CSS 位置 z-index 属性
CSS z-index 属性
CSS z-index 属性用于控制网页中重叠的元素在相同层叠上下文中的堆叠顺序。具有较高 z-index 值的元素会显示在具有较低值的元素的前面。
以下图示演示了层叠顺序布局的参考:
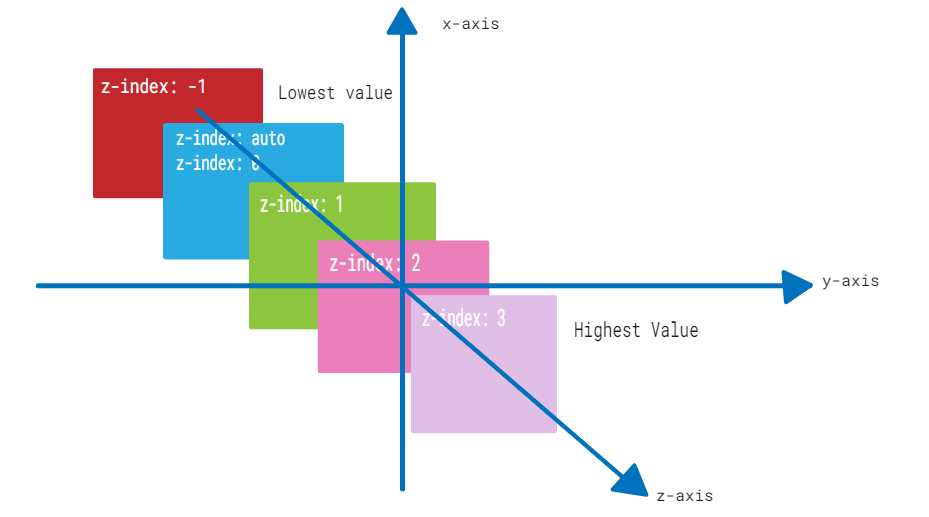
z-index属性可以与嵌套在其他已定位元素内的已定位元素一起使用。
语法
CSS允许以多种方式设置元素的z-index属性。让我们检查设置元素z-index的所有可能的可用语法。
关键字值
默认值。堆叠顺序与父元素相同。
z-index: auto;
整数值
一个正数或负数的整数。它将元素的堆栈级别设置为给定值。较低的值将具有较低的优先级,元素将位于其他元素的后一层。
z-index: 0;
z-index: 5;
z-index: 100;
z-index: -1;
适用于
所有定位元素。
DOM语法
object.style.zIndex = "2";
CSS z-index自动
CSS z-index:auto 将一个元素的z-index设置为其父元素的堆叠顺序。这是z-index属性的默认值。
示例
这是一个示例 –
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box1 {
position: absolute;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: auto;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.box2 {
position: absolute;
height: 120px;
width: 200px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: 1;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 20px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
p {
margin-top: 250px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>The element with z-index value of auto appears behind the element with the z-index value of 1.</p>
<div class="box1">
<span>CSS z-index: auto</span>
<div class="box2">
<span>CSS z-index: 1</span>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS z-index – 正整数
CSS的z-index属性可以具有正整数值。具有较高整数值的元素将在层叠顺序中出现在具有较低值的元素上方。
示例
这里是一个示例 –
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box1 {
position: absolute;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: 1;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.box2 {
position: absolute;
height: 140px;
width: 220px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: 2;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
.box3 {
position: absolute;
height: 90px;
width: 160px;
background-color: #b7c8ae;
z-index: 3;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 20px;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
p {
margin-top: 250px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>The element with z-index value of 1 appears behind the element with the z-index value of 2 and 3.</p>
<div class="box1">
CSS z-index: 1
</div>
<div class="box2">
CSS z-index: 2
</div>
<div class="box3">
CSS z-index: 3
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS z-index – 负整数
您还可以使用负整数值来设置 z-index 属性。具有负 z-index 值的元素将位于具有较高 z-index 值的元素下方。
示例
以下是一个示例 –
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box1 {
position: absolute;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: -3;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.box2 {
position: absolute;
height: 140px;
width: 220px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: -2;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
.box3 {
position: absolute;
height: 90px;
width: 160px;
background-color: #b7c8ae;
z-index: -1;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 20px;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
p {
margin-top: 250px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>The element with z-index value of -3 appears behind the element with the z-index value of -2 and -1.</p>
<div class="box1">
CSS z-index: -3
</div>
<div class="box2">
CSS z-index: -2
</div>
<div class="box3">
CSS z-index: -1
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS z-index属性 position: sticky
下面的例子演示了如何使用z-index属性来控制带有position: sticky属性的元素的堆叠顺序,以使它们在页面滚动时保持固定位置−
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box1 {
position: sticky;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: 1;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
margin: 10px;
left: 10px;
top: 80px;
}
.box2 {
position: sticky;
height: 140px;
width: 220px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: 2;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 40px;
top: 200px;
}
.box3 {
position: sticky;
height: 90px;
width: 160px;
background-color: #b7c8ae;
z-index: 3;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 70px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Move cursor upward to see the effect.</p>
<div class="box1">
CSS z-index: 1
</div>
<div class="box2">
CSS z-index: 2
</div>
<div class="box3">
CSS z-index: 3
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS z-index width position: fixed
下面的示例演示了如何使用 z-index 属性使元素在用户向下滚动时始终保持在内容之上,即使它具有 position: fixed 属性−
<html>
<head>
<style>
.container {
position: relative;
height: 350px;
}
.box1 {
position: fixed;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: -3;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.box2 {
position: fixed;
height: 140px;
width: 220px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: -2;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
.box3 {
position: fixed;
height: 90px;
width: 160px;
background-color: #b7c8ae;
z-index: -1;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 20px;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
h3 {
margin-top: 320px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Scroll down the content to see the effect.</h3>
<div class="container">
<div class="box1">
CSS z-index: -3
</div>
<div class="box2">
CSS z-index: -2
</div>
<div class="box3">
CSS z-index: -1
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS z-index width position: static
以下示例显示了z-index属性对具有position: static属性的元素的堆叠顺序没有影响−
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box1 {
position: static;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: 1;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
margin: 10px;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.box2 {
position: static;
height: 140px;
width: 220px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: 2;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
.box3 {
position: static;
height: 90px;
width: 160px;
background-color: #b7c8ae;
z-index: 3;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>The z-index property has no effect on the stacking order of elements if the position property is set to static.</p>
<div class="box1">
CSS z-index: 1
</div>
<div class="box2">
CSS z-index: 2
</div>
<div class="box3">
CSS z-index: 3
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS z-index 属性
示例表明当元素具有 position: relative 属性时, z-index 属性会将元素相对于其在文档流中的原始位置进行定位。
<html>
<head>
<style>
.box1 {
position: relative;
height: 200px;
width: 280px;
background-color: #f0baba;
z-index: 1;
text-align: center;
padding: 3px;
margin: 10px;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
.box2 {
position: relative;
height: 140px;
width: 220px;
background-color: #eae98f;
z-index: 2;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 30px;
top: 30px;
}
.box3 {
position: relative;
height: 90px;
width: 160px;
background-color: #b7c8ae;
z-index: 3;
text-align: center;
padding: 5px;
margin: 10px;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>The z-index property positions the element relative to its original position if position is relative.</p>
<div class="box1">
CSS z-index: 1
</div>
<div class="box2">
CSS z-index: 2
</div>
<div class="box3">
CSS z-index: 3
</div>
</body>
</html>
 极客教程
极客教程