R语言 创建热图
热图是一种表示数据的图形方式。它最常用于数据分析。在数据分析中,我们探索数据集并从数据集中获得洞察力,我们试图通过对数据进行可视化分析来找到数据中的隐藏模式。热图用颜色将矩阵的值可视化,颜色越亮意味着值越高,颜色越浅意味着值越低。在Heatmap中,我们使用从暖到冷的颜色方案。热力图是所谓的热力图,因为在热力图中,我们把颜色映射到我们的数据集中的不同数值上。
在这篇文章中,我们将讨论如何在R编程语言中创建热图。
方法1:使用ggplot2软件包中的geom_tile()
geom_tile() 用于创建一个带有平面矩形砖的二维热图。它预先安装在R编程的 ggplot2 包中。
语法
geom_tile( mapping =NULL, data=NULL, stat=”identity”,…)
参数
- mapping : 可以是 “Aes”。”ais “是美学映射的首字母缩写。它描述了数据中的变量是如何被映射到几何体的视觉属性上的。
- data : 它持有数据集变量,一个我们在脚本中存储数据 的 变量 。
- stat : 它用于对数据集进行任何形式的统计操作。
要创建一个热图,首先要导入所需的库,然后创建或加载一个数据集。现在简单地调用geom_tile()函数,并为参数设置适当的值。
例子
# Plotting Heatmap in R
# adding ggplot2 library for plotting
library(ggplot2)
# Creating random dataset
# with 20 alphabets and 20 animal names
letters <- LETTERS[1:20]
animal_names <- c("Canidae","Felidae","Cat","Cattle",
"Dog","Donkey","Goat","Guinea pig",
"Horse","Pig","Rabbit","Badger",
"Bald eagle","Bandicoot","Barnacle",
"Bass","Bat","Bear","Beaver","Bedbug",
"Bee","Beetle")
data <- expand.grid(X=letters, Y=animal_names)
data$count <- runif(440, 0, 6)
# plotting the heatmap
plt <- ggplot(data,aes( X, Y,fill=count))
plt <- plt + geom_tile()
# further customizing the heatmap by
# applying colors and title
plt <- plt + theme_minimal()
# setting gradient color as red and white
plt <- plt + scale_fill_gradient(low="white", high="red")
# setting the title and subtitles using
# title and subtitle
plt <- plt + labs(title = "Heatmap")
plt <- plt + labs(subtitle = "A simple heatmap using geom_tile()")
# setting x and y labels using labs
plt <- plt + labs(x ="Alphabets", y ="Random column names")
# plotting the Heatmap
plt
# Plotting Heatmap in R
# adding ggplot2 library for plotting
library(ggplot2)
# Creating random dataset
# with 20 alphabets and 20 animal names
letters <- LETTERS[1:20]
animal_names <- c("Canidae","Felidae","Cat","Cattle",
"Dog","Donkey","Goat","Guinea pig",
"Horse","Pig","Rabbit","Badger",
"Bald eagle","Bandicoot","Barnacle",
"Bass","Bat","Bear","Beaver","Bedbug",
"Bee","Beetle")
data <- expand.grid(X=letters, Y=animal_names)
data$count <- runif(440, 0, 6)
# plotting the heatmap
plt <- ggplot(data,aes( X, Y,fill=count))
plt <- plt + geom_tile()
# further customizing the heatmap by
# applying colors and title
plt <- plt + theme_minimal()
# setting gradient color as red and white
plt <- plt + scale_fill_gradient(low="white", high="red")
# setting the title and subtitles using
# title and subtitle
plt <- plt + labs(title = "Heatmap")
plt <- plt + labs(subtitle = "A simple heatmap using geom_tile()")
# setting x and y labels using labs
plt <- plt + labs(x ="Alphabets", y ="Random column names")
# plotting the Heatmap
plt
输出
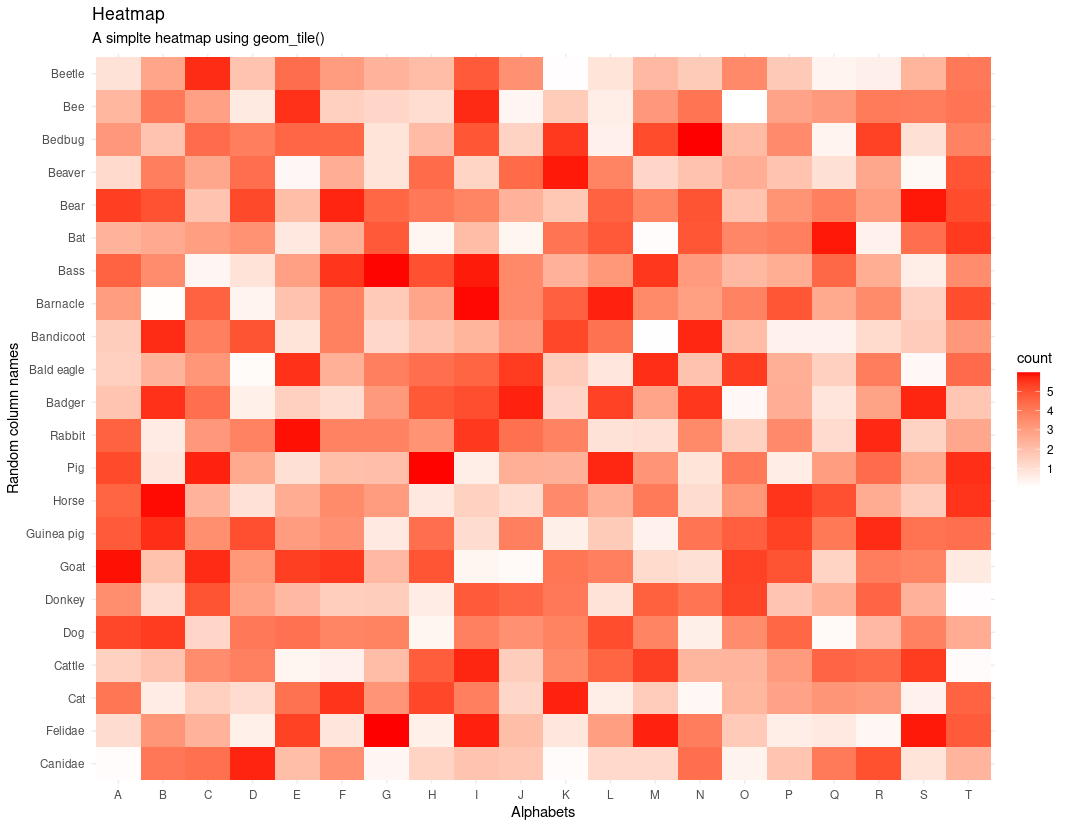
使用ggplot2绘制热图
方法2:使用b ase R 的heatmap()函数
heatmap()函数是默认安装的基础R。如果不想安装任何额外的软件包,也可以使用默认的heatmap()。我们可以使用R的这个heatmap函数绘制数据集的热图。
语法:
heatmap(data,main = NULL, xlab = NULL, ylab = NULL, …)
参数
data: data指定了我们想要绘制热图的数据矩阵。
main: main是一个字符串参数,它指定了绘图的标题。
xlab: xlab用于指定x轴的标签。
ylab : ylab用于指定 y 轴的标签。
这里的任务是直接的。你只需要输入函数heatmap()所要求的值。
例子
# Heatplot from Base R
# using default mtcars dataset from the R
x <- as.matrix(mtcars)
# custom colors
new_colors <- colorRampPalette(c("cyan", "darkgreen"))
# plotting the heatmap
plt <- heatmap(x,
# assigning new colors
col = new_colors(100),
# adding title
main = "Heatmap for mtcars dataset",
# adding some margin so that
# it doesn not drawn over the
# y-axis label
margins = c(5,10),
# adding x-axis labels
xlab = "variables",
# adding y-axis labels
ylab = "Car Models",
# to scaled the values into
# column direction
scale = "column"
)
输出
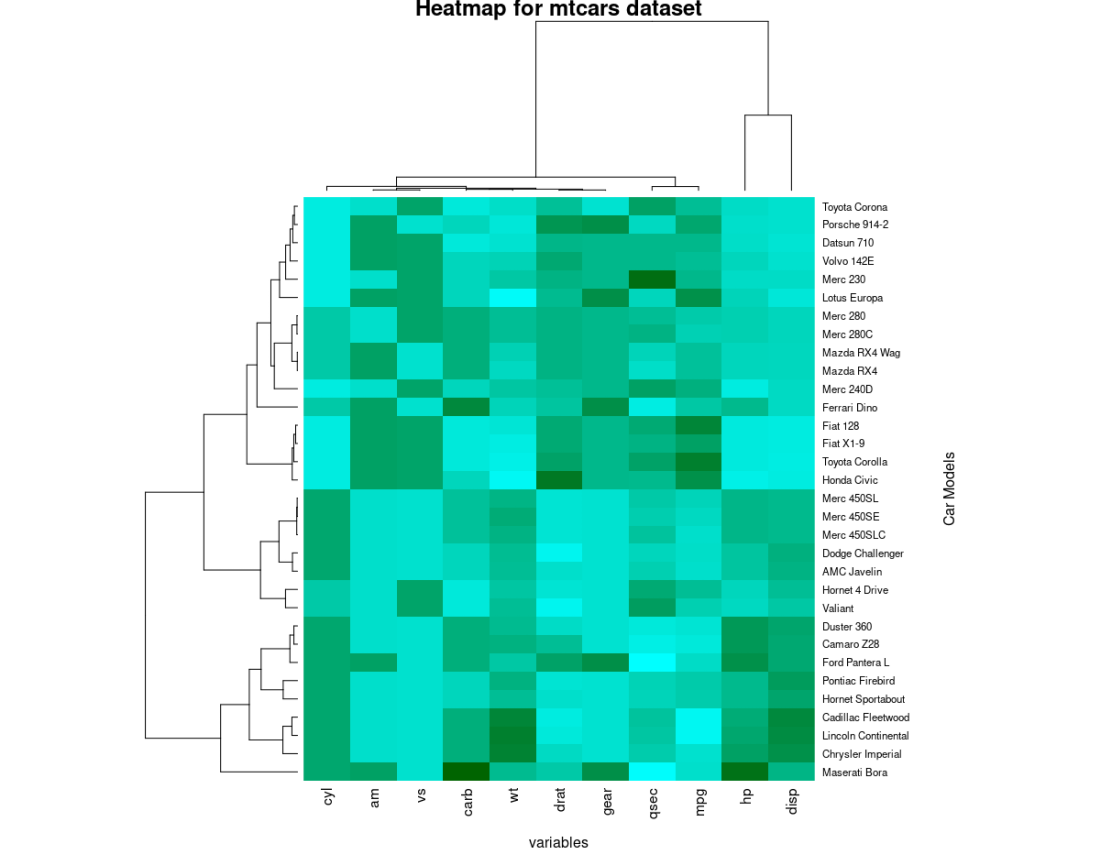
热图
 极客教程
极客教程