Java servlet 分页教程显示了如何使用 Java servlet 进行分页。 在示例中,Bootstrap 用于 UI。
分页
分页是将内容分为几页的过程。 用户具有用于通过特定页面链接访问这些页面的导航界面。 导航通常包括上一个/下一个和第一个/最后一个链接。 当数据库中有大量数据或一页中显示许多注释时,将使用分页。
Java Servlet
Servlet 是 Java 类,可响应特定类型的网络请求-最常见的是 HTTP 请求。 Java servlet 用于创建 Web 应用。 它们在 servlet 容器(例如 Tomcat 或 Jetty)中运行。 现代 Java Web 开发使用在 servlet 之上构建的框架。
Bootstrap
Bootstrap 是 Twitter 的一个 UI 库,用于创建响应式,移动优先的 Web 应用。
Java Servlet 分页示例
在以下应用中,我们从 MySQL 数据库加载数据并将其显示在表中。 有一个导航系统可以遍历数据库表中的所有数据。 在将数据显示在表中之前,用户可以选择表将显示多少行。
除了从数据库表中获取数据之外,我们还需要知道数据库表中所有行的数量,每页的记录数以及要在导航中显示的页面数。 SQL 语句可以计算出数据库中所有行的数量。 用户以 HTML 格式选择每页的记录数。 最后,从其他两个值计算分页中的页数。
countries_mysql.sql
CREATE TABLE Countries(ID BIGINT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
Name VARCHAR(100), Population INT);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('China', 1382050000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('India', 1313210000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('USA', 324666000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Indonesia', 260581000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Brazil', 207221000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Pakistan', 196626000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Nigeria', 186988000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Bangladesh', 162099000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Nigeria', 186988000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Russia', 146838000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Japan', 126830000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Mexico', 122273000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Philippines', 103738000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Ethiopia', 101853000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Vietnam', 92700000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Egypt', 92641000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Germany', 82800000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('the Congo', 82243000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Iran', 82800000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Turkey', 79814000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Thailand', 68147000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('France', 66984000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('United Kingdom', 60589000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('South Africa', 55908000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Myanmar', 51446000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('South Korea', 68147000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Colombia', 49129000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Kenya', 47251000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Spain', 46812000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Argentina', 43850000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Ukraine', 42603000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Sudan', 41176000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Algeria', 40400000);
INSERT INTO Countries(Name, Population) VALUES('Poland', 38439000);
该 SQL 脚本在 MySQL 中创建Countries表。
$ tree
.
├── nb-configuration.xml
├── pom.xml
└── src
├── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── com
│ │ └── zetcode
│ │ ├── bean
│ │ │ └── Country.java
│ │ ├── service
│ │ │ ├── CountryService.java
│ │ │ └── ICountryService.java
│ │ └── web
│ │ └── ReadCountries.java
│ ├── resources
│ └── webapp
│ ├── index.html
│ ├── listCountries.jsp
│ ├── META-INF
│ │ └── context.xml
│ └── WEB-INF
└── test
└── java
这是项目结构。
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.zetcode</groupId>
<artifactId>JavaServletPagination</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>JavaServletPagination</name>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.45</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
<configuration>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
这是 Maven POM 文件。 javax.servlet-api工件用于 servlet。 spring-jdbc依赖性用于 JdbcTemplate 库,该库简化了 Java 中的数据库编程。 mysql-connector-java是 Java 语言的 MySQL 驱动程序。 jstl依赖性为 JSP 页面提供了一些附加功能。 maven-war-plugin负责收集 Web 应用的所有工件依赖项,类和资源,并将它们打包到 Web 应用存档(WAR)中。
context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Context path="/JavaServletPagination"/>
在 Tomcat context.xml文件中,我们定义了上下文路径。 它是 Web 应用的名称。
Country.java
package com.zetcode.bean;
public class Country {
private String name;
private int population;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getPopulation() {
return population;
}
public void setPopulation(int population) {
this.population = population;
}
}
Country bean 从Countries数据库表中保留一行。
ReadCountries.java
package com.zetcode.web;
import com.zetcode.bean.Country;
import com.zetcode.service.CountryService;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet(name = "ReadCountries", urlPatterns = {"/ReadCountries"})
public class ReadCountries extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
int currentPage = Integer.valueOf(request.getParameter("currentPage"));
int recordsPerPage = Integer.valueOf(request.getParameter("recordsPerPage"));
CountryService countryService = new CountryService();
List<Country> countries = countryService.findCountries(currentPage,
recordsPerPage);
request.setAttribute("countries", countries);
int rows = countryService.getNumberOfRows();
int nOfPages = rows / recordsPerPage;
if (nOfPages % recordsPerPage > 0) {
nOfPages++;
}
request.setAttribute("noOfPages", nOfPages);
request.setAttribute("currentPage", currentPage);
request.setAttribute("recordsPerPage", recordsPerPage);
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher("listCountries.jsp");
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
}
}
ReadCountries Servlet 确定将从请求属性中检索多少数据,并从数据库表中读取指定的行数。
@WebServlet(name = "ReadCountries", urlPatterns = {"/ReadCountries"})
Java 类用@WebServlet注释修饰。 它映射到ReadCountries URL 模式。
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
Servlet 将以 HTML 输出数据,并且数据的编码设置为 UTF-8。
int currentPage = Integer.valueOf(request.getParameter("currentPage"));
int recordsPerPage = Integer.valueOf(request.getParameter("recordsPerPage"));
从请求中我们得到两个重要的值:当前页和每页的记录数。
CountryService countryService = new CountryService();
List<Country> countries = countryService.findCountries(currentPage,
recordsPerPage);
request.setAttribute("countries", countries);
CountryService是用于连接到数据库并读取数据的服务类。 检索国家列表并将其设置为请求的属性。 稍后将由目标 JSP 页面使用。
int rows = countryService.getNumberOfRows();
int nOfPages = rows / recordsPerPage;
if (nOfPages % recordsPerPage > 0) {
nOfPages++;
}
我们使用getNumberOfRows()服务方法从数据库表中获取所有行的数目。 我们计算导航中的页面数。
request.setAttribute("noOfPages", nOfPages);
request.setAttribute("currentPage", currentPage);
request.setAttribute("recordsPerPage", recordsPerPage);
页数,当前页和每页的记录数是我们建立分页所需的值。
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher("listCountries.jsp");
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
处理被转发到listCountries.jsp页面。
ICountryService.java
package com.zetcode.service;
import com.zetcode.bean.Country;
import java.util.List;
public interface ICountryService {
public List<Country> findCountries(int currentPage, int numOfRecords);
public int getNumberOfRows();
}
ICountryService包含两种签约方法:findCountries()和getNumberOfRows()。
CountryService.java
package com.zetcode.service;
import com.zetcode.bean.Country;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.SimpleDriverDataSource;
public class CountryService implements ICountryService {
@Override
public List<Country> findCountries(int currentPage, int recordsPerPage) {
List<Country> countries = null;
int start = currentPage * recordsPerPage - recordsPerPage;
try {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM Countries LIMIT ?, ?";
SimpleDriverDataSource ds = new SimpleDriverDataSource();
ds.setDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb");
ds.setUsername("testuser");
ds.setPassword("test623");
JdbcTemplate jtm = new JdbcTemplate(ds);
countries = jtm.query(sql, new Object[] {start, recordsPerPage},
new BeanPropertyRowMapper(Country.class));
} catch (SQLException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(CountryService.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE,
null, ex);
}
return countries;
}
@Override
public int getNumberOfRows() {
int numOfRows = 0;
try {
String sql = "SELECT COUNT(Id) FROM Countries";
SimpleDriverDataSource ds = new SimpleDriverDataSource();
ds.setDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testdb");
ds.setUsername("testuser");
ds.setPassword("test623");
JdbcTemplate jtm = new JdbcTemplate(ds);
numOfRows = jtm.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class);
} catch (SQLException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(CountryService.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE,
null, ex);
}
return numOfRows;
}
}
CountryService包含两种合同方法的实现。
String sql = "SELECT * FROM Countries LIMIT ?, ?";
SQL LIMIT 子句用于获取当前页面的行数。
JdbcTemplate jtm = new JdbcTemplate(ds);
countries = jtm.query(sql, new Object[] {start, recordsPerPage},
new BeanPropertyRowMapper(Country.class));
JdbcTemplate用于执行 SQL 语句。 在BeanPropertyRowMapper的帮助下,行自动映射到Country bean。
String sql = "SELECT COUNT(Id) FROM Countries";
通过此 SQL 语句,我们从数据库表中获取行数。
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Home page</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.0.0-alpha.6/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body class="m-3">
<h1>Show countries</h1>
<form action="ReadCountries">
<input type="hidden" name="currentPage" value="1">
<div class="form-group col-md-4">
<label for="records">Select records per page:</label>
<select class="form-control" id="records" name="recordsPerPage">
<option value="5">5</option>
<option value="10" selected>10</option>
<option value="15">15</option>
</select>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</form>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.1.1.slim.min.js" ></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/tether/1.4.0/js/tether.min.js" ></script>
<script src="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.0.0-alpha.6/js/bootstrap.min.js" ></script>
</body>
</html>
这是主页。 它包含一个 HTML 表单,用于通过select标签选择每页的记录数。 该表单使用 Bootstrap 库中的样式类。 提交表单后,处理将发送到ReadCountries Servlet。
<input type="hidden" name="currentPage" value="1">
该表单包含一个隐藏的input标记,该标记将currentPage参数设置为 1。
<select class="form-control" id="records" name="recordsPerPage">
<option value="5">5</option>
<option value="10" selected>10</option>
<option value="15">15</option>
</select>
select标签允许每页选择 5、10 或 15 条记录。
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
提交按钮执行表单。
listCountries.jsp
<%@page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Countries</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.0.0-alpha.6/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body class="m-3">
<div class="row col-md-6">
<table class="table table-striped table-bordered table-sm">
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Population</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="{countries}" var="country">
<tr>
<td>{country.getName()}</td>
<td>{country.getPopulation()}</td> </tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</div>
<nav aria-label="Navigation for countries">
<ul class="pagination">
<c:if test="{currentPage != 1}">
<li class="page-item"><a class="page-link"
href="ReadCountries?recordsPerPage={recordsPerPage}¤tPage={currentPage-1}">Previous</a>
</li>
</c:if>
<c:forEach begin="1" end="{noOfPages}" var="i">
<c:choose>
<c:when test="{currentPage eq i}">
<li class="page-item active"><a class="page-link">
{i} <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
<li class="page-item"><a class="page-link" href="ReadCountries?recordsPerPage={recordsPerPage}¤tPage={i}">{i}</a>
</li>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
</c:forEach>
<c:if test="{currentPage lt noOfPages}">
<li class="page-item"><a class="page-link" href="ReadCountries?recordsPerPage={recordsPerPage}¤tPage=${currentPage+1}">Next</a>
</li>
</c:if>
</ul>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.1.1.slim.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/tether/1.4.0/js/tether.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.0.0-alpha.6/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
listCountries.jsp在表格和分页系统中显示数据。 Bootstrap 用于使 UI 响应并看起来不错。
<table class="table table-striped table-bordered table-sm">
table,table-striped,table-bordered和table-sm都是 Bootstrap 类。
<c:forEach items="{countries}" var="country">
<tr>
<td>{country.getName()}</td>
<td>${country.getPopulation()}</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
使用 JSTL 的forEach标签,我们可以显示当前页面的所有数据。
<c:if test="{currentPage != 1}">
<li class="page-item"><a class="page-link" href="ReadCountries?recordsPerPage={recordsPerPage}¤tPage=${currentPage-1}">Previous</a>
</li>
</c:if>
使用c:if标签,我们仅在存在前一个链接时显示它。 在链接中,我们将recordsPerPage和currentPage值传递给请求对象。
<c:forEach begin="1" end="{noOfPages}" var="i">
<c:choose>
<c:when test="{currentPage eq i}">
<li class="page-item active"><a class="page-link">
{i} <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
<li class="page-item"><a class="page-link" href="ReadCountries?recordsPerPage={recordsPerPage}¤tPage={i}">{i}</a>
</li>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
</c:forEach>
使用forEach标签,我们显示所有页面链接。
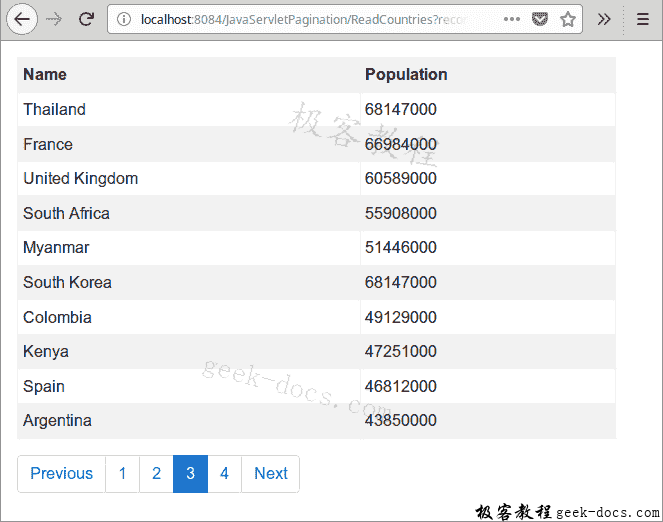
该示例显示了一个装有数据和分页系统的表。 当前选择的页面突出显示。
您可能也对以下相关教程感兴趣: Java Servlet 上传文件, Java Log4j 教程, Java Servlet RESTful 客户端,Java servlet 图像教程或 Java 教程提供纯文本。
 极客教程
极客教程