R语言 如何用数据点制作小提琴图
在这篇文章中,我们将讨论如何在R编程语言中用数据点制作小提琴图。
小提琴图是一个连续分布的紧凑显示。R语言中的geom_violin()方法用于在工作空间中构建一个小提琴图,它可以理解各种美学映射,如alpha、颜色或填充。
语法
geom_violin()
要构建一个常规的小提琴图,只需在可视化之后调用geom_violin()函数。
例子: 一个有规律的小提琴图
library("ggplot2")
# defining the columns of the data frame
data_frame <- data.frame(col1=c(rep("A", 10) , rep("B", 12) , rep("C", 18)),
col2=c( sample(2:5, 10 , replace=T) ,
sample(4:10, 12 , replace=T),
sample(1:7, 18 , replace=T))
)
# plotting the data frame
ggplot(data_frame, aes(x = col1, y = col2, fill = col1)) +
# adding violin plot
geom_violin()
输出
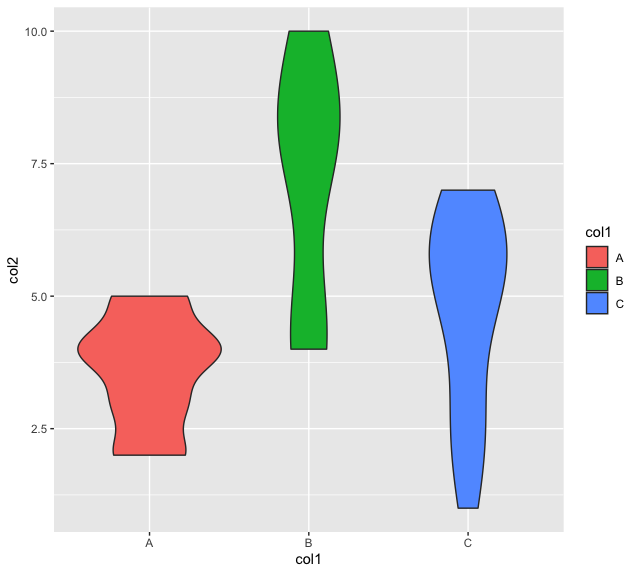
将数据点添加到violinplot中
在点阵图的情况下,点的宽度对应于bin的宽度。其次是点的堆叠情况,每个点代表一个观测值。为了添加数据点,我们在创建一个小提琴图后使用geom_dotplot()。
语法
geom_dotplot(mapping = NULL,data = NULL,binwidth = NULL,binaxis = “x”,stackdir = “up”)
参数:
- mapping – 由aeS()创建的美学映射集
- data – 要显示的数据
- binaxis – 沿着 “x “或 “y “的轴进行分类。
- stackdir – 定义点应该被堆叠的方向
- dotsize – 相对于binwidth的点的直径。
例子: 在violinplot上添加数据点
# defining the columns of the data frame
data_frame <- data.frame(col1=c(rep("A", 10) , rep("B", 12) , rep("C", 18)),
col2=c( sample(2:5, 10 , replace=T) ,
sample(4:10, 12 , replace=T),
sample(1:7, 18 , replace=T))
)
# plotting the data frame
ggplot(data_frame, aes(x = col1, y = col2, fill = col1)) +
# adding violin plot
geom_violin(alpha = 0.5) +
geom_dotplot(binaxis = "y",
stackdir = "center",
dotsize = 0.5)
输出
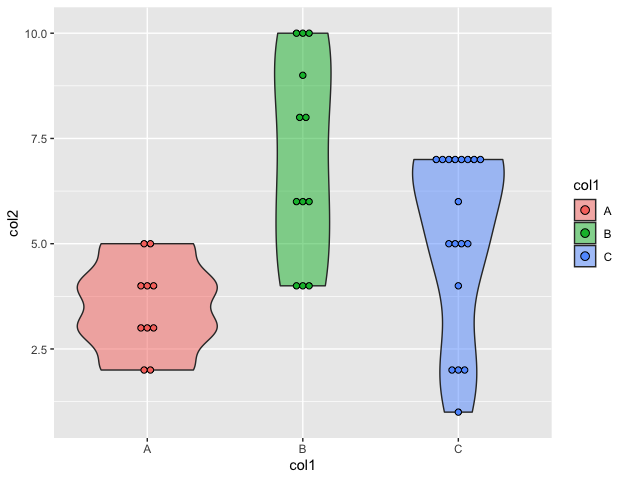
在小提琴图中加入抖动因素
geom_plot()可以通过在x轴上的实际数据点上使用随机噪声绘制小提琴图来改进。这些数据点被称为 “抖动”。R中的geom_jitter()方法被用来给每个点的位置增加少量的随机变化。
例子: 在小提琴图上添加抖动点
library("ggplot2")
# defining the columns of the data frame
data_frame <- data.frame(col1=c(rep("A", 10) , rep("B", 12) , rep("C", 18)),
col2=c( sample(2:5, 10 , replace=T) ,
sample(4:10, 12 , replace=T),
sample(1:7, 18 , replace=T))
)
# plotting the data frame
ggplot(data_frame, aes(x = col1, y = col2, fill = col1)) +
# adding violin plot
geom_violin() +
geom_jitter()
输出
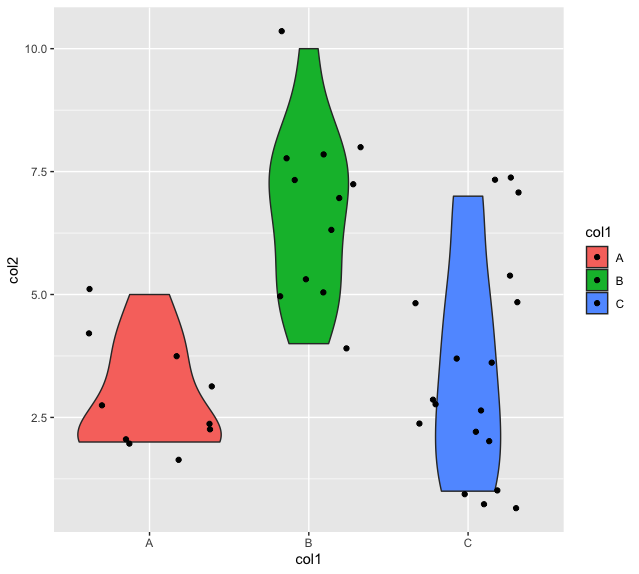
在小提琴图中指定抖动宽度
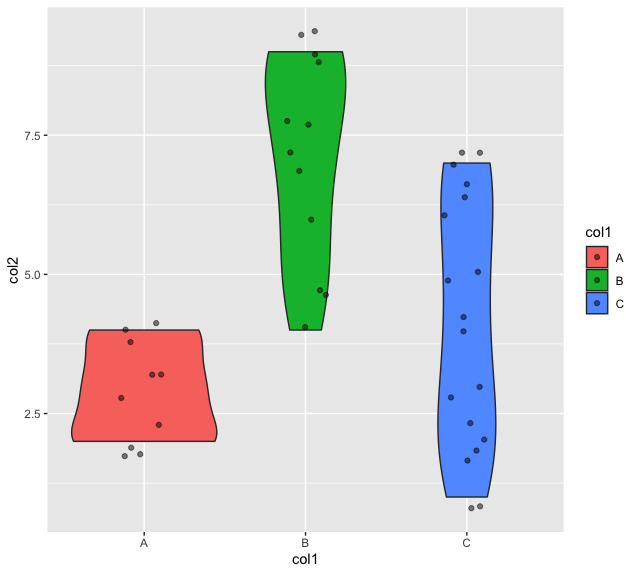
通过在R的geom_jitter方法中指定参数、宽度和阿尔法,小提琴图中的透明度以及数据点的宽度可以随机应变。
语法
geom_jitter(alpha, width)
参数
- alpha:固定透明度
- 宽度:用于指定抖动点的宽度
例子: 在小提琴图中指定抖动宽度
library("ggplot2")
# defining the columns of the data frame
data_frame <- data.frame(col1=c(rep("A", 10) , rep("B", 12) , rep("C", 18)),
col2=c( sample(2:5, 10 , replace=T) ,
sample(4:10, 12 , replace=T),
sample(1:7, 18 , replace=T))
)
# plotting the data frame
ggplot(data_frame, aes(x = col1, y = col2, fill = col1)) +
# adding violin plot
geom_violin() +
geom_jitter(width=0.15, alpha=0.5)
输出
 极客教程
极客教程