转换和重新取样。对象必须有一个类似日期的索引(DatetimeIndex、PeriodIndex或TimedeltaIndex),或者将类似日期的值传递给on或level关键字。
语法 : DataFrame.resample(rule, how=None, axis=0, fill_method=None, closed=None, label=None, convention=’start’, kind=None, loffset=None, limit=None, base=0, on=None, level=None)
参数 :
rule:代表目标转换的偏移字符串或对象
axis : int, optional, default 0
closed: {‘右’, ‘左’}
label: {‘右’,’左’}
convention:仅对于PeriodIndex,控制是否使用规则的开始或结束。
loffset :调整重新采样的时间标签
base : 对于均匀地划分为1天的频率,聚集区间的 “原点”。例如,对于 “5分钟 “的频率,基数可以从0到4。默认为0。
on : 对于一个DataFrame,在重新取样时要用列来代替索引。列必须是类似于数据时间的。
level : 对于一个MultiIndex,要用于重采样的级别(名称或数字)。水平必须是类似日期的。
重采样在实际数据的基础上产生了一个独特的采样分布。我们可以应用各种频率来重新取样我们的时间序列数据。这在分析领域是非常重要的技术。
最常用的时间序列频率是–
W :每周的频率
M :月末频率
SM :半月末频率(15日和月底)。
Q :季度末频率
还有许多其他类型的时间序列频率可用。让我们看看如何在数据上应用这些时间序列频率并重新取样。
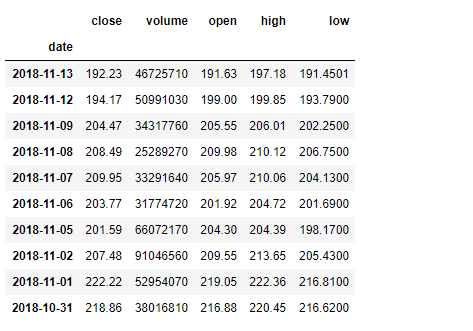
这是苹果公司从(13-11-17)到(13-11-18)一年的股票价格数据。
例子#1:按月频率对数据进行重采样
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# By default the "date" column was in string format,
# we need to convert it into date-time format
# parse_dates =["date"], converts the "date"
# column to date-time format. We know that
# resampling works with time-series data only
# so convert "date" column to index
# index_col ="date", makes "date" column, the index of the data frame
df = pd.read_csv("apple.csv", parse_dates =["date"], index_col ="date")
# Printing the first 10 rows of dataframe
df[:10]
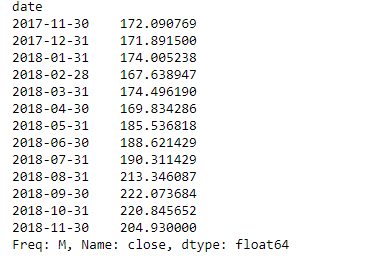
# Resampling the time series data based on months
# we apply it on stock close price
# 'M' indicates month
monthly_resampled_data = df.close.resample('M').mean()
# the above command will find the mean closing price
# of each month for a duration of 12 months.
monthly_resampled_data
输出 :
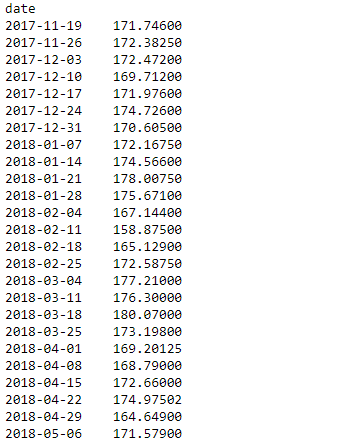
例子#2:对每周的数据进行重新取样。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# We know that resampling works with time-series data
# only so convert "date" column to index
# index_col ="date", makes "date" column.
df = pd.read_csv("apple.csv", parse_dates =["date"], index_col ="date")
# Resampling the time series data based on weekly frequency
# we apply it on stock open price 'W' indicates week
weekly_resampled_data = df.open.resample('W').mean()
# find the mean opening price of each week
# for each week over a period of 1 year.
weekly_resampled_data
输出 :
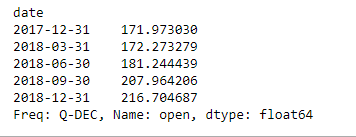
例子#3:按季度对数据进行重采样
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# We know that resampling works with time-series
# data only so convert our "date" column to index
# index_col ="date", makes "date" column
df = pd.read_csv("apple.csv", parse_dates =["date"], index_col ="date")
# Resampling the time series data
# based on Quarterly frequency
# 'Q' indicates quarter
Quarterly_resampled_data = df.open.resample('Q').mean()
# mean opening price of each quarter
# over a period of 1 year.
Quarterly_resampled_data
输出 :
 极客教程
极客教程