Numpy.random中的rand与normal的对比
在本文中,我们将详细研究Numpy.random.rand()方法和Numpy.random.normal()方法之间的主要区别。
- 关于random:对于随机变量,我们使用 .rand()
numpy.random.rand (d0, d1,…,dn):
创建指定形状和的数组,用随机值填充它。
参数 :
d0, d1, …, dn : [int, optional] 我们需要的返回数组的尺寸。 如果没有给出参数,则返回一个单一的Python float 将被返回。
返回 :定义形状的数组,用随机值填充。
- 关于normal:对于随机变量,我们使用 .normal()
numpy.random.normal(loc = 0.0, scale = 1.0, size = None):创建一个指定形状的数组,并将其填充为随机值,这实际上是正态(高斯)分布的一部分。这一分布因其独特的形状又被称为钟形曲线。参数 :
loc : [float or array_like]分布的平均值。分布的平均值。
scale : [float or array_like]标准 分布的推导。
size : [int或int图元]。输出形状给定为(m, n, k),那么 mnk的样本被抽取。如果大小是 无(默认),则返回一个单一的值 将被返回
返回 :
定义形状的数组,按照正态分布填充 随机值,符合正态 分布。
代码1:随机构造1D数组
# Python Program illustrating
# numpy.random.rand() method
import numpy as geek
# 1D Array
array = geek.random.rand(5)
print("1D Array filled with random values : \n", array)
输出 :
1D Array filled with random values :
[ 0.84503968 0.61570994 0.7619945 0.34994803 0.40113761]
代码2:按照高斯分布随机构造1D数组
# Python Program illustrating
# numpy.random.normal() method
import numpy as geek
# 1D Array
array = geek.random.normal(0.0, 1.0, 5)
print("1D Array filled with random values "
"as per gaussian distribution : \n", array)
# 3D array
array = geek.random.normal(0.0, 1.0, (2, 1, 2))
print("\n\n3D Array filled with random values "
"as per gaussian distribution : \n", array)
输出 :
1D Array filled with random values as per gaussian distribution :
[-0.99013172 -1.52521808 0.37955684 0.57859283 1.34336863]
3D Array filled with random values as per gaussian distribution :
[[[-0.0320374 2.14977849]]
[[ 0.3789585 0.17692125]]]
代码3:演示NumPy中随机与正常的图形表示的Python程序
# Python Program illustrating
# graphical representation of
# numpy.random.normal() method
# numpy.random.rand() method
import numpy as geek
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
# 1D Array as per Gaussian Distribution
mean = 0
std = 0.1
array = geek.random.normal(0, 0.1, 1000)
print("1D Array filled with random values "
"as per gaussian distribution : \n", array);
# Source Code :
# https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.13.0/reference/
# generated/numpy-random-normal-1.py
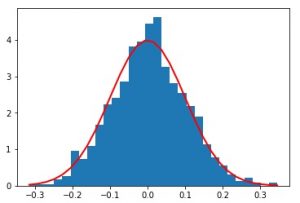
count, bins, ignored = plot.hist(array, 30, normed=True)
plot.plot(bins, 1/(std * geek.sqrt(2 * geek.pi)) *
geek.exp( - (bins - mean)**2 / (2 * std**2) ),
linewidth=2, color='r')
plot.show()
# 1D Array constructed Randomly
random_array = geek.random.rand(5)
print("1D Array filled with random values : \n", random_array)
plot.plot(random_array)
plot.show()
输出 :
1D Array filled with random values as per gaussian distribution :
[ 0.12413355 0.01868444 0.08841698 ..., -0.01523021 -0.14621625
-0.09157214]
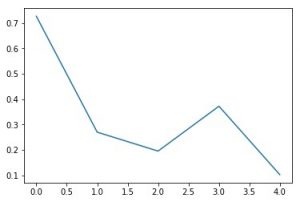
1D Array filled with random values :
[ 0.72654409 0.26955422 0.19500427 0.37178803 0.10196284]
注意:
在代码3中,图1清楚地显示了高斯分布,因为它是由random.normal()方法生成的值创建的,因此遵循了高斯分布。图2不遵循任何分布,因为它是由random.rand()方法生成的随机值创建的。
 极客教程
极客教程