使用Python预测空气质量指数
让我们看看如何用Python预测空气质量指数。空气质量指数是根据化学污染物的数量来计算的。通过使用机器学习,我们可以预测空气质量指数。
空气质量指数:空气质量指数是一个报告每日空气质量的指数。换句话说,它是衡量空气污染在短时间内如何影响人的健康。空气质量指数是根据在一个标准时间间隔内测得的特定污染物的平均浓度计算的。一般来说,大多数污染物的时间间隔为24小时,一氧化碳和臭氧的时间间隔为8小时。
我们可以通过查看AQI来了解空气污染的情况
| AQI水平 | AQI范围 |
|---|---|
| 良好 | 0 – 50 |
| 中等 | 51 – 100 |
| 不健康的 | 101 – 150 |
| 对强壮的人不健康 | 151 – 200 |
| 有害的 | 201+ |
让我们用机器学习的概念找到基于化学污染物的空气质量指数。
数据集描述
它包含8个属性,其中7个是化学污染量,一个是空气质量指数。PM2.5-AVG, PM10-AVG, NO2-AVG, NH3-AVG, SO2-AG, OZONE-AVG是独立属性。因为空气质量指数是根据7个属性计算的。
由于数据是数字的,而且数据中没有缺失值,所以不需要进行预处理。我们的目标是预测空气质量指数,所以这项任务要么是分类,要么是回归。因此,由于我们的类标签是连续的,所以需要回归技术。
回归是有监督的学习技术,在给定范围内对数据进行拟合。Python中的回归技术实例。
- 随机森林调节器
- Ada Boost Regressor
- Bagging Regressor
- 线性回归等。
# importing pandas module for data frame
import pandas as pd
# loading dataset and storing in train variable
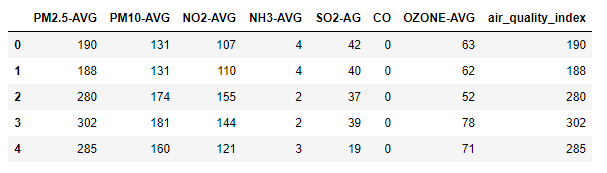
train=pd.read_csv('AQI.csv')
# display top 5 data
train.head()
输出:
# importing Randomforest
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostRegressor
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
# creating model
m1 = RandomForestRegressor()
# separating class label and other attributes
train1 = train.drop(['air_quality_index'], axis=1)
target = train['air_quality_index']
# Fitting the model
m1.fit(train1, target)
'''RandomForestRegressor(bootstrap=True, ccp_alpha=0.0, criterion='mse',
max_depth=None, max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
max_samples=None, min_impurity_decrease=0.0,
min_impurity_split=None, min_samples_leaf=1,
min_samples_split=2, min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0,
n_estimators=100, n_jobs=None, oob_score=False,
random_state=None, verbose=0, warm_start=False)'''
# calculating the score and the score is 97.96360799890066%
m1.score(train1, target) * 100
# predicting the model with other values (testing the data)
# so AQI is 123.71
m1.predict([[123, 45, 67, 34, 5, 0, 23]])
# Adaboost model
# importing module
# defining model
m2 = AdaBoostRegressor()
# Fitting the model
m2.fit(train1, target)
'''AdaBoostRegressor(base_estimator=None, learning_rate=1.0, loss='linear',
n_estimators=50, random_state=None)'''
# calculating the score and the score is 96.15377360010211%
m2.score(train1, target)*100
# predicting the model with other values (testing the data)
# so AQI is 94.42105263
m2.predict([[123, 45, 67, 34, 5, 0, 23]])
 极客教程
极客教程