Python Pandas dataframe.at_time()
Python是一种进行数据分析的伟大语言,主要是因为以数据为中心的Python软件包的奇妙生态系统。Pandas就是这些包中的一个,使导入和分析数据变得更加容易。
Pandas dataframe.at_time()函数用于选择一行中对应于一天中输入时间的所有值。如果输入的时间不在数据帧中,那么将返回一个空数据帧。
语法: DataFrame.at_time(time, asof=False)
参数:
time: datetime.time 或字符串
返回: values_at_time : 调用者的类型
注意: at_time()函数在数据帧的索引不是DatetimeIndex时引发异常。
例子#1:创建一个日期时间索引的数据框架,并在任何特定的时间检索数值。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating row index values for dataframe
# Taken time frequency to be of 12 hours interval
# Generating five index value using "period = 5" parameter
ind = pd.date_range('01/ 01/2000', periods = 5, freq ='12H')
# Creating a dataframe with 2 columns
# using "ind" as the index for our dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
"B":[10, 20, 30, 40, 50]},
index = ind)
# Printing the dataframe
# for visualization
df
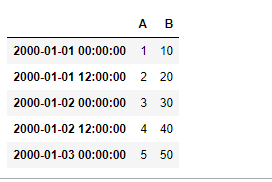
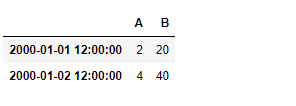
现在找出时间 “12:00 “的数值
df.at_time('12:00')
输出 :
例子#2:将date_time索引的频率设置为30分钟,并查询有效和无效的时间(不存在于数据帧中)。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating row index values for our data frame
# We have taken time frequency to be of 30 minutes interval
# We are generating eight index value using "period = 8" parameter
ind = pd.date_range('01/01/2000', periods = 8, freq ='30T')
# Creating a dataframe with 2 columns
# using "ind" as the index for our dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8],
"B":[10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80]},
index = ind)
# Printing the dataframe
df
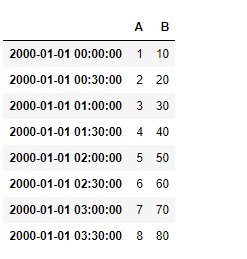
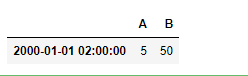
现在我们来查询时间 “02:00”
# Find the row values at time "02:00"
df.at_time('02:00')
输出 :
 极客教程
极客教程