将Pandas交叉表转换为堆叠数据框架
在这篇文章中,我们将讨论如何将pandas串联表转换为堆叠数据框架。
堆叠的DataFrame是一个多级索引,与原始DataFrame相比,有一个或多个新的内部级别。如果列有一个单层,那么结果就是一个系列对象。
Pandas的crosstab功能是一个频率表,通过建立一个交叉表来显示两个或多个变量之间的关系,计算某些数据组之间的频率。
语法:
pandas.crosstab(index, columns, rownames=None, colnames=None)
参数 :
- index – 数组或系列或类似数组的对象的列表。该值用于在行中分组
- columns – 数组或系列或类似数组的对象的列表。这个值用于在列中进行分组
- rownames – 这里指定的名称必须与所传递的行数组的数量相匹配。
- colnames – 这里指定的名称必须与所传递的列数组的数量相符。
示例:
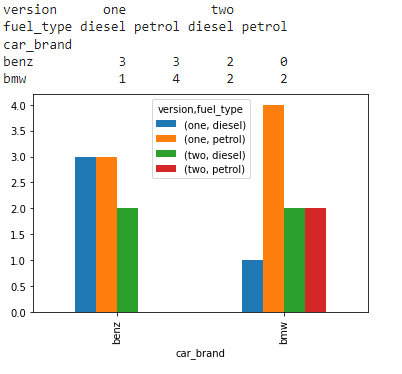
在这个例子中,我们创建了3个样本数组,即car_brand, version, fuel_type,如图所示。现在,我们将这些数组作为索引、列、行和列的名称传递给crosstab函数,如图所示。
最后,crosstab数据框架还可以使用python plot.bar()函数进行可视化。
# import the numpy and pandas package
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# create three separate arrays namely car_brand,
# version, fuel_type as shown
car_brand = np.array(["bmw", "bmw", "bmw", "bmw", "benz", "benz",
"bmw", "bmw", "benz", "benz", "benz", "benz",
"bmw", "bmw", "bmw", "benz", "benz", ],
dtype=object)
version = np.array(["one", "one", "one", "two", "one", "one", "one",
"two", "one", "one", "one", "two", "two", "two",
"one", "two", "one"], dtype=object)
fuel_type = np.array(["petrol", "petrol", "petrol", "diesel", "diesel",
"petrol", "diesel", "diesel", "diesel", "petrol",
"petrol", "diesel", "petrol", "petrol", "petrol",
"diesel", "diesel", ],
dtype=object)
# use pandas crosstab and pass the three arrays
# as index and columns to create a crosstab table.
cross_tab_data = pd.crosstab(index=car_brand,
columns=[version, fuel_type],
rownames=['car_brand'],
colnames=['version', 'fuel_type'])
print(cross_tab_data)
barplot = cross_tab_data.plot.bar()
输出:
将串联表转换为堆叠数据框架。
这里我们要指定要堆叠的层数。这将根据pandas DataFrame的特定列上的轴级别进行转换。
语法:
pandas.DataFrame.stack(level, dropna)
参数 :
- level – 指定在生成的数据框架中从列轴到索引轴堆叠的层次。
- dropna – 一个bool类型。是否在生成的DataFrame/Series中删除缺失值的行。
示例 1:
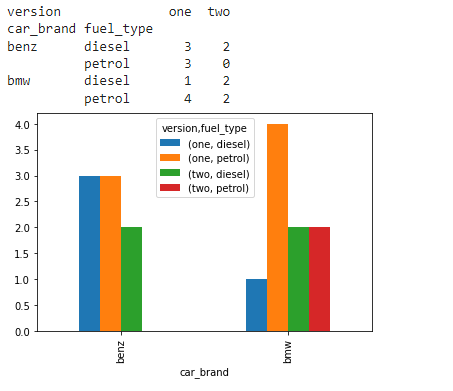
在这里,我们将把交叉表转换为一个堆叠的数据框架。Fuel_type级别将作为一个列堆积在结果数据框架中。
# import the numpy and pandas package
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# create three separate arrays namely car_brand,
# version, fuel_type as shown
car_brand = np.array(["bmw", "bmw", "bmw", "bmw", "benz", "benz",
"bmw", "bmw", "benz", "benz", "benz", "benz",
"bmw", "bmw", "bmw", "benz", "benz", ],
dtype=object)
version = np.array(["one", "one", "one", "two", "one", "one", "one",
"two", "one", "one", "one", "two", "two", "two",
"one", "two", "one"], dtype=object)
fuel_type = np.array(["petrol", "petrol", "petrol", "diesel", "diesel",
"petrol", "diesel", "diesel", "diesel", "petrol",
"petrol", "diesel", "petrol", "petrol", "petrol",
"diesel", "diesel", ],
dtype=object)
# use pandas crosstab and pass the three
# arrays as index and columns
# to create a crosstab table.
cross_tab_data = pd.crosstab(index=car_brand,
columns=[version, fuel_type],
rownames=['car_brand'],
colnames=['version', 'fuel_type'])
barplot = cross_tab_data.plot.bar()
# use the created sample crosstab data
# to convert it to a stacked dataframe
stacked_data = cross_tab_data.stack(level=1)
print(stacked_data)
输出:
例子2
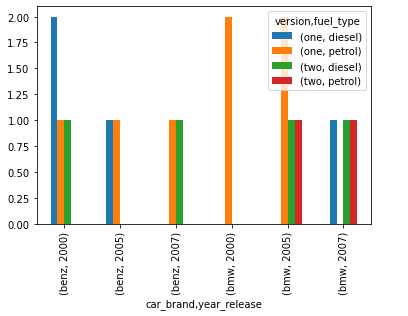
在这个例子中,我们展示了1和2两个级别的结果。
# import the numpy and pandas package
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# create three separate arrays namely car_brand,
# version, fuel_type as shown
car_brand = np.array(["bmw", "bmw", "bmw", "bmw", "benz",
"benz", "bmw", "bmw", "benz", "benz",
"benz", "benz", "bmw", "bmw", "bmw",
"benz", "benz", ], dtype=object)
version = np.array(["one", "one", "one", "two", "one", "one",
"one", "two", "one", "one", "one", "two",
"two", "two", "one", "two", "one"],
dtype=object)
fuel_type = np.array(["petrol", "petrol", "petrol", "diesel",
"diesel", "petrol", "diesel", "diesel",
"diesel", "petrol", "petrol", "diesel",
"petrol", "petrol", "petrol", "diesel",
"diesel", ], dtype=object)
year_release = np.array([2000, 2005, 2000, 2007, 2000, 2005,
2007, 2005, 2005, 2000, 2007, 2000,
2007, 2005, 2005, 2007, 2000],
dtype=object)
# use pandas crosstab and pass the three arrays
# as index and columns to create a crosstab table.
cross_tab_data = pd.crosstab(index=car_brand,
columns=[version, fuel_type, year_release],
rownames=['car_brand'],
colnames=['version', 'fuel_type', 'year_release'])
barplot = cross_tab_data.plot.bar()
# use the created sample crosstab data to
# convert it to a stacked dataframe with
# level 1
stacked_data = cross_tab_data.stack(level=1)
barplot = stacked_data.plot.bar()
# use the created sample crosstab data to
# convert it to a stacked dataframe with
# level 2
stacked_data = cross_tab_data.stack(level=2)
barplot = stacked_data.plot.bar()
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程