将Lambda函数应用于Pandas Dataframe
在Pandas中,我们可以自由地在需要时添加不同的函数,如lambda函数、排序函数等。我们可以对Pandas数据框架的列和行都应用一个lambda函数。
语法: lambda参数:表达式
一个匿名函数,我们可以立即传入,而不需要定义名称或任何像完整的传统函数的东西。
例子1:使用Dataframe.assign()将lambda函数应用于单列。
# importing pandas library
import pandas as pd
# creating and initializing a list
values= [['Rohan',455],['Elvish',250],['Deepak',495],
['Soni',400],['Radhika',350],['Vansh',450]]
# creating a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(values,columns=['Name','Total_Marks'])
# Applying lambda function to find
# percentage of 'Total_Marks' column
# using df.assign()
df = df.assign(Percentage = lambda x: (x['Total_Marks'] /500 * 100))
# displaying the data frame
df
输出 :
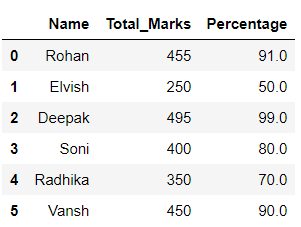
在上面的例子中,lambda函数被应用于’Total_Marks’列,并在它的帮助下形成了一个新的列’Percate’。
示例2:使用Dataframe.assign()将lambda函数应用于**多列。
# importing pandas library
import pandas as pd
# creating and initializing a nested list
values_list = [[15, 2.5, 100], [20, 4.5, 50], [25, 5.2, 80],
[45, 5.8, 48], [40, 6.3, 70], [41, 6.4, 90],
[51, 2.3, 111]]
# creating a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(values_list, columns=['Field_1', 'Field_2', 'Field_3'])
# Applying lambda function to find
# the product of 3 columns using
# df.assign()
df = df.assign(Product=lambda x: (x['Field_1'] * x['Field_2'] * x['Field_3']))
# printing dataframe
df
输出 :
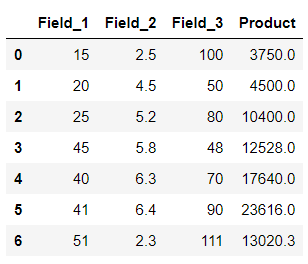
在上面的例子中,lambda函数被应用于3列,即’Field_1′, ‘Field_2’, 和’Field_3’。
例子3 :使用Dataframe.apply()将lambda函数应用于单行。
# importing pandas and numpy libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# creating and initializing a nested list
values_list = [[15, 2.5, 100], [20, 4.5, 50], [25, 5.2, 80],
[45, 5.8, 48], [40, 6.3, 70], [41, 6.4, 90],
[51, 2.3, 111]]
# creating a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(values_list, columns=['Field_1', 'Field_2', 'Field_3'],
index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g'])
# Apply function numpy.square() to square
# the values of one row only i.e. row
# with index name 'd'
df = df.apply(lambda x: np.square(x) if x.name == 'd' else x, axis=1)
# printing dataframe
df
输出 :
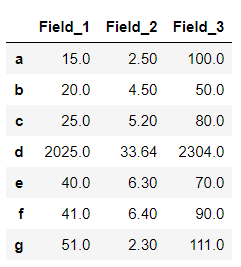
在上面的例子中,一个lambda函数被应用于以’d’开始的行,因此,所有的值都是与之相对应的。
示例4:使用Dataframe.apply()将lambda函数应用于多条记录。
# importing pandas and numpylibraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# creating and initializing a nested list
values_list = [[15, 2.5, 100], [20, 4.5, 50], [25, 5.2, 80],
[45, 5.8, 48], [40, 6.3, 70], [41, 6.4, 90],
[51, 2.3, 111]]
# creating a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(values_list, columns=['Field_1', 'Field_2', 'Field_3'],
index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g'])
# Apply function numpy.square() to square
# the values of 3 rows only i.e. with row
# index name 'a', 'e' and 'g' only
df = df.apply(lambda x: np.square(x) if x.name in [
'a', 'e', 'g'] else x, axis=1)
# printing dataframe
df
输出 :

在上面的例子中,一个lambda函数被应用于以’a’、’e’和’g’开始的3行。
例子5:将lambda函数同时应用于多列和行。
# importing pandas and numpylibraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# creating and initializing a nested list
values_list = [[1.5, 2.5, 10.0], [2.0, 4.5, 5.0], [2.5, 5.2, 8.0],
[4.5, 5.8, 4.8], [4.0, 6.3, 70], [4.1, 6.4, 9.0],
[5.1, 2.3, 11.1]]
# creating a pandas dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame(values_list, columns=['Field_1', 'Field_2', 'Field_3'],
index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g'])
# Apply function numpy.square() to square
# the values of 2 rows only i.e. with row
# index name 'b' and 'f' only
df = df.apply(lambda x: np.square(x) if x.name in ['b', 'f'] else x, axis=1)
# Applying lambda function to find product of 3 columns
# i.e 'Field_1', 'Field_2' and 'Field_3'
df = df.assign(Product=lambda x: (x['Field_1'] * x['Field_2'] * x['Field_3']))
# printing dataframe
df
输出 :
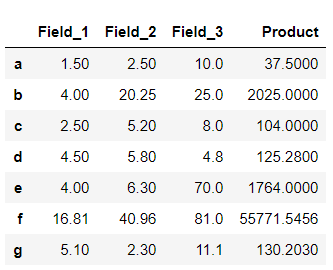
在这个例子中,一个lambda函数被应用于两行和三列。
 极客教程
极客教程