R语言 对R数据框中的每个值应用函数
在R编程语言中,要对数据框中的每个整数类型的值应用一个函数,我们可以使用 dplyr 包中的 lapply 函数。如果数值的数据类型是字符串,那么我们可以使用 粘贴() 和 lapply。 让我们在一个例子的帮助下理解这个问题。
使用中的数据集
| 编号 | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1 | 8 | 21 | 4 |
| 2. | 9 | 2 | 0 | 6 |
| 3. | 6 | 3 | 14 | 3 |
| 4. | 5 | 6 | 5 | 7 |
| 5. | 9 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 6. | 6 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
在对数据帧的每个值应用value*7+1之后
预期的结果
| 编号 | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 8 | 57 | 148 | 29 |
| 2. | 64 | 15 | 1 | 43 |
| 3. | 43 | 22 | 99 | 22 |
| 4. | 36 | 43 | 36 | 50 |
| 5. | 64 | 29 | 22 | 8 |
| 6. | 43 | 22 | 15 | 22 |
方法1:使用lapply函数
lapply 是apply家族的一个函数。通过使用lapply,我们可以避免for循环,因为for循环比lapply慢。lapply比普通的循环快,因为它不会扰乱你的工作环境。它以列表形式返回输出。lapply中的’l’表示列表。
语法
lapply(X, FUN, …)
这里,X可以是一个向量列表或数据框。而FUN以一个你希望应用于数据框的函数作为参数。
方法
- 创建一个假数据集。
- 创建一个你想应用于数据框中每个值的自定义函数。
- 在lapply的帮助下,将这个自定义函数应用到数据框中的每个值。
- 显示结果
例子
# Apply function to every value in dataframe
# Creating dataset
m <- c(1,9,6,5,9,6)
n <- c(8,2,3,6,4,3)
o <- c(21,0,14,5,3,2)
p <- c(4,6,3,7,1,3)
# creating dataframe
df <- data.frame(A=m,B=n,C=o,D=p)
# creating function
# that will multiply
# each value by 7 and then add 1
magic_fun <- function(x){
return (x*7+1)}
# applying the custom function to every value and converting
# it to dataframe, as lapply returns result in list
# we have to convert it to data frame
data.frame(lapply(df,magic_fun))
输出:

使用lapply
方法2:使用粘贴和应用功能 。
paste() 将一个R对象作为参数,并将其转换为字符,然后用另一个字符串粘贴回来,也就是说,它将参数转换为字符串,并将它们连接起来。
语法
paste (..., sep = " ")
我们的R对象将被转换为字符串,代替”…”,sep=” “代表一个字符串来分隔术语。
方法
- 创建一个假数据集。
- 应用自定义函数,将打印 “Hello” ,然后在数据框中显示数值
- 显示结果
例子
# Apply function to every value in dataframe
# Creating dataset
m <- c("Vikas","Varun","Deepak")
n <- c("Komal","Suneha","Priya")
# creating dataframe
df <- data.frame(A=m,B=n)
# Applying custom function to every element in dataframe
df[]<-data.frame(lapply(df,function(x) paste("Hello,",x,sep="")))
# display dataset
df
输出

使用粘贴和应用
方法3:使用purrr
purrr 是一个函数式编程工具包。它带有许多有用的函数,如 map。 map()函数遍历向量的所有条目,并以列表形式返回输出 。 它允许我们在代码中替换for循环,使其更容易阅读。
语法:
map(.x, .f) returns a list
map_df(.x, .f) returns a data frame
map_dbl(.x, .f) returns a numeric (double) vector
map_chr(.x, .f) returns a character vector
map_lgl(.x, .f) returns a logical vector
这里, .x 是输入, .f 是你想应用的函数。map函数的输入可以是一个列表、一个向量或一个数据框。
注意:你需要用以下命令明确安装 purrr 包。
install.packages("purrr")
方法:
- 创建一个向量、一个列表和一个数据框
- 创建一个你想应用的自定义函数。
- 使用map()在向量、列表和数据框上应用自定义函数。
- 显示结果
使用整数数据类型工作
程序
# Apply function to every value in dataframe
# install and load the purrr
install.packages("purrr")
library("purrr")
# Creating a vector
x <- c(1,2,3,4,5,7,8,9)
# creating list
y <- list(2,4,9,6,3,7,1,5,4)
# creating dataframe
df <- data.frame(A=c(1,2,3,4,5),B=c(6,7,8,9,10))
# creating custom function
custom_f <- function(x){
return(x*2)
}
# applying function to vector
# and return output as vector
map_dbl(x,.f=custom_f)
# applying function to list
# and return output as vector
map(y,.f=custom_f)
# applying function to dataframe
# and return output as dataframe
map_df(df,.f=custom_f)
输出
对于一个矢量:
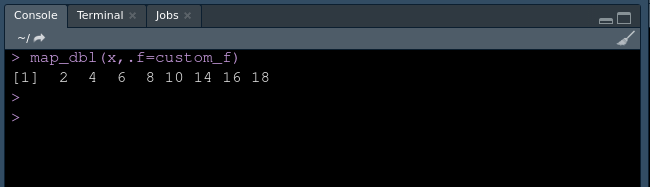
矢量输出
对于一个列表:
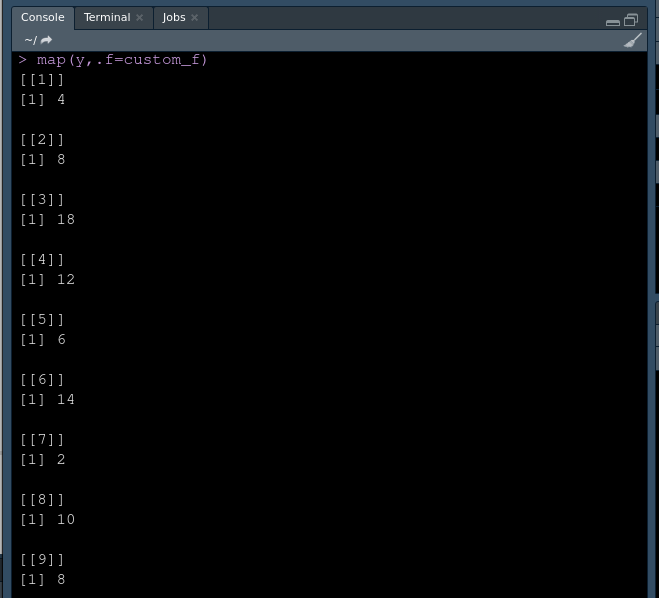
列表输出
对于一个数据框。
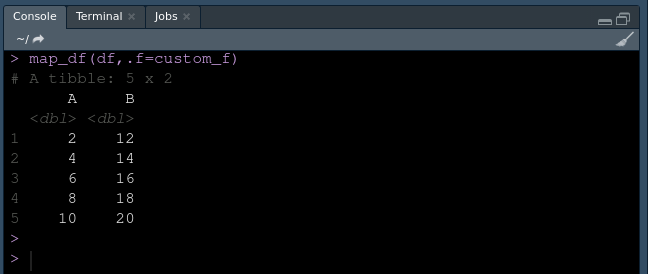
数据框架输出
与字符数据类型一起工作
程序
# Apply function to every value in dataframe
#install and load the purrr
#install.packages("purrr")
library("purrr")
# Creating a vector
x <- c("Red","Blue", "Green","Yellow","Orange")
# creating list
y <- list("spring","summer", "fall","winter")
# creating dataframe
df <- data.frame(Working_days=c("Mon","Tues","Wednes"),
off_days=c("Sun","Satur","Thurs") )
# applying function to vector
# and return output as vector
map_chr(x,paste0," color")
# applying function to list
# and return output as vector
map(y,paste0," season")
# applying function to dataframe
# and return output as dataframe
map_df(df,paste0,"day")
输出
对于一个矢量。
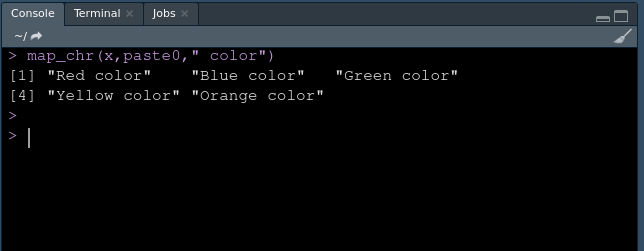
矢量作为输出
对于一个列表。
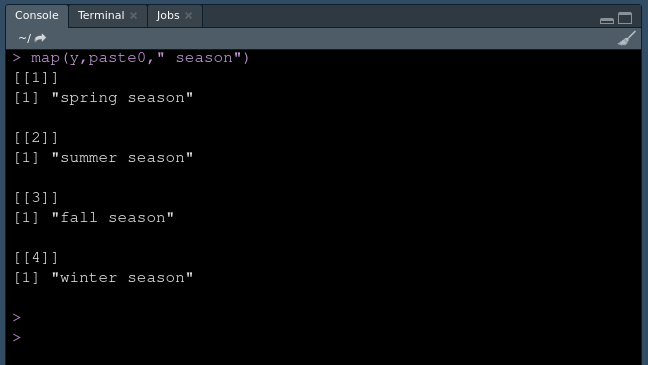
列表作为输出
对于一个数据框:
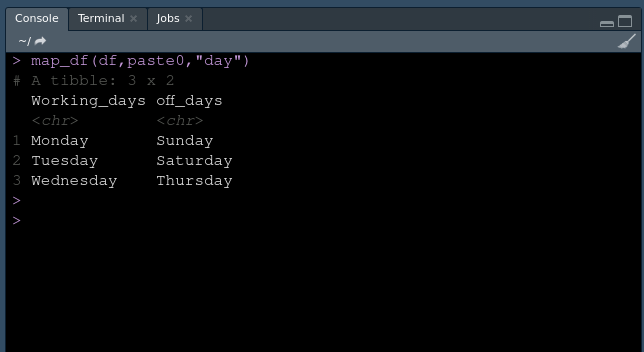
数据帧作为输出
 极客教程
极客教程