在Pandas DataFrame中进行字符串操作
字符串操作是改变、解析、拼接、粘贴或分析字符串的过程。正如我们所知,有时,字符串中的数据不适合操作分析或得到数据的描述。但是Python以其对字符串的操作能力而闻名。因此,通过扩展,我们将了解Pandas是如何使用一些内置函数为我们提供操作修改和处理字符串数据帧的方法。Pandas库有一些内置函数,经常用于字符串数据框架的操作。
首先,我们将知道如何使用pandas创建一个字符串数据框。
# Importing the necessary libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# df stands for dataframe
df = pd.Series(['Gulshan', 'Shashank', 'Bablu',
'Abhishek', 'Anand', np.nan, 'Pratap'])
print(df)
输出:

让我们把上面创建的数据框架的类型改为字符串类型。有多种方法可以做到这一点。让我们在下面的例子中看一看。
例子1:我们可以在创建数据框后改变dtype。
# we can change the dtype after
# creation of dataframe
print(df.astype('string'))
输出:

示例2:创建dtype = ‘string’的数据框架。
# now creating the dataframe as dtype = 'string'
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.Series(['Gulshan', 'Shashank', 'Bablu', 'Abhishek',
'Anand', np.nan, 'Pratap'], dtype='string')
print(df)
输出:

示例3:创建数据框架为dtype = pd.StringDtype()。
# now creating the dataframe as dtype = pd.StringDtype()
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.Series(['Gulshan', 'Shashank', 'Bablu', 'Abhishek',
'Anand', np.nan, 'Pratap'], dtype=pd.StringDtype())
print(df)
输出:

Pandas中的字符串操作
现在,我们看到在pandas数据框内的字符串操作,所以首先创建一个数据框,并在下面这个单一的数据框上操作所有的字符串操作,这样大家就可以很容易的了解到。
示例:
# python script for create a dataframe
# for string manipulations
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
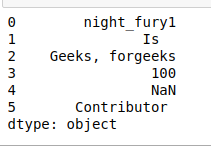
df = pd.Series(['night_fury1', 'Is ', 'Geeks, forgeeks',
'100', np.nan, ' Contributor '])
df
输出:
让我们来看看这个库所提供的用于操作字符串的各种方法。
- lower():将DataFrame中字符串的所有大写字符转换为小写,并返回结果中的小写字符串。
# lower()
print(df.str.lower())
0 night_fury1
1 is
2 geeks, forgeeks
3 100
4 NaN
5 contributor
dtype: object
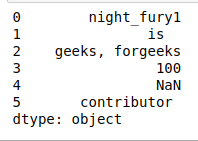
- upper()。将DataFrame中字符串的所有小写字符转换为大写,并在结果中返回大写的字符串。
#upper()
print(df.str.upper())
输出:
- strip()。如果字符串的开头或结尾有空格,我们应该使用strip()修剪字符串以消除空格,或者删除DataFrame中的字符串所包含的额外空格。
# strip()
print(df)
print('\nAfter using the strip:')
print(df.str.strip())
输出:

- split(‘ ‘)。用给定的模式拆分每个字符串。字符串被分割,执行分割操作后的新元素被存储在一个列表中。
# split(pattern)
print(df)
print('\nAfter using the strip:')
print(df.str.split(','))
# now we can use [] or get() to fetch
# the index values
print('\nusing []:')
print(df.str.split(',').str[0])
print('\nusing get():')
print(df.str.split(',').str.get(1))
输出:

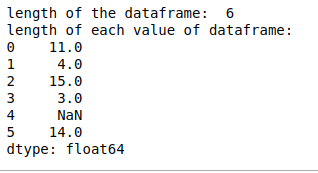
- len()。在len()的帮助下,我们可以计算出DataFrame中每个字符串的长度,如果DataFrame中存在空数据,它将返回NaN。
# len()
print("length of the dataframe: ", len(df))
print("length of each value of dataframe:")
print(df.str.len())
输出:
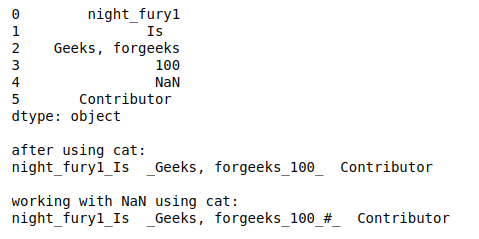
- cat(sep=’ ‘)。它将数据框架的索引元素或数据框架中的每个字符串与给定的分隔符连接起来。
# cat(sep=pattern)
print(df)
print("\nafter using cat:")
print(df.str.cat(sep='_'))
print("\nworking with NaN using cat:")
print(df.str.cat(sep='_', na_rep='#'))
输出:
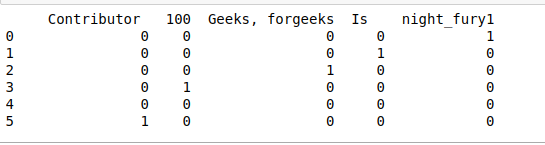
- get_dummies()。它返回带有一热编码值的DataFrame,比如我们可以看到,如果它存在于相对索引中,则返回布尔值1,如果不存在则返回0。
# get_dummies()
print(df.str.get_dummies())
输出:
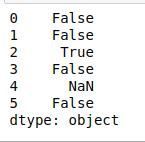
- startswith(pattern)。如果DataFrame Index中的元素或字符串以该模式开始,则返回true。
# startswith(pattern)
print(df.str.startswith('G'))
输出:
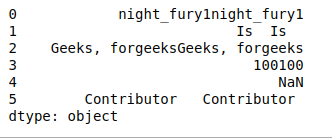
- endswith(pattern)。如果DataFrame Index中的元素或字符串以该模式结束,则返回true。
# endswith(pattern)
print(df.str.endswith('1'))
输出:

- replace(a,b)。它用值b替换值a,如下面的例子,’Geeks’被’Gulshan’所替换。
# replace(a,b)
print(df)
print("\nAfter using replace:")
print(df.str.replace('Geeks', 'Gulshan'))
输出:

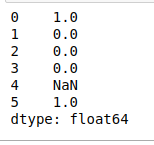
- repeat(value)。它以给定的次数重复每个元素,如下面的例子,每个字符串在DataFrame中出现了两次。
# repeat(value)
print(df.str.repeat(2))
输出:
- count(pattern)。它返回模式在Data-Frame中每个元素中出现的次数,比如下面的例子,它对DataFrame中每个字符串中的’n’进行计数,并返回每个字符串中’n’的总计数。
# count(pattern)
print(df.str.count('n'))
输出:
- find(pattern)。它返回该模式第一次出现的第一个位置。我们可以在下面的例子中看到,它返回整个DataFrame中每个字符串中出现的字符’n’的索引值。
# find(pattern)
# in result '-1' indicates there is no
# value matching with given pattern in
# particular row
print(df.str.find('n'))
输出:

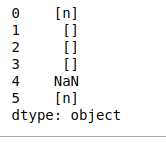
- findall(pattern)。它返回该模式的所有出现的列表。正如我们在下面看到的,有一个返回的列表由n组成,因为它在字符串中只出现一次。
# findall(pattern)
# in result [] indicates null list as
# there is no value matching with given
# pattern in particular row
print(df.str.findall('n'))
输出:
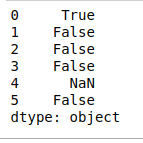
- islower()。它检查数据框架索引中每个字符串的所有字符是否为小写,并返回一个布尔值。
# islower()
print(df.str.islower())
输出:
- isupper()。它检查数据框架索引中每个字符串的所有字符是否为大写字母,并返回一个布尔值。
# isupper()
print(df.str.isupper())
输出:

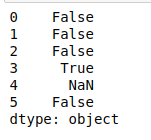
- isnumeric()。它检查数据框架索引中每个字符串中的所有字符是否为数字,并返回一个布尔值。
# isnumeric()
print(df.str.isnumeric())
输出:
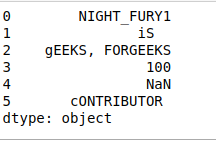
- swapcase()。它将小写字母换成大写字母,反之亦然。就像下面的例子一样,它将每个字符串中的所有大写字母转换为小写字母,反之亦然(小写->大写)。
# swapcase()
print(df.str.swapcase())
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程