Python中的OS模块及实例
Python 中的 OS 模块提供了与操作系统交互的功能。OS属于Python的标准工具模块。这个模块提供了一种可移植的方式来使用依赖于操作系统的功能。os 和 os.path 模块包括许多与文件系统交互的函数。
处理当前工作目录
将当前工作目录(CWD)视为一个文件夹,Python在其中运行。每当文件只通过名字被调用时,Python 假设它从 CWD 开始,这意味着只有当文件在 Python 的 CWD 中时,只用名字的引用才会成功。注意:Python 脚本运行的文件夹被称为当前目录。这并不是Python脚本所在的路径。获取当前工作目录为了获取当前工作目录的位置,使用了os.getcwd()。
例子:
# Python program to explain os.getcwd() method
# importing os module
import os
# Get the current working
# directory (CWD)
cwd = os.getcwd()
# Print the current working
# directory (CWD)
print("Current working directory:", cwd)
输出:
Current working directory: /home/nikhil/Desktop/gfg
改变当前工作目录
要改变当前工作目录(CWD),需要使用os.chdir()方法。这个方法将CWD改变为一个指定的路径。它只接受一个参数作为新的目录路径。
注意:当前工作目录是Python脚本所处的文件夹。
例子:
# Python program to change the
# current working directory
import os
# Function to Get the current
# working directory
def current_path():
print("Current working directory before")
print(os.getcwd())
print()
# Driver's code
# Printing CWD before
current_path()
# Changing the CWD
os.chdir('../')
# Printing CWD after
current_path()
输出:
Current working directory before
C:\Users\Nikhil Aggarwal\Desktop\gfg
Current working directory after
C:\Users\Nikhil Aggarwal\Desktop
创建一个目录
在操作系统模块中,有不同的方法可用于创建一个目录。这些方法是–
- os.mkdir()
- os.makedirs()
使用os.mkdir()
os.mkdir()方法在Python中用来创建一个名为path的目录,并指定数字模式。如果要创建的目录已经存在,该方法会引发FileExistsError。
例子:
# Python program to explain os.mkdir() method
# importing os module
import os
# Directory
directory = "GeeksforGeeks"
# Parent Directory path
parent_dir = "D:/Pycharm projects/"
# Path
path = os.path.join(parent_dir, directory)
# Create the directory
# 'GeeksForGeeks' in
# '/home / User / Documents'
os.mkdir(path)
print("Directory '% s' created" % directory)
# Directory
directory = "Geeks"
# Parent Directory path
parent_dir = "D:/Pycharm projects"
# mode
mode = 0o666
# Path
path = os.path.join(parent_dir, directory)
# Create the directory
# 'GeeksForGeeks' in
# '/home / User / Documents'
# with mode 0o666
os.mkdir(path, mode)
print("Directory '% s' created" % directory)
输出:
Directory 'GeeksforGeeks' created
Directory 'Geeks' created
使用 os.makedirs()
Python中的os.makedirs()方法用于递归地创建一个目录。这意味着在创建叶子目录时,如果缺少任何中间层次的目录,os.makedirs()方法将创建它们全部。
例子:
# Python program to explain os.makedirs() method
# importing os module
import os
# Leaf directory
directory = "Nikhil"
# Parent Directories
parent_dir = "D:/Pycharm projects/GeeksForGeeks/Authors"
# Path
path = os.path.join(parent_dir, directory)
# Create the directory
# 'Nikhil'
os.makedirs(path)
print("Directory '% s' created" % directory)
# Directory 'GeeksForGeeks' and 'Authors' will
# be created too
# if it does not exists
# Leaf directory
directory = "c"
# Parent Directories
parent_dir = "D:/Pycharm projects/GeeksforGeeks/a/b"
# mode
mode = 0o666
path = os.path.join(parent_dir, directory)
# Create the directory 'c'
os.makedirs(path, mode)
print("Directory '% s' created" % directory)
# 'GeeksForGeeks', 'a', and 'b'
# will also be created if
# it does not exists
# If any of the intermediate level
# directory is missing
# os.makedirs() method will
# create them
# os.makedirs() method can be
# used to create a directory tree
输出:
Directory 'Nikhil' created
Directory 'c' created
用Python列出文件和目录
Python中的os.listdir()方法是用来获取指定目录下的所有文件和目录的列表。如果我们没有指定任何目录,那么将返回当前工作目录中的文件和目录列表。
例子:
# Python program to explain os.listdir() method
# importing os module
import os
# Get the list of all files and directories
# in the root directory
path = "/"
dir_list = os.listdir(path)
print("Files and directories in '", path, "' :")
# print the list
print(dir_list)
输出:
Files and directories in ' / ' :
['sys', 'run', 'tmp', 'boot', 'mnt', 'dev', 'proc', 'var', 'bin', 'lib64', 'usr',
'lib', 'srv', 'home', 'etc', 'opt', 'sbin', 'media']
使用Python删除目录或文件
OS模块证明了在Python中删除目录和文件的不同方法。这些方法是–
- 使用os.remove()
- 使用os.rmdir()
使用 os.remove()
Python中的os.remove()方法用于移除或删除一个文件路径。这个方法不能移除或删除一个目录。如果指定的路径是一个目录,那么该方法将引发 OSError。
例子: 假设文件夹中包含的文件是。
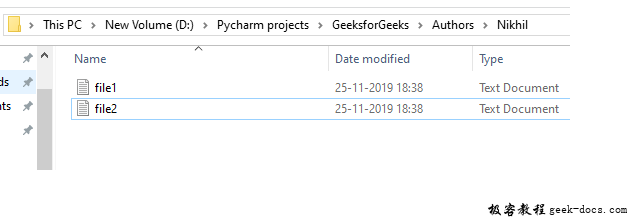
# Python program to explain os.remove() method
# importing os module
import os
# File name
file = 'file1.txt'
# File location
location = "D:/Pycharm projects/GeeksforGeeks/Authors/Nikhil/"
# Path
path = os.path.join(location, file)
# Remove the file
# 'file.txt'
os.remove(path)
输出:
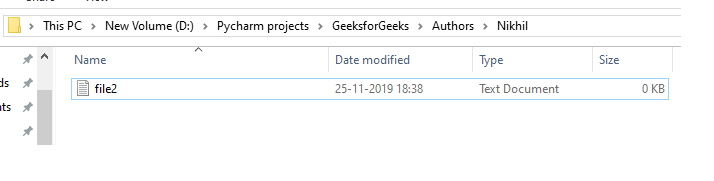
使用 os.rmdir()
Python中的os.rmdir()方法用于移除或删除一个空目录。如果指定的路径不是一个空目录,将引发 OSError。
例子: 假设这些目录是
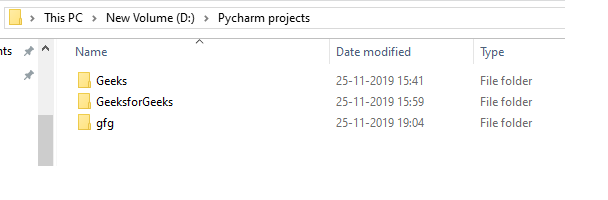
# Python program to explain os.rmdir() method
# importing os module
import os
# Directory name
directory = "Geeks"
# Parent Directory
parent = "D:/Pycharm projects/"
# Path
path = os.path.join(parent, directory)
# Remove the Directory
# "Geeks"
os.rmdir(path)
输出:
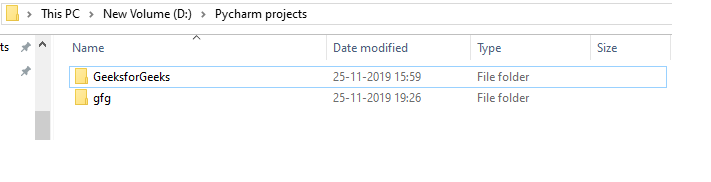
常用的函数
1. os.name:
这个函数给出了导入的依赖于操作系统的模块的名称。目前已注册的名称有:’posix’、’nt’、’os2’、’ce’、’java’和’riscos’。
import os
print(os.name)
输出:
posix
注意:在不同的解释器上可能会有不同的输出,比如你在这里运行代码时,’posix’。
2. os.error
本模块中的所有函数在文件名和路径无效或不可访问,或其他参数类型正确,但不被操作系统接受的情况下引发OSError。os.error是内置OSError异常的一个别名。
import os
try:
# If the file does not exist,
# then it would throw an IOError
filename = 'GFG.txt'
f = open(filename, 'rU')
text = f.read()
f.close()
# Control jumps directly to here if
# any of the above lines throws IOError.
except IOError:
# print(os.error) will <class 'OSError'>
print('Problem reading: ' + filename)
# In any case, the code then continues with
# the line after the try/except
输出:
Problem reading: GFG.txt
3. os.popen()
这个方法打开一个通往或来自命令的管道。根据模式是’r’还是’w’,返回值可以是读或写。语法。
os.popen(command[, mode[, bufsize]])
参数mode和bufsize不是必要的参数,如果没有提供,mode将采用默认的’r’。
import os
fd = "GFG.txt"
# popen() is similar to open()
file = open(fd, 'w')
file.write("Hello")
file.close()
file = open(fd, 'r')
text = file.read()
print(text)
# popen() provides a pipe/gateway and accesses the file directly
file = os.popen(fd, 'w')
file.write("Hello")
# File not closed, shown in next function.
输出:
Hello
注意:popen()的输出不会被显示,会有直接的变化进入文件。
4. os.close()
关闭文件描述符fd。一个用open()打开的文件,只能用close()来关闭。但通过os.popen()打开的文件,可以用close()或os.close()关闭。如果我们试图用 os.close() 关闭一个用 open() 打开的文件,Python 会抛出 TypeError。
import os
fd = "GFG.txt"
file = open(fd, 'r')
text = file.read()
print(text)
os.close(file)
输出:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Users\GFG\Desktop\GeeksForGeeksOSFile.py", line 6, in
os.close(file)
TypeError: an integer is required (got type _io.TextIOWrapper)
注意:同样的错误可能不会被抛出,由于不存在文件或权限特权。
5. os.rename()
一个文件old.txt可以被重命名为new.txt,使用函数os.rename()。只有当文件存在并且用户有足够的权限来改变文件时,文件的名称才会改变。
import os
fd = "GFG.txt"
os.rename(fd,'New.txt')
os.rename(fd,'New.txt')
输出:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Users\GFG\Desktop\ModuleOS\GeeksForGeeksOSFile.py", line 3, in
os.rename(fd,'New.txt')
FileNotFoundError: [WinError 2] The system cannot find the
file specified: 'GFG.txt' -> 'New.txt'
理解输出。一个文件名 “GFG.txt “存在,因此当第一次使用os.rename()时,该文件被重命名。第二次调用函数os.rename()时,文件 “New.txt “存在,而不是 “GFG.txt”,因此Python抛出FileNotFoundError。
6. os.remove()
使用Os模块,我们可以使用remove()方法在系统中删除一个文件。要删除一个文件,我们需要把文件的名称作为一个参数传给它。
import os #importing os module.
os.remove("file_name.txt") #removing the file.
操作系统模块在我们和操作系统之间提供了一个抽象层。当我们使用OS模块时,总是根据操作系统指定绝对路径,代码可以在任何操作系统上运行,但我们需要准确地改变路径。如果你试图删除一个不存在的文件,你会得到FileNotFoundError。
7. os.path.exists()
这个方法将通过传递文件名作为参数来检查一个文件是否存在。操作系统模块有一个名为PATH的子模块,通过它我们可以执行许多其他功能。
import os
#importing os module
result = os.path.exists("file_name") #giving the name of the file as a parameter.
print(result)
输出:
False
在上面的代码中,如果文件不存在,它将给出False的输出。如果文件存在,它将给我们输出True。
8. os.path.getsize()
在这个方法中,Python将给我们以字节为单位的文件大小。要使用这个方法,我们需要把文件的名称作为一个参数传给它。
import os #importing os module
size = os.path.getsize("filename")
print("Size of the file is", size," bytes.")
输出:
Size of the file is 192 bytes.
 极客教程
极客教程