R语言 使用ggplot2绘制散点图的综合指南
在这篇文章中,我们将看到如何使用R编程语言中的ggplot2来绘制散点图。
ggplot2包是一个免费的、开源的、易于使用的可视化包,在R中广泛使用。这个包可以用R函数install.packages()来安装。
install.packages("ggplot2")
散点图用点来表示两个不同数字变量的值,用来观察这些变量之间的关系。为了绘制散点图,我们将使用 geom_point()函数。 以下是关于ggplot函数geom_point()的简要信息。
语法: geom_point(size, color, fill, shape, stroke)
参数 :
- size : 点的大小
-
color : 点的颜色/边界
-
fill : 点的颜色
-
shape : 点的形状,范围从0到25
-
stroke。点边界的厚度
返回:它创建散点图。
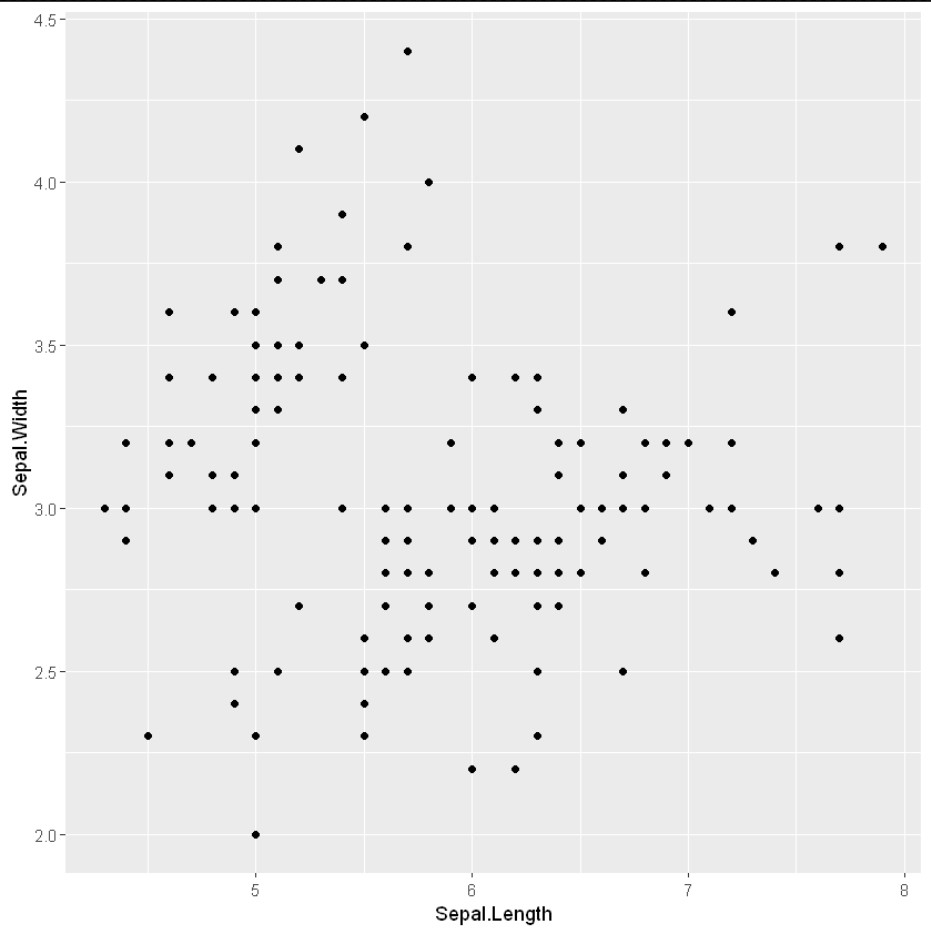
例子: 简单散点图
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point()
输出
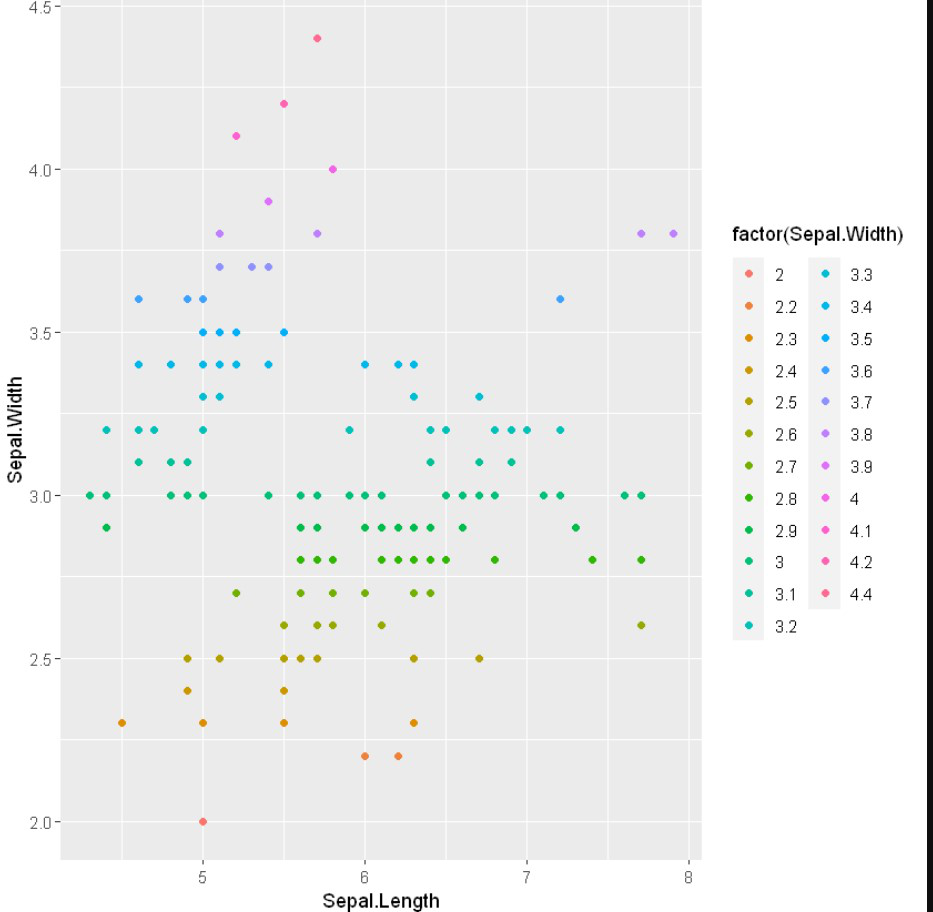
带组的散点图
这里我们将用一组数据(即因子级数据)来区分数值。 aes()函数 控制组的颜色,它应该是因子变量。
语法
aes(color = factor(variable))
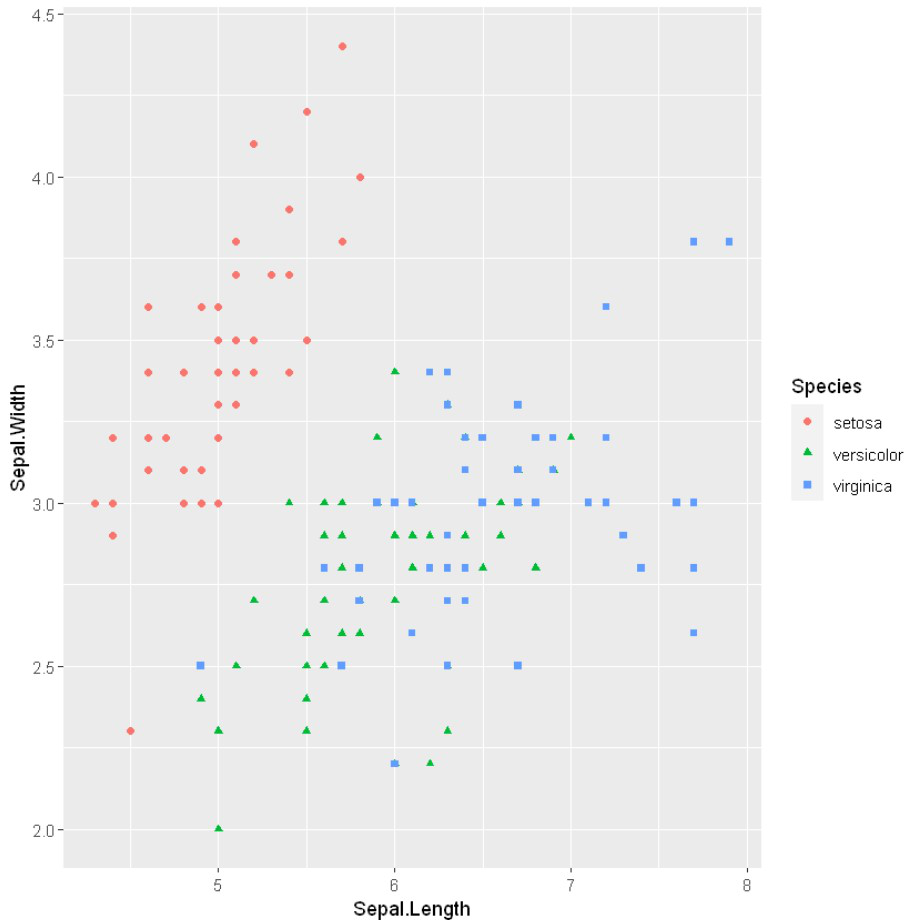
例子: 带组的散点图
# Scatter plot with groups
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point(aes(color = factor(Sepal.Width)))
输出
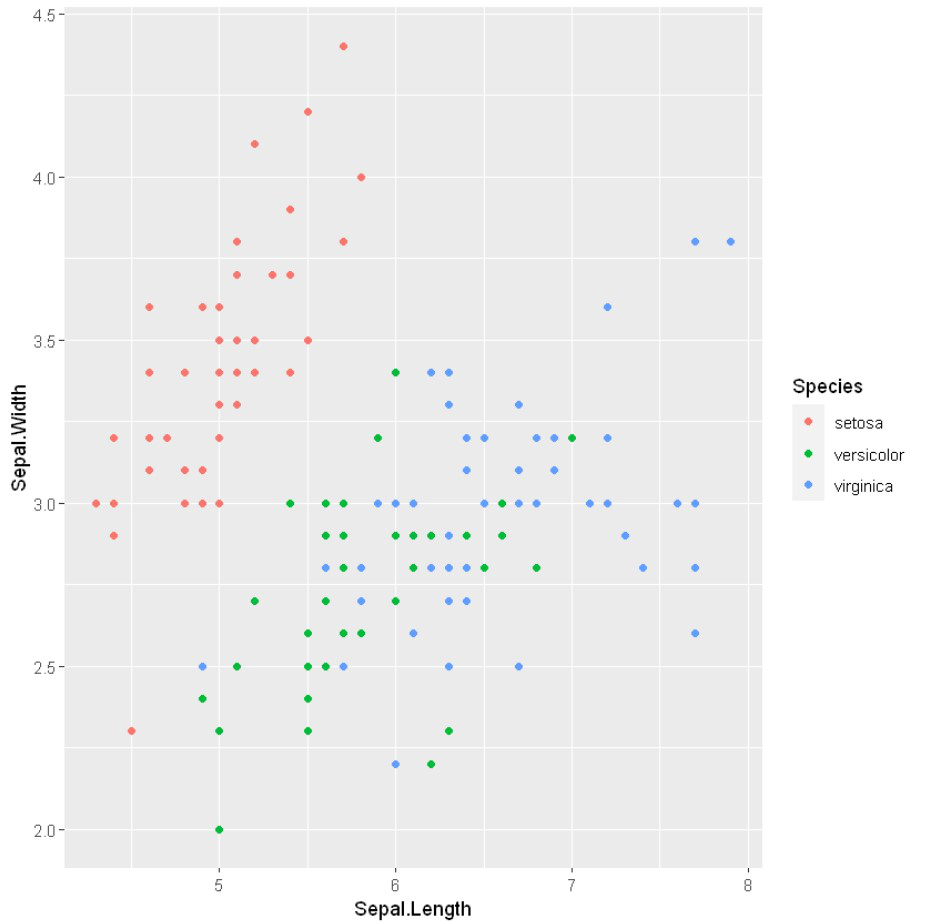
改变颜色
在这里,我们使用 ais()方法 的颜色属性来改变具有特定变量的数据点的颜色。
例子: 改变颜色
# Changing color
ggplot(iris) +
geom_point(aes(x = Sepal.Length,
y = Sepal.Width,
color = Species))
输出
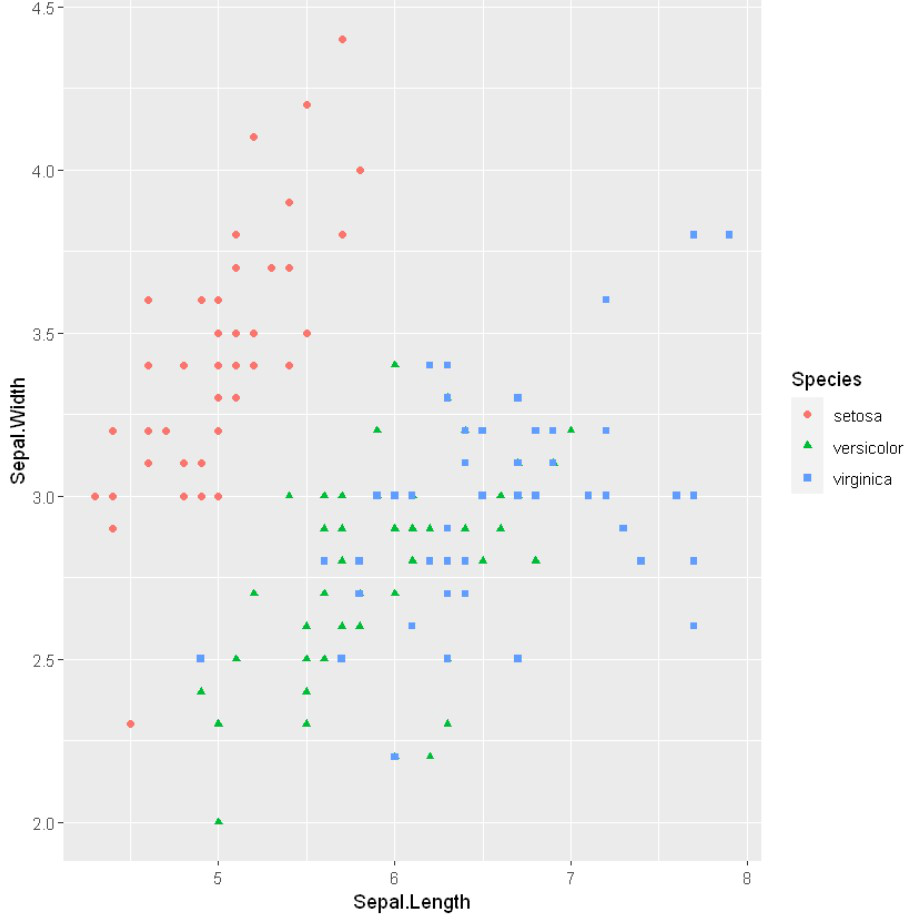
改变形状
为了改变数据点的形状,我们将使用带有ais()方法的 形状 属性。
例子: 改变形状
# Changing point shapes in a ggplot scatter plot
# Changing color
ggplot(iris) +
geom_point(aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width,
shape = Species , color = Species))
输出
改变尺寸美学
为了改变审美或数据点,我们将在ais()方法中使用尺寸 属性 。
例子: 改变大小
# Changing the size aesthetic mapping in a
# ggplot scatter plot
ggplot(iris) +
geom_point(aes(x = Sepal.Length,
y = Sepal.Width,
size = .5))
输出
散点图中的标签点
为了在数据点上部署标签,我们将在 geom_text()方法 中使用标签。
例子: 在散点图中标记点
# Label points in the scatter plot
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point() +
geom_text(label=rownames(iris))
输出
ggplot2中的回归线
回归模型是一个支持自变量的目标预测值,主要用于找出变量之间的关系和预测。在R中,我们可以使用stat_smooth()函数来平滑可视化。
语法: stat_smooth(method=”method_name”, formula=fromula_to_be_used, geom=’方法名称’)
参数
- method。它是用于平滑线条的平滑方法(函数)。
- formula。它是在平滑函数中使用的公式。
- geom:它是用来显示数据的几何对象
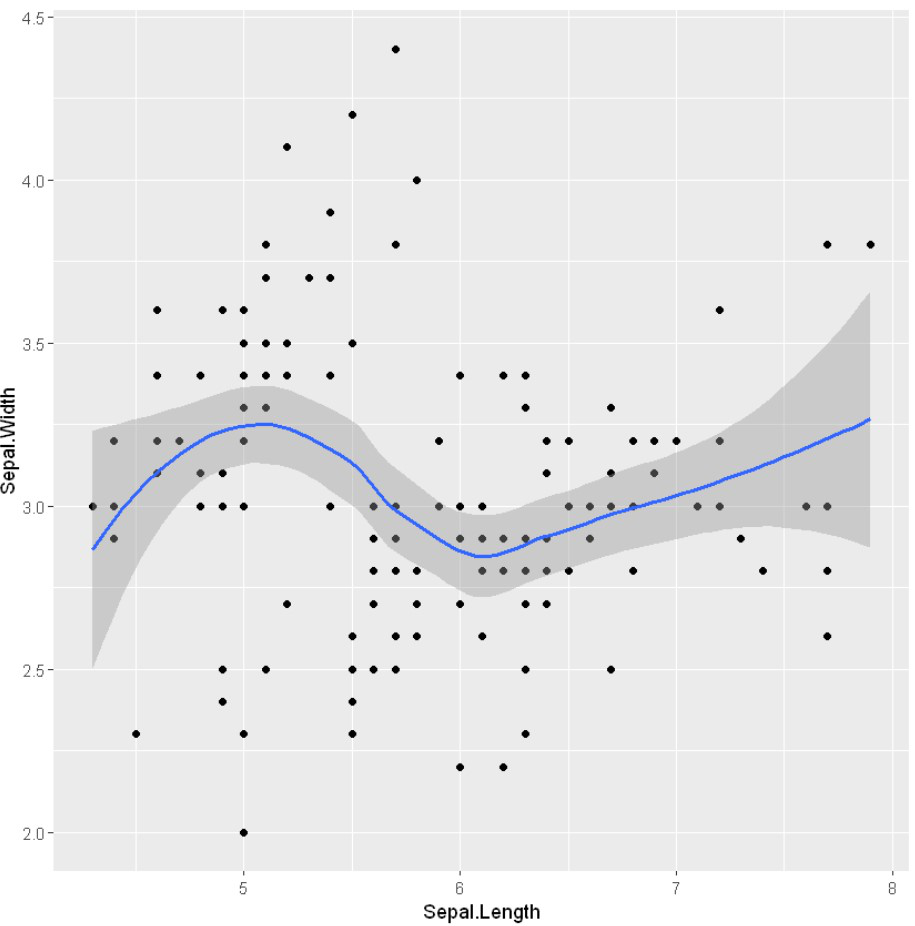
例子: 回归线
# Add regression lines with stat_smooth
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point() +
stat_smooth(method=lm)
输出
例子: 使用stat_mooth与loess模式
# Add regression lines with stat_smooth
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point() +
stat_smooth()
输出
geom_smooth()函数用于表示回归线并使其平滑化。
语法: geom_smooth(method=”method_name”, formula=fromula_to_be_used)
参数
- method。它是用于平滑线的平滑方法(函数)。
- formula。它是在平滑函数中使用的公式。
例子: 使用geom_smooth()
# Add regression lines with geom_smooth
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth()
输出
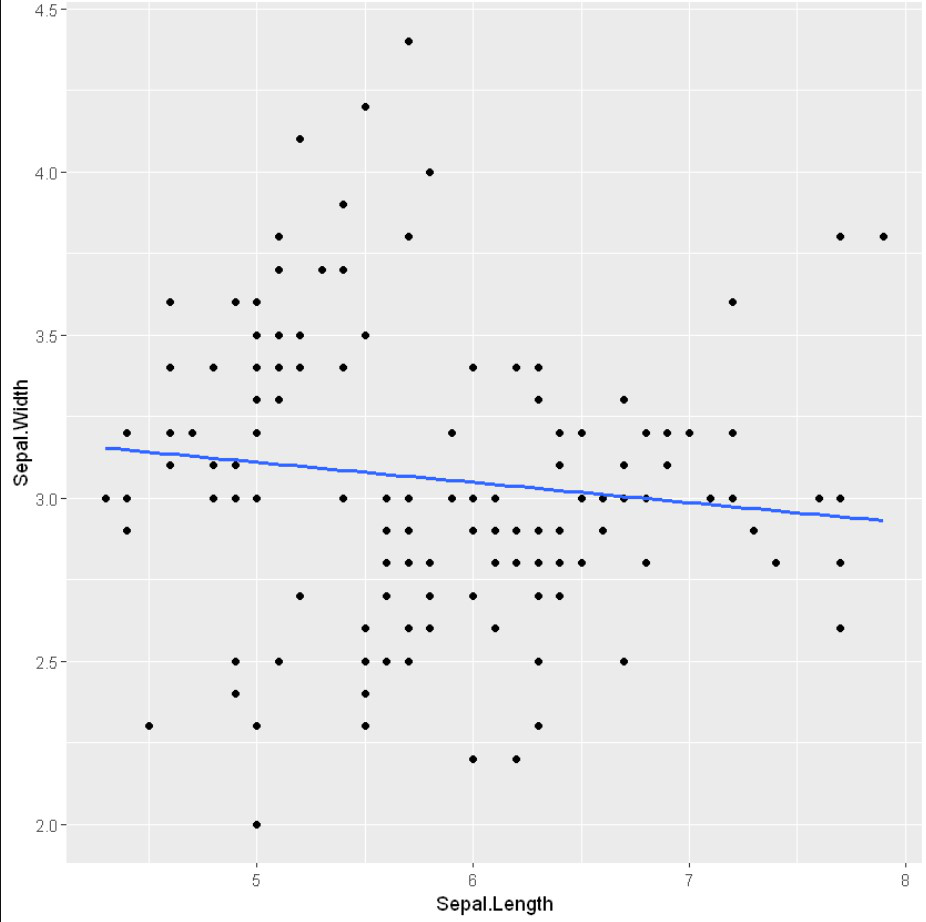
为了在geom_smooth()函数的帮助下在图形媒介上显示回归线,我们传递方法为 “loess”,所用公式为y ~ x。
例子: geom_smooth与loess模式
# Add regression lines with geom_smooth
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method=lm, se=FALSE)
输出
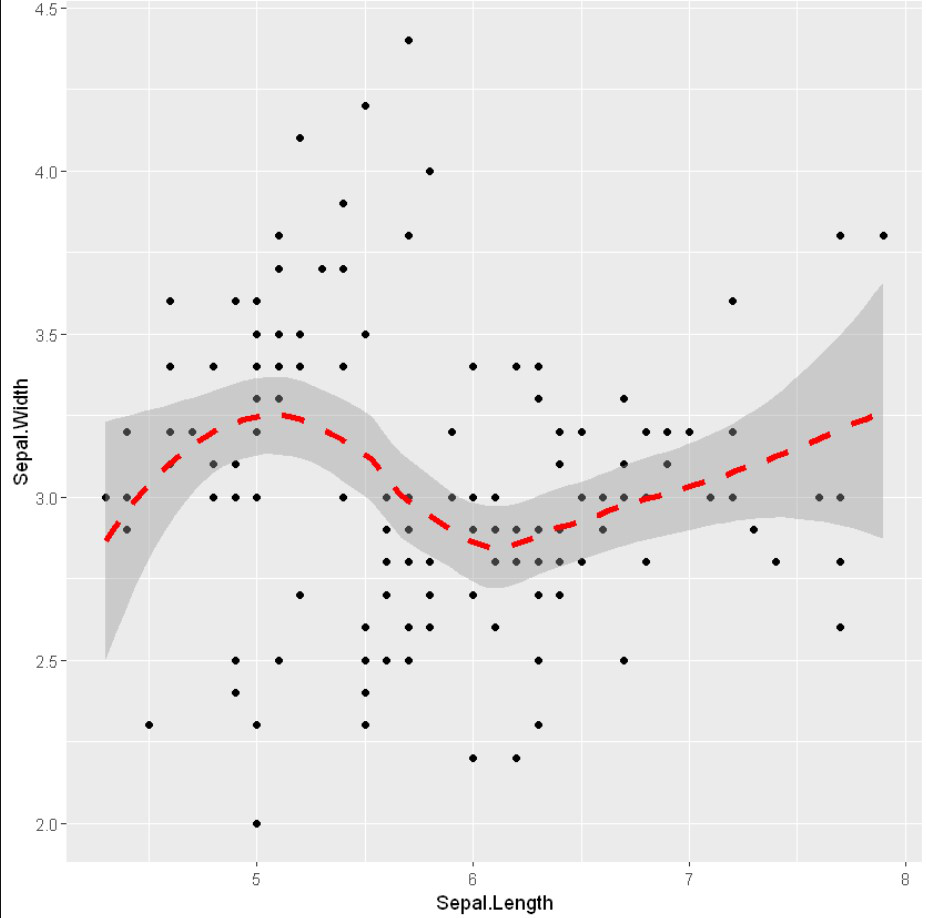
截距和斜率可以通过lm()函数轻松计算出来,该函数用于线性回归,然后是coefficients()。
例子: 截距和斜率
# Add regression lines with geom_smooth
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(intercept = 37, slope = -5, color="red",
linetype="dashed", size=1.5)
输出
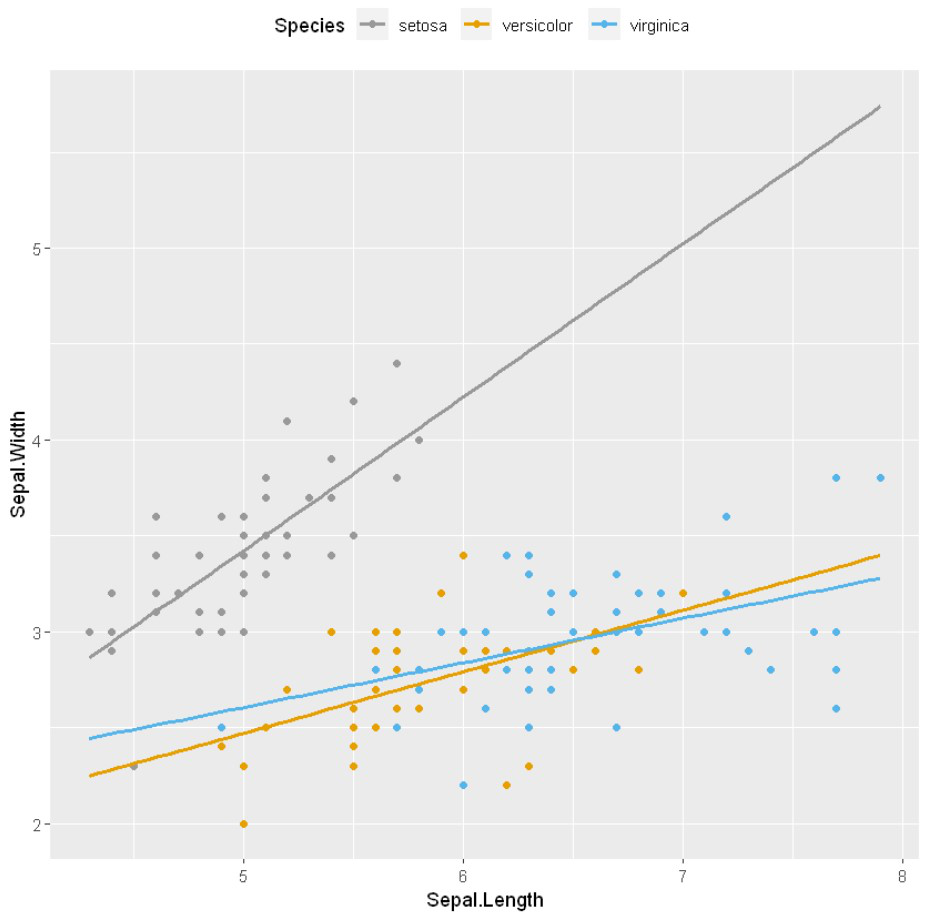
手动改变点的颜色/形状/大小
scale_fill_manual, scale_size_manual, scale_shape_manual, scale_linetype_manual, 是为分类数据分配所需颜色的内置类型,我们使用其中的scale_color_manual()函数,它用于缩放(地图)。
语法:
- scale_shape_manualValue)用于点状图形
- scale_color_manual(Value) 用于点的颜色。
- scale_size_manual(Value)用于点的大小。
参数:
- Value :一组用于映射数据的美学值。在这里,我们采取所需的颜色集。
返回: 缩放数据上的手动颜色值
例子: 改变美学值
# Change the point color/shape/size manually
library(ggplot2)
# Change point shapes and colors manually
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, color = Species)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method=lm, se=FALSE, fullrange=TRUE)+
scale_shape_manual(values=c(3, 16, 17))+
scale_color_manual(values=c('#999999','#E69F00', '#56B4E9'))+
theme(legend.position="top")
输出
散点图中的边际地毯
为了在散点图中添加边际地毯,我们将使用geom_rug()方法。
例子: 边际地毯
# Add marginal rugs to a scatter plot
# Changing point shapes in a ggplot scatter plot
# Changing color
ggplot(iris) +
geom_point(aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width,
shape = Species , color = Species))+
geom_rug()
输出
这里我们将在散点图中添加边际地毯。
例子: 边际废墟
# Add marginal rugs to a scatter plot
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point()+
geom_rug()
输出
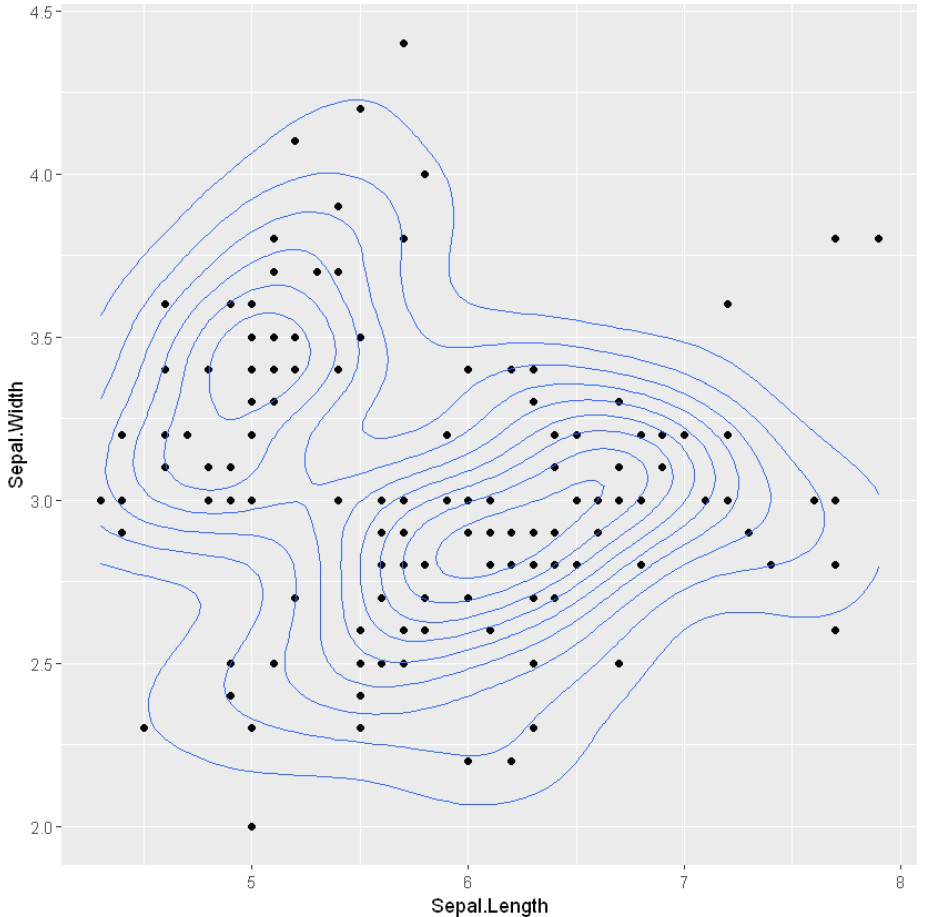
带有二维密度估计的散点图
为了在散点图中创建密度估计,我们将使用ggplot2的 geom_density_2d()方法和geom_density_2d_filled() 。
语法: ggplot( aes(x))+ geom_density_2d( fill, color, alpha)
参数
- fill:绘图下方的背景颜色
- color: 绘图线的颜色
- alpha:图形的透明度
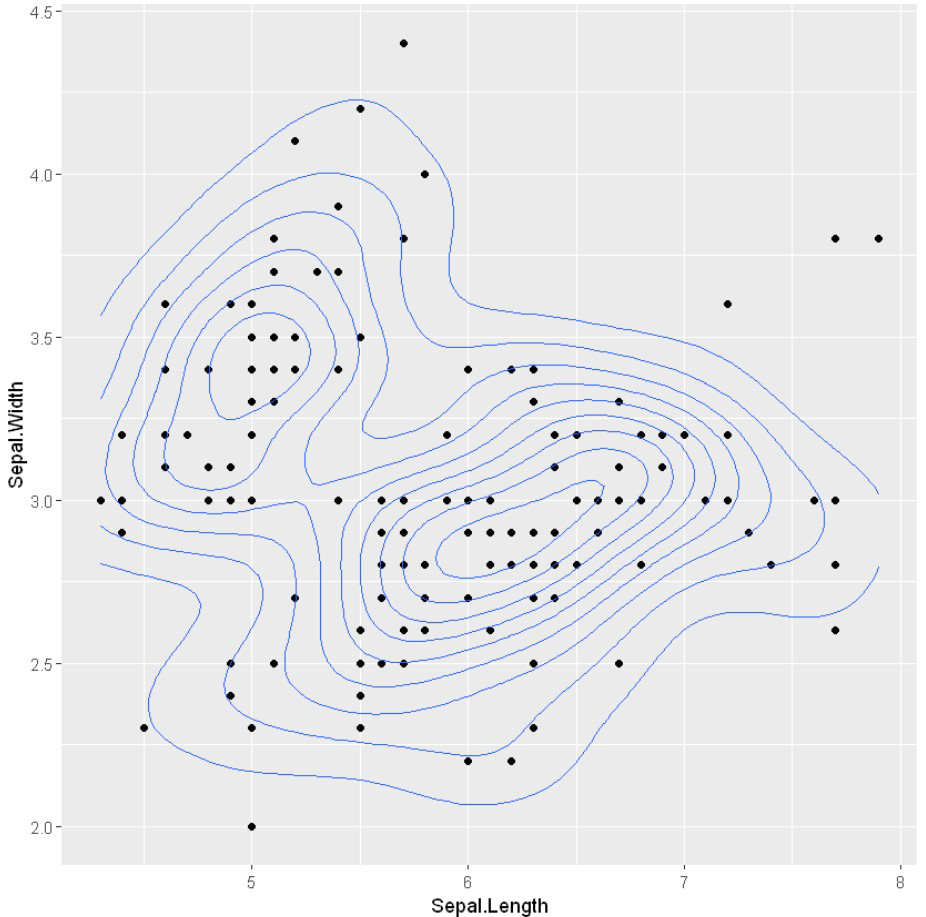
例子: 带有二维密度估计的散点图
# Scatter plots with the 2d density estimation
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point()+
geom_density_2d()
输出
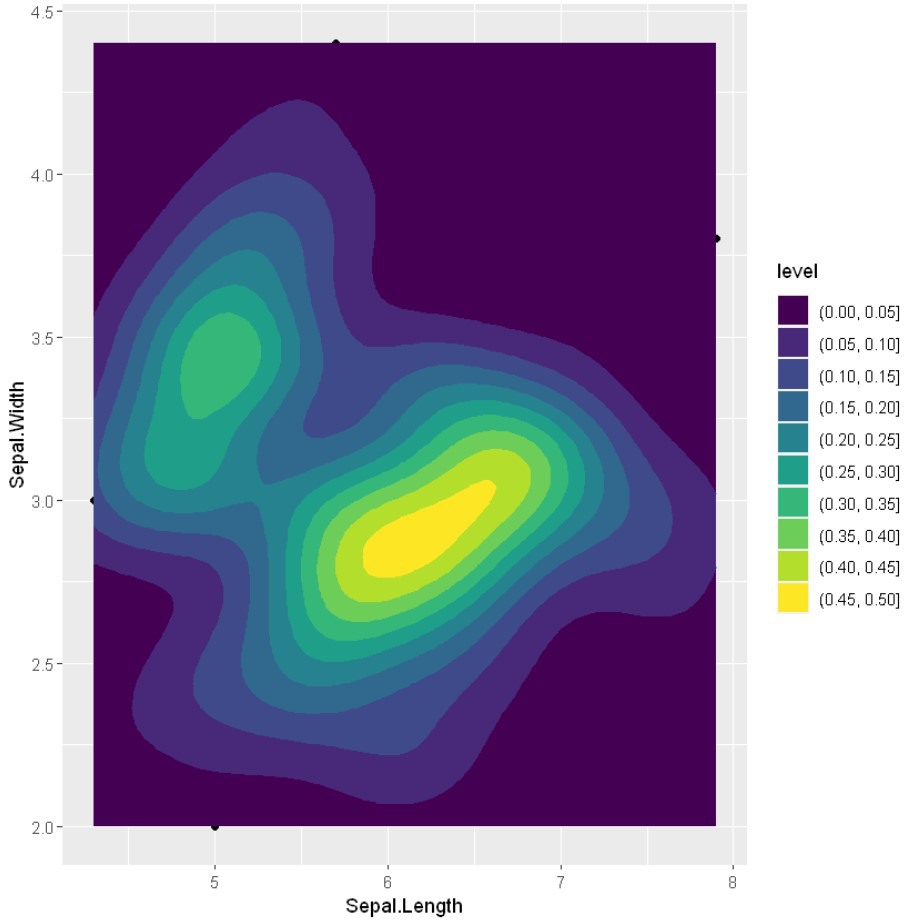
使用geom_density_2d_filled()来可视化数据点内的颜色情况
例子: 增加美感
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point()+
geom_density_2d(alpha = 0.5)+
geom_density_2d_filled()
输出
stat_density_2d()也可以用来部署2d密度估计。
例子: 部署密度估计
# Scatter plots with the 2d density estimation
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point()+
stat_density_2d()
输出
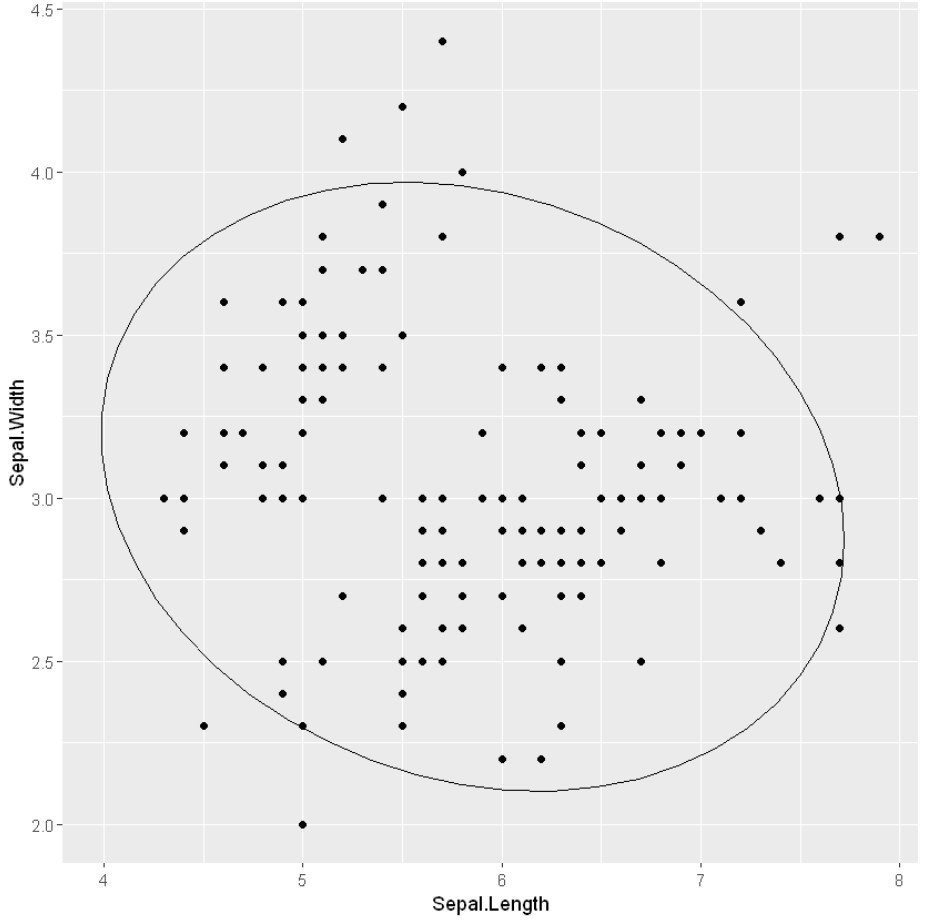
带有椭圆的散点图
为了在数据点群周围添加一个圆或椭圆,我们使用 stat_ellipse() 函数。这个函数会自动计算出圆/椭圆半径,以便在分类数据的点簇周围绘制圆/椭圆。
例子: 带椭圆的散点图
# Scatter plots with ellipses
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point()+
stat_ellipse()
输出
 极客教程
极客教程