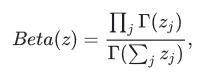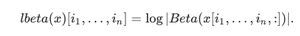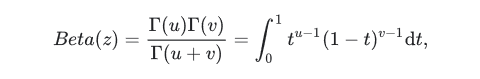Python – tensorflow.math.lbeta()
TensorFlow是谷歌设计的开源Python库,用于开发机器学习模型和深度学习神经网络。
lbeta()是用来计算ln(|Beta(x)|)的。它沿着最后一个维度减少张量。如果一维的z是[z1, …, zk],那么Beta(z)被定义为
如果x是形状为[N 1 , …, N n , k]的n+1维张量,最后一维被视为z矢量和。
如果z=[u,v],那么传统的双变量β函数定义为
语法: tensorflow.math.lbeta( x, name)
参数:
- x:它是具有n+1级的输入张量,其中n>=0。允许的dtypes是float或double。
- name(可选):它定义了该操作的名称。
返回值:
它返回|Beta(x)|沿最后一个维度减少的对数。
示例 1:
# Importing the library
import tensorflow as tf
# Initializing the input tensor
a = tf.constant([[7, 8], [13, 11]], dtype = tf.float64)
# Printing the input tensor
print('a: ', a)
# Calculating the result
res = tf.math.lbeta(x = a)
# Printing the result
print('Result: ', res)
输出:
a: tf.Tensor(
[[ 7. 8.]
[13. 11.]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float64)
Result: tf.Tensor([-10.08680861 -16.5150485 ], shape=(2, ), dtype=float64)
示例 2:
# Importing the library
import tensorflow as tf
# Initializing the input tensor
a = tf.constant([7, 8, 13, 11], dtype = tf.float64)
# Printing the input tensor
print('a: ', a)
# Calculating the result
res = tf.math.lbeta(x = a)
# Printing the result
print('Result: ', res)
输出:
a: tf.Tensor([ 7. 8. 13. 11.], shape=(4, ), dtype=float64)
Result: tf.Tensor(-52.77215897270088, shape=(), dtype=float64)
 极客教程
极客教程