Python Pandas dataframe.pow()
Python是一种进行数据分析的伟大语言,主要是因为以数据为中心的Python包的奇妙生态系统。Pandas就是这些包中的一个,它使导入和分析数据变得更加容易。
Pandas dataframe.pow()函数计算dataframe和other的指数幂,从元素上看(二进制运算符pow)。这个函数本质上与dataframe other相同,但支持填补其中一个输入数据中的缺失值。
语法: DataFrame.pow(other, axis=’columns’, level=None, fill_value=None)
参数 :
other:系列,数据框架,或常数
axis:对于系列输入,axis要与系列的索引相匹配。
level :跨层广播,与通过的MultiIndex层的索引值相匹配。
fill_value : 在计算前用这个值填充现有的缺失(NaN)值,以及成功的DataFrame对齐所需的任何新元素。如果两个对应的DataFrame位置的数据都缺失,结果将是缺失。
**kwargs :额外的关键字参数被传递到DataFrame.shift或Series.shift。
返回 : result : DataFrame
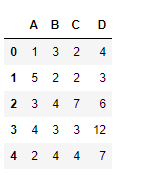
例子#1:使用pow()函数查找数据框中每个元素的幂。使用数列将一行中的每个元素提高到不同的幂。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the dataframe
df1 = pd.DataFrame({"A":[14, 4, 5, 4, 1],
"B":[5, 2, 54, 3, 2],
"C":[20, 20, 7, 3, 8],
"D":[14, 3, 6, 2, 6]})
# Print the dataframe
df
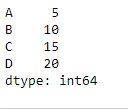
让我们创建一个系列
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Create the Series
sr = pd.Series([2, 3, 4, 2], index =["A", "B", "C", "D"])
# Print the series
sr
现在,让我们使用dataframe.pow()函数将一行中的每个元素提高到不同的功率。
# find the power
df.pow(sr, axis = 1)
输出 :

例子2:使用pow()函数将第一个数据框中的每个元素提升到另一个数据框中相应元素的幂。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the first dataframe
df1 = pd.DataFrame({"A":[14, 4, 5, 4, 1],
"B":[5, 2, 54, 3, 2],
"C":[20, 20, 7, 3, 8],
"D":[14, 3, 6, 2, 6]})
# Creating the second dataframe
df2 = pd.DataFrame({"A":[1, 5, 3, 4, 2],
"B":[3, 2, 4, 3, 4],
"C":[2, 2, 7, 3, 4],
"D":[4, 3, 6, 12, 7]})
# using pow() function to raise each element
# in df1 to the power of corresponding element in df2
df1.pow(df2)
输出 :

 极客教程
极客教程