如何在Python中重新取样时间序列数据
在时间序列中,数据的一致性是最重要的,重采样可以确保数据以一致的频率分布。重采样还可以提供一种看待数据的不同看法,换句话说,它可以根据重采样频率增加对数据的额外洞察力。
resample()函数:它主要用于时间序列数据。
语法:
# import the python pandas library
import pandas as pd
# 语法 for the resample function.
pd.series.resample(rule, axis=0, closed='left',
convention='start', kind=None, offset=None,
origin='start_day')
重采样主要涉及改变原始观测值的时间频率。在时间序列中,两种流行的重采样方法如下
- Upsampling
- Downsampling
上采样
提前取样涉及到增加数据的时间频率,这是一种数据分解程序,我们将时间频率从高层次分解到低层次。例如,将时间频率从月分解到天,或从天分解到小时,或从小时分解到秒。根据采样频率的不同,升频通常会吹大数据的大小。如果D是原始数据的大小,D’是升频数据的大小,那么D’>D
现在,让我们看一个使用Python在时间序列数据中进行重采样的例子。
点击这里下载用于实施的实践数据集洗涤剂销售数据.csv。
示例:
# import the python pandas library
import pandas as pd
# read data using read_csv
data = pd.read_csv("Detergent sales data.csv", header=0,
index_col=0, parse_dates=True, squeeze=True)
输出:
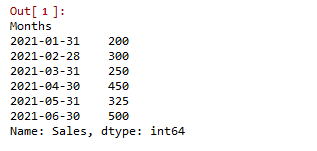
洗涤剂的销售数据显示了前6个月的销售价值。假设这里的任务是预测每日的销售值。考虑到每月的数据,我们被要求预测每日的销售数据,这就意味着使用了升值法。
# Use resample function to upsample months
# to days using the mean sales of month
upsampled = data.resample('D').mean()
输出:
输出显示了数据集的一些样本,这些样本根据月份的平均值从月到天进行了向上采样。你也可以尝试使用最适合该问题的sum()、median()。

除了我们的数据集中原本就有的那些日子外,其余日子的数据集已经用纳米值进行了上采样。(每个月的总销售数据)。
现在,我们可以使用一种叫做插值的技术来填充这些纳值。Pandas为此提供了一个名为DataFrame.interpolate()的函数。插值是一种方法,涉及到使用其中一种技术来填充nan值,如最近的’、’零’、’直线’、’二次’、’三次’、’花键’、’巴里中心’、’多项式’。我们将选择 “线性 “内插法。这在可用的数据之间画一条直线,在这种情况下是在一个月的最后一天,并从这条线上填入选定频率的值。
# use interpolate function with method linear
# to upsample the values of the upsampled days
# linearly
interpolated = upsampled.interpolate(method='linear')
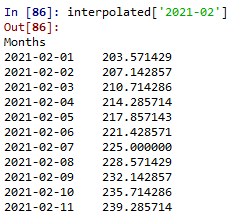
# Printing the linear interpolated values for month 2
print(interpolated['2021-02']) .
输出:
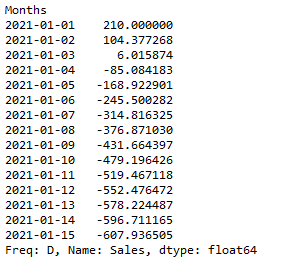
用多项式插值进行上采样
另一种常见的插值方法是使用多项式或花键来连接这些值。这可以创建更多的曲线,在许多数据集上看起来很真实。使用花键插值需要你指定顺序(多项式中的项数)。
# use interpolate function with method polynomial
# This upsamples the values of the remaining
# days with a quadratic function of degree 2.
interpolated = upsampled.interpolate(method='polynomial', order=2)
# Printing the polynomial interpolated value
print(interpolated)
输出:
因此,我们可以使用resample()和interpolate()函数对数据进行向上采样。使用这些函数的不同配置进行尝试。
下采样
下采样涉及降低数据的时间频率,它是一种数据汇总程序,我们将时间频率从较低水平汇总到较高水平。例如,将时间频率从天汇总到月,或从小时汇总到天,或从秒汇总到小时。下采样通常会缩减数据的大小,这取决于采样频率。如果D是原始数据的大小,D’是上升数据的大小,那么D'<D。
例如,汽车销售数据显示前6个月逐日的销售价值。假设这里的任务是预测季度销售的价值。鉴于每天的数据,我们被要求预测季度的销售数据,这就意味着使用了下抽样。
点击这里下载本实施方案中使用的实践数据集car-sales.csv。
示例:
# import the python pandas library
import pandas as pd
# read the data using pandas read_csv() function.
data = pd.read_csv("car-sales.csv", header=0,
index_col=0, parse_dates=True,
squeeze=True)
# printing the first 6 rows of the dataset
print(data.head(6))
输出:

我们可以使用季度重采样频率’Q’来按季度汇总数据。
# Use resample function to downsample days
# to months using the mean sales of month.
downsampled = data.resample('Q').mean()
# printing the downsampled data.
print(downsampled)
输出:
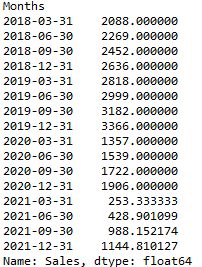
现在,这个下采样的数据可以用来预测季度销售。
 极客教程
极客教程