C++程序 计算已排序旋转链表中的旋转数
给定一个有n个节点的链表,首先是已排序的,然后旋转了k个元素。找到k的值。
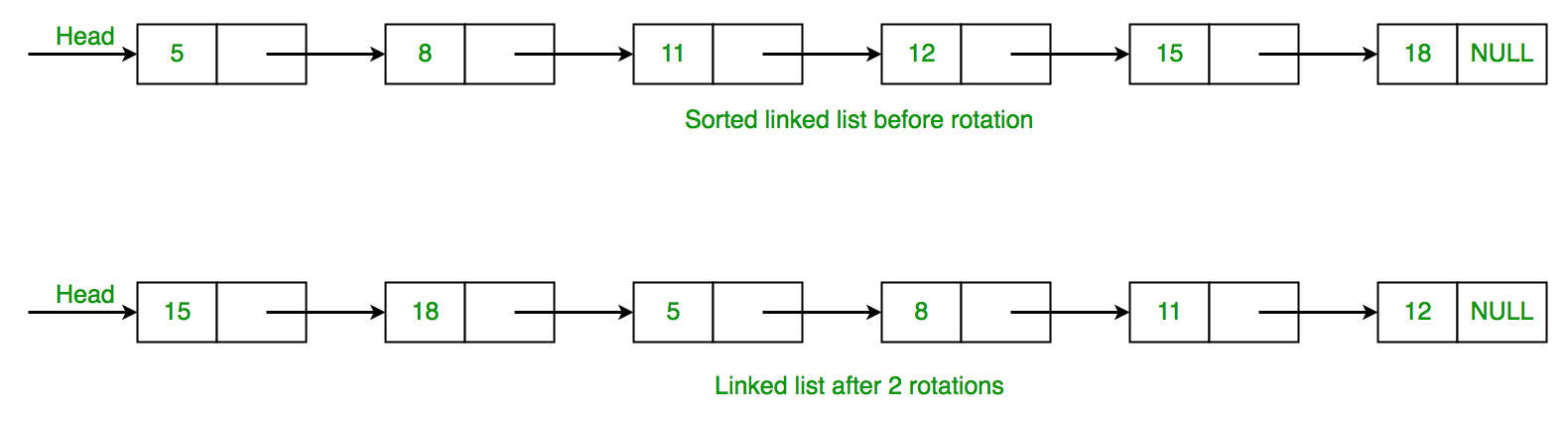
思路是遍历单链表,检查当前节点值是否大于下一个节点的值。如果给定条件为真,则中断循环。否则增加计数器变量,并逐个节点增加节点->next。下面是此方法的实现。
// 计算已排序链表中旋转数量的程序。
#include
using namespace std;
/* 链表节点 */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// 在单链表中计数旋转数的函数。
int countRotation(struct Node* head)
{
// 声明计数变量并将其分配为1。
int count = 0;
// 声明min变量并将其分配为
// 头结点的数据。
int min = head->data;
// 检查头是否不等于NULL。
while (head != NULL) {
// 如果min值大于head->data,那么它将中断循环,
// 并返回计数的值。
if (min > head->data)
break;
count++;
// 头分配头的下一个值。
head = head->next;
}
return count;
}
// 在链接列表中推入元素的函数。
void push(struct Node** head, int data)
{
// 为新节点分配动态内存。
struct Node* newNode = new Node;
// 将数据分配给newNode。
newNode->data = data;
// newNode->next分配头节点的地址。
newNode->next = (*head);
// newNode变成headNode。
(*head) = newNode;
}
// 显示链接列表。
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
// 驱动程序函数
int main()
{
// 创建一个节点并初始化为NULL
struct Node* head = NULL;
// push()在链表中插入节点。
// 15 -> 18 -> 5 -> 8 -> 11 -> 12
push(&head;, 12);
push(&head;, 11);
push(&head;, 8);
push(&head;, 5);
push(&head;, 18);
push(&head;, 15);
printList(head);
cout << endl;
cout << "Linked list rotated elements: ";
// 调用函数countRotation()
cout << countRotation(head) << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
15 18 5 8 11 12
Linked list rotated elements: 2
时间复杂度: O(N),其中N表示链表的长度。
辅助空间: O(1),不需要额外的空间,因此是一个常数。
 极客教程
极客教程