Golang 指针
Go编程语言或Golang中的指针是一个变量,用来存储另一个变量的内存地址。Golang中的指针也被称为特殊变量。这些变量用于在系统中的特定内存地址上存储一些数据。内存地址总是以十六进制格式出现(以0x开头,如0xFFAAF等)。
对指针的需求是什么
为了理解这一需求,首先,我们必须理解变量的概念。变量是对存储实际数据的内存位置的命名。为了访问存储的数据,我们需要该特定内存位置的地址。手动记住所有的内存地址(十六进制格式)是一种开销,这就是为什么我们使用变量来存储数据,并且可以通过使用它们的名字来访问变量。
Golang也允许使用字面表达式将十六进制数字保存到变量中,即从 0x 开始的数字是一个十六进制数字。
例子: 在下面的程序中,我们将十六进制的数字存储到一个变量中。但你可以看到,数值的类型是 int ,并保存为十进制,或者你可以说 int 类型的十进制值正在存储。但解释这个例子的重点是,我们正在存储一个十六进制的数值(将其视为一个内存地址),但它不是一个指针,因为它没有指向另一个变量的任何其他内存位置。它只是一个用户定义的变量。所以这就产生了对指针的需求。
// Golang program to demonstrate the variables
// storing the hexadecimal values
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// storing the hexadecimal
// values in variables
x := 0xFF
y := 0x9C
// Displaying the values
fmt.Printf("Type of variable x is %T\n", x)
fmt.Printf("Value of x in hexadecimal is %X\n", x)
fmt.Printf("Value of x in decimal is %v\n", x)
fmt.Printf("Type of variable y is %T\n", y)
fmt.Printf("Value of y in hexadecimal is %X\n", y)
fmt.Printf("Value of y in decimal is %v\n", y)
}
输出
Type of variable x is int
Value of x in hexadecimal is FF
Value of x in decimal is 255
Type of variable y is int
Value of y in hexadecimal is 9C
Value of y in decimal is 156
指针是一种特殊的变量,它不仅用来存储其他变量的内存地址,而且还指出内存的位置,并提供找出存储在该内存位置的值的方法。它通常被称为一种特殊的变量,因为它几乎是作为一个变量来声明的,但有* (解除引用操作符)。
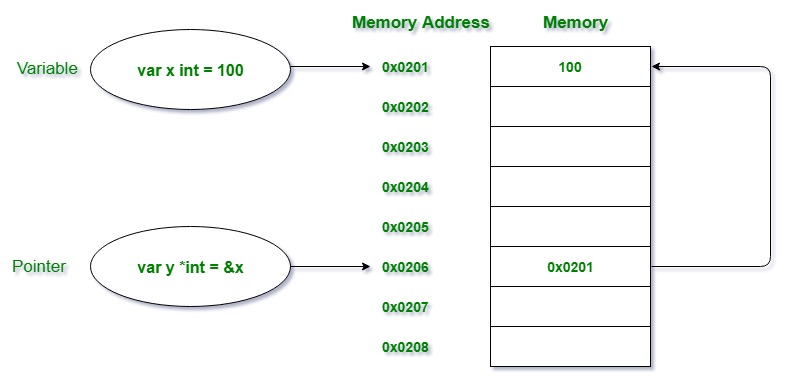
指针的声明和初始化
在我们开始之前,有两个重要的运算符我们将在指针中使用,即。
- *操作符 也被称为去引用操作符,用于声明指针变量和访问存储在地址中的值。
- 操作符 被称为地址操作符,用于返回变量的地址或访问指针变量的地址。
声明一个指针:
var pointer_name *Data_Type
例如: 下面是一个字符串类型的指针,它只能存储字符串变量的内存地址。
var s *string
指针的初始化: 要做到这一点,你需要使用地址操作符用另一个变量的内存地址初始化一个指针,如下例所示:
// normal variable declaration
var a = 45
// Initialization of pointer s with
// memory address of variable a
var s *int = &a
例子
// Golang program to demonstrate the declaration
// and initialization of pointers
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// taking a normal variable
var x int = 5748
// declaration of pointer
var p *int
// initialization of pointer
p = &x
// displaying the result
fmt.Println("Value stored in x = ", x)
fmt.Println("Address of x = ", &x)
fmt.Println("Value stored in variable p = ", p)
}
输出:
Value stored in x = 5748
Address of x = 0x414020
Value stored in variable p = 0x414020
重要观点
1. 一个指针的默认值或零值总是为 零。 或者你可以说,一个未初始化的指针总是有一个nil值。
例子
// Golang program to demonstrate
// the nil value of the pointer
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// taking a pointer
var s *int
// displaying the result
fmt.Println("s = ", s)
}
输出:
s = <nil>
2. 指针的声明和初始化可以在一行中完成。
例如:
var s *int = &a
3. 如果你在声明指针时指定了数据类型,那么指针将能够处理指定数据类型变量的内存地址。例如,如果你采取一个字符串类型的指针,那么你给指针的变量地址将只是字符串数据类型的变量,而不是任何其他类型。
4. 为了克服上述问题,你可以使用var关键字的类型推理概念。在声明时不需要指定数据类型。指针型变量的类型也可以像普通变量一样由编译器决定。这里我们将不使用*操作符。它将由编译器内部决定,因为我们正在用另一个变量的地址初始化该变量。
例子
// Golang program to demonstrate
// the use of type inference in
// Pointer variables
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// using var keyword
// we are not defining
// any type with variable
var y = 458
// taking a pointer variable using
// var keyword without specifying
// the type
var p = &y
fmt.Println("Value stored in y = ", y)
fmt.Println("Address of y = ", &y)
fmt.Println("Value stored in pointer variable p = ", p)
}
输出:
Value stored in y = 458
Address of y = 0x414020
Value stored in pointer variable p = 0x414020
5. 你也可以使用速记(:=)语法来声明和初始化指针变量。如果我们使用&(address) 操作符将变量的地址传递给它,编译器将在内部确定该变量是一个指针变量。
例子
// Golang program to demonstrate
// the use of shorthand syntax in
// Pointer variables
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// using := operator to declare
// and initialize the variable
y := 458
// taking a pointer variable using
// := by assigning it with the
// address of variable y
p := &y
fmt.Println("Value stored in y = ", y)
fmt.Println("Address of y = ", &y)
fmt.Println("Value stored in pointer variable p = ", p)
}
输出
Value stored in y = 458
Address of y = 0x414020
Value stored in pointer variable p = 0x414020
解除对指针的引用
正如我们所知,*操作符也被称为去参考操作符。它不仅用于声明指针变量,而且还用于访问指针所指向的变量中存储的值,这通常被称为 间接或解除引用。 *操作符也被称为.NET地址的值。 让我们举一个例子来更好地理解这个概念。
例子:
// Golang program to illustrate the
// concept of dereferencing a pointer
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// using var keyword
// we are not defining
// any type with variable
var y = 458
// taking a pointer variable using
// var keyword without specifying
// the type
var p = &y
fmt.Println("Value stored in y = ", y)
fmt.Println("Address of y = ", &y)
fmt.Println("Value stored in pointer variable p = ", p)
// this is dereferencing a pointer
// using * operator before a pointer
// variable to access the value stored
// at the variable at which it is pointing
fmt.Println("Value stored in y(*p) = ", *p)
}
输出:
Value stored in y = 458
Address of y = 0x414020
Value stored in pointer variable p = 0x414020
Value stored in y(*p) = 458
你也可以改变指针的值或在内存位置的值,而不是给变量分配一个新值。
例如:
// Golang program to illustrate the
// above mentioned concept
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// using var keyword
// we are not defining
// any type with variable
var y = 458
// taking a pointer variable using
// var keyword without specifying
// the type
var p = &y
fmt.Println("Value stored in y before changing = ", y)
fmt.Println("Address of y = ", &y)
fmt.Println("Value stored in pointer variable p = ", p)
// this is dereferencing a pointer
// using * operator before a pointer
// variable to access the value stored
// at the variable at which it is pointing
fmt.Println("Value stored in y(*p) Before Changing = ", *p)
// changing the value of y by assigning
// the new value to the pointer
*p = 500
fmt.Println("Value stored in y(*p) after Changing = ",y)
}
输出
Value stored in y before changing = 458
Address of y = 0x414020
Value stored in pointer variable p = 0x414020
Value stored in y(*p) Before Changing = 458
Value stored in y(*p) after Changing = 500
 极客教程
极客教程