Node.js 如何创建和验证JWT令牌
在本文中,我们将看到如何在Node.js中创建和验证JWT令牌。
先决条件:
- 对JavaScript有良好的了解。
- 对ExpressJs有基本的了解。
- 对API认证有基本的了解。
- 对postman和它们的用途有基本的了解。
在Web开发中,我们还希望保护我们的路由,因此我们有3种方式来保护我们的路由,它们是cookies、session或API认证。cookies和session只适用于浏览器,如果您想在API的端点中保护路由。因此,您必须需要API的认证机制。或者在现在的时间里,我们大多数人都使用API,所以制作安全的API端点是非常重要的。API认证中最流行的方式是使用JsonWebToken,它可以与许多技术一起使用,包括NodeJs。在本文中,我们使用ExpressJs创建了一些虚拟的API端点,并通过JWT令牌机制使其路由安全,并了解它们的工作原理和如何验证令牌。JsonWebToken的缩写是JWT。
方法: 在开始本文之前,我们将在这里讨论本文的问题细节,我们正在谈论最流行的保护API端点的方法。JWT提供了这一点。我们将首先设置NodeJs来编写我们的代码,然后我们将看到如何创建和验证JWT令牌,最后,我们将使用Postman API测试工具来查看我们API的输出。
逐步实施步骤:
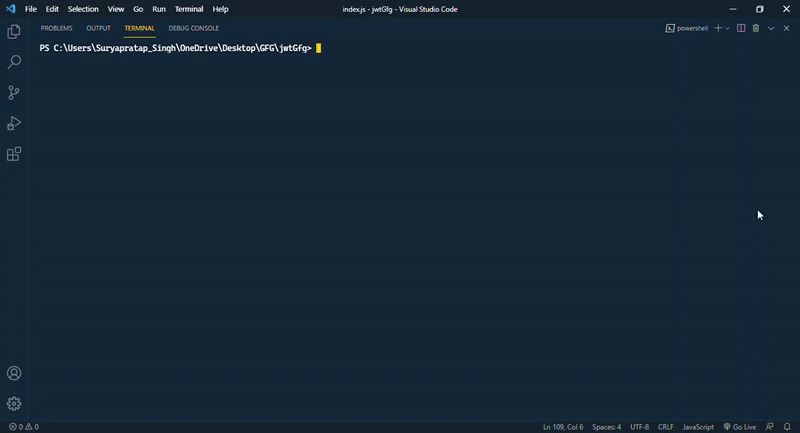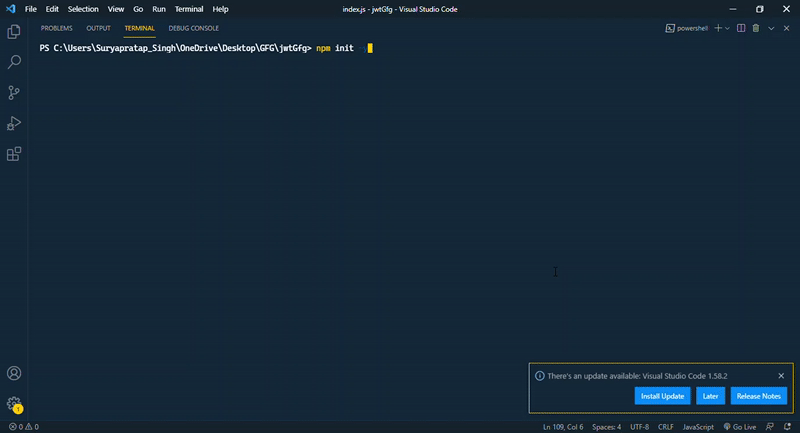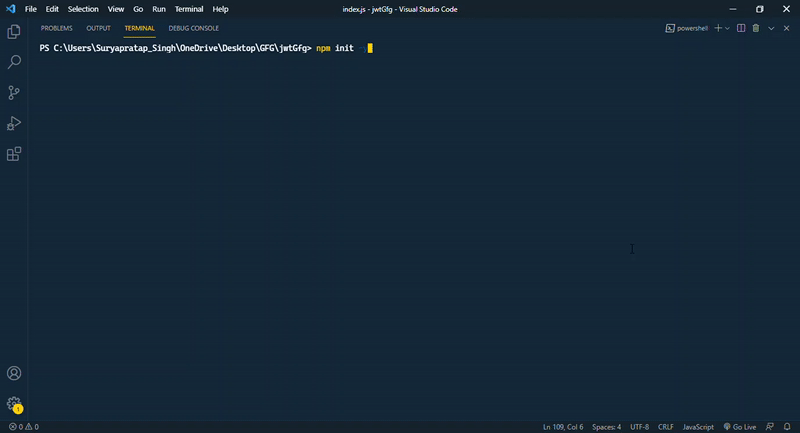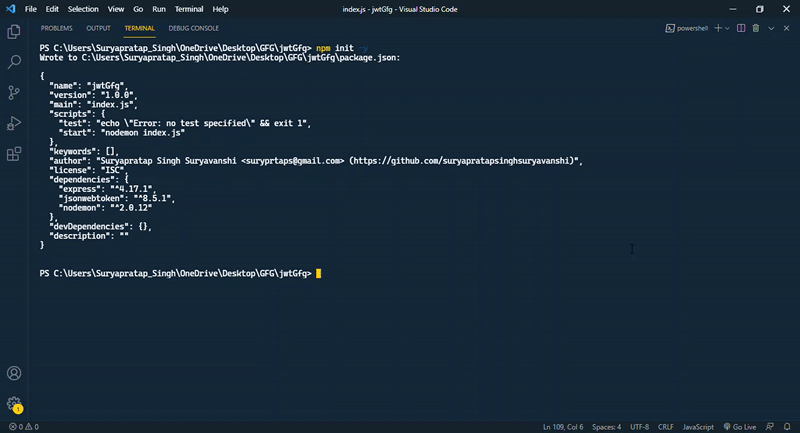
步骤1: 首先设置NodeJs项目。如果您没有NodeJs或NPM,请参考本文。使用npm初始化NodeJs项目。
npm init -y
“-y” 将所有问题的答案标记为默认。
在启动NodeJs项目后,进行第二步。
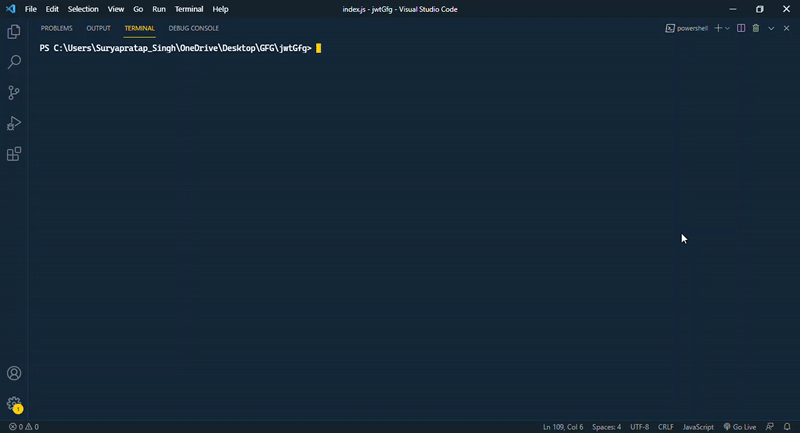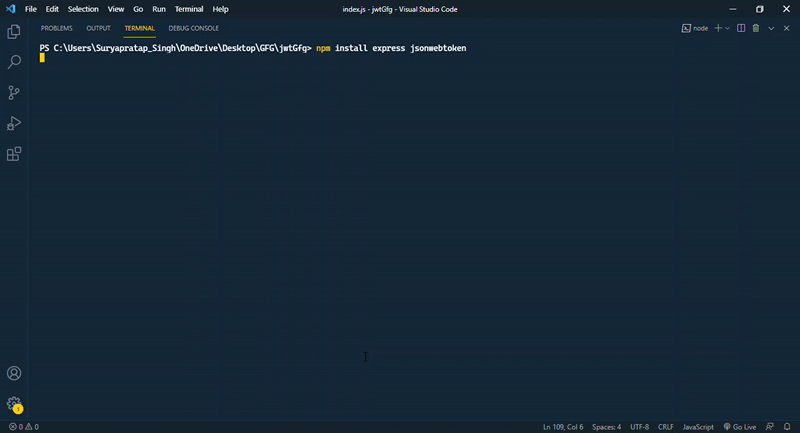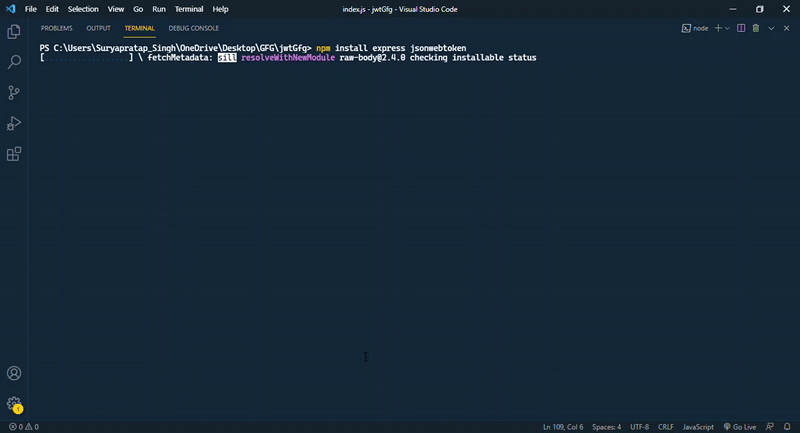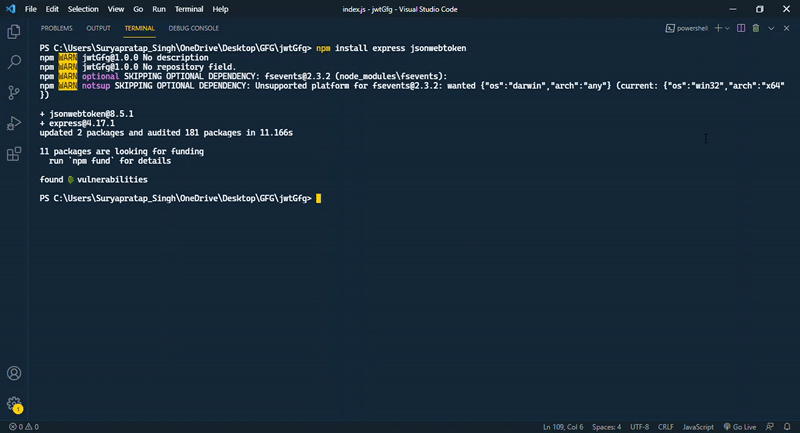
步骤2: 在初始化项目后,通过npm安装一些依赖。安装express和jsonwebtoken。
npm install express jsonwebtoken
步骤3: 将nodemon作为开发依赖安装。
npm install -d nodemon
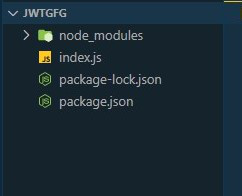
项目结构: 安装完成后,创建一个index.js文件,你的目录结构现在看起来是这样的。
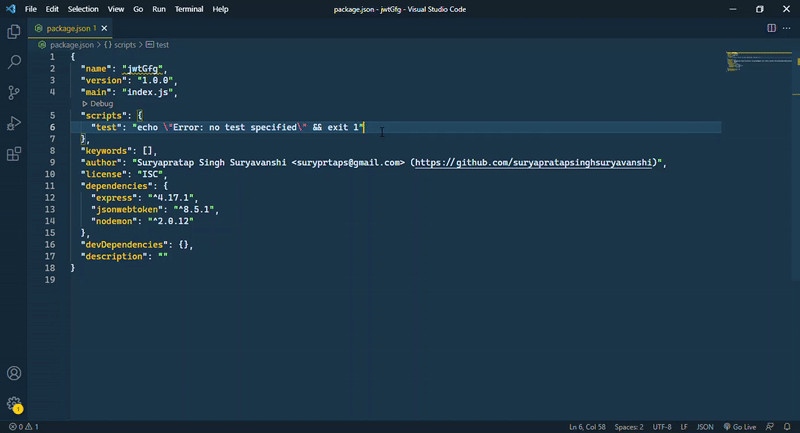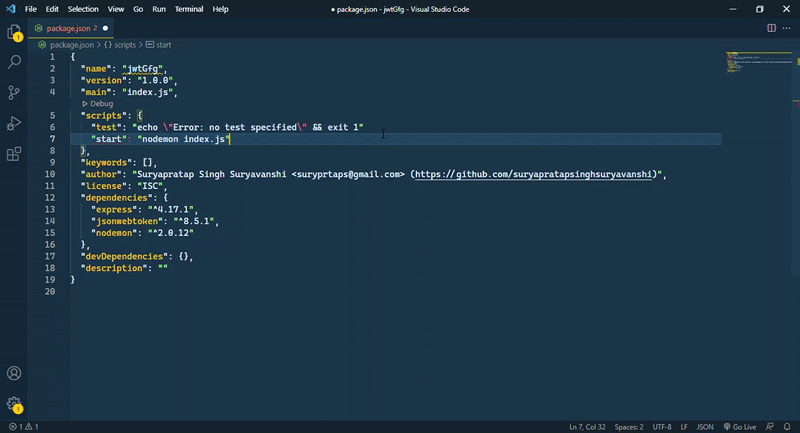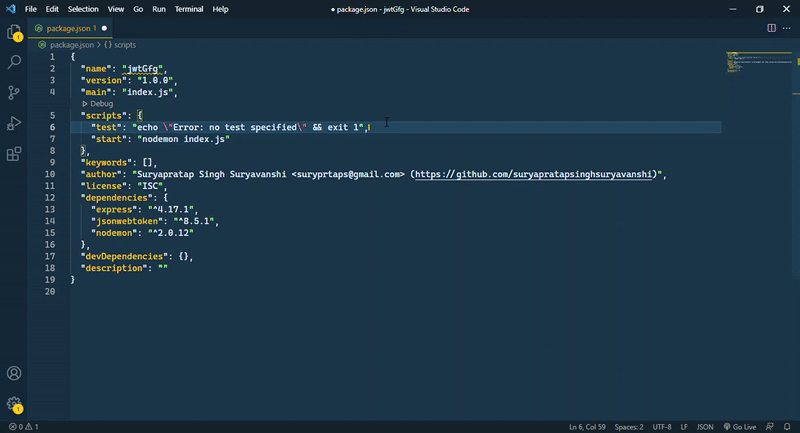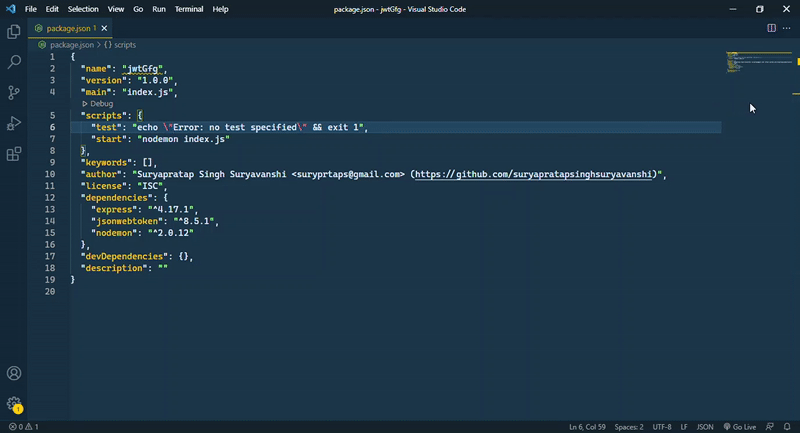
步骤4: 在package.json文件中添加一个脚本。打开package.json文件,在test脚本下面添加一行。
步骤5: 在使用JWT和express创建和验证API端点之前,首先编写一些代码以供进一步使用。
文件名:index.js
// Import express for creating API's endpoints
const express = require('express');
// Import jwt for API's endpoints authentication
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
// Creates an Express application, initiate
// express top level function
const app = express();
// A port for serving API's
const port = 3000;
// A demo get route
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.json({
route: '/',
authentication: false
});
});
// Listen the server
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running : http://localhost:${port}/`);
});
步骤6: 虚拟代码准备完毕后,创建一个json数据库对象并存储一些虚拟数据。
文件名:index.js
// A fake database object.
let database = [
{
name: 'gfg',
work: 'knowledge provider',
password: 'abc'
},
{
name: 'suryapratap',
work: 'technical content writer',
password: '123'
}
];
步骤7: 允许JSON数据与API进行通信。通过为请求增加body解析器的中间件来允许JSON数据。
文件名: index.js
// Allow json data
app.use(express.json());
步骤8: 创建一个登录路由并创建一个JWT令牌。在这里,创建一个登录的POST路由并创建一个JWT令牌,并将其返回给响应。阅读代码注释以便更好地理解。
文件名:index.js
// Login route.
app.post('/login', (req, res) => {
// Get the name to the json body data
const name = req.body.name;
// Get the password to the json body data
const password = req.body.password;
// Make two variable for further use
let isPresent = false;
let isPresentIndex = null;
// Iterate a loop to the data items and
// check what data are method
for(let i=0; i<database.length; i++){
// If data name are matched so check
// the password are correct or not
if(database[i].name === name &&
database[i].password === password){
// If both are correct so make
// isPresent variable true
isPresent = true;
// And store the data index
isPresentIndex = i;
// Break the loop after matching
// successfully
break;
}
}
// If isPresent is true, then create a
// token and pass to the response
if(isPresent){
// The jwt.sign method are used
// to create token
const token = jwt.sign(
database[isPresentIndex],
'secret'
);
// Pass the data or token in response
res.json({
login: true,
token: token,
data: database[isPresentIndex]
});
}else{
// If isPresent is false return the error
res.json({
login: false,
error: 'please check name and password.'
});
}
});
步骤9: JWT签名方法用于创建一个令牌,它需要三个参数,一个是响应对象,第二个是密钥,最后一个是选项对象,以更好地使用令牌。
文件名:index.js
jwt.sign(
{data_obeject},
"secret_key",
{Options}
)
如果您想要了解有关jwt.sign 方法的更多信息,请参考官方文档。
步骤10: 现在我们将为身份验证jwt令牌创建另一个路由。在这里,我们创建一个身份验证路由并对传入的JWT令牌进行身份验证。
文件名:index.js
// Verify route
app.get('/auth', (req, res) => {
// Get token value to the json body
const token = req.body.token;
// If the token is present
if(token){
// Verify the token using jwt.verify method
const decode = jwt.verify(token, 'secret');
// Return response with decode data
res.json({
login: true,
data: decode
});
}else{
// Return response with error
res.json({
login: false,
data: 'error'
});
}
});
步骤11:
JWT验证方法用于验证令牌,它接受两个参数,一个是令牌字符串值,另一个是用于匹配令牌是否有效的秘钥。验证方法返回一个解码对象,我们将令牌存储在其中。
文件名:index.js
jwt.verify(token_value, 'secret_key');
如果你想了解更多关于jwt.verify方法的信息,请参考官方文档。
下面是以上逐步实现的完整代码:
文件名:index.js
// Import express for creating API's endpoints
const express = require("express");
// Import jwt for API's endpoints authentication
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
// Creates an Express application, initiate
// express top level function
const app = express();
// A port for serving API's
const port = 3000;
// A fake database object
let database = [
{
name: "gfg",
work: "knowledge provider",
password: "abc",
},
{
name: "suryapratap",
work: "technical content writer",
password: "123",
},
];
// A demo get route
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.json({
route: "/",
authentication: false,
});
});
// Allow json data
app.use(express.json());
// Login route
app.post("/login", (req, res) => {
// Get the name to the json body data
const name = req.body.name;
// Get the password to the json body data
const password = req.body.password;
// Make two variable for further use
let isPresent = false;
let isPresentIndex = null;
// iterate a loop to the data items and
// check what data are matched.
for (let i = 0; i < database.length; i++) {
// If data name are matched so check
// the password are correct or not
if (database[i].name === name
&& database[i].password === password) {
// If both are correct so make
// isPresent variable true
isPresent = true;
// And store the data index
isPresentIndex = i;
// Break the loop after matching successfully
break;
}
}
// If isPresent is true, then create a
// token and pass to the response
if (isPresent) {
// The jwt.sign method are used
// to create token
const token = jwt.sign(database[isPresentIndex], "secret");
// Pass the data or token in response
res.json({
login: true,
token: token,
data: database[isPresentIndex],
});
} else {
// If isPresent is false return the error
res.json({
login: false,
error: "please check name and password.",
});
}
});
// Verify route
app.get("/auth", (req, res) => {
// Get token value to the json body
const token = req.body.token;
// If the token is present
if (token) {
// Verify the token using jwt.verify method
const decode = jwt.verify(token, "secret");
// Return response with decode data
res.json({
login: true,
data: decode,
});
} else {
// Return response with error
res.json({
login: false,
data: "error",
});
}
});
// Listen the server
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running :
http://localhost:${port}/`);
});
测试路由的步骤: 我们将使用Postman测试API路由。首先测试登录路由。打开Postman,对 ‘/login’ 路由进行POST请求,并提供合适的JSON数据。
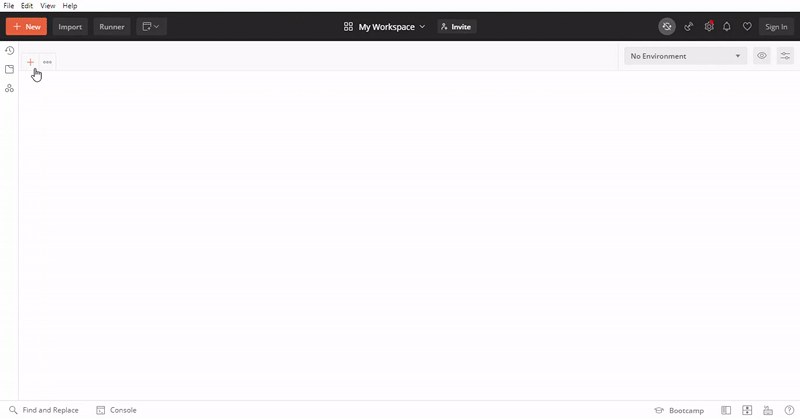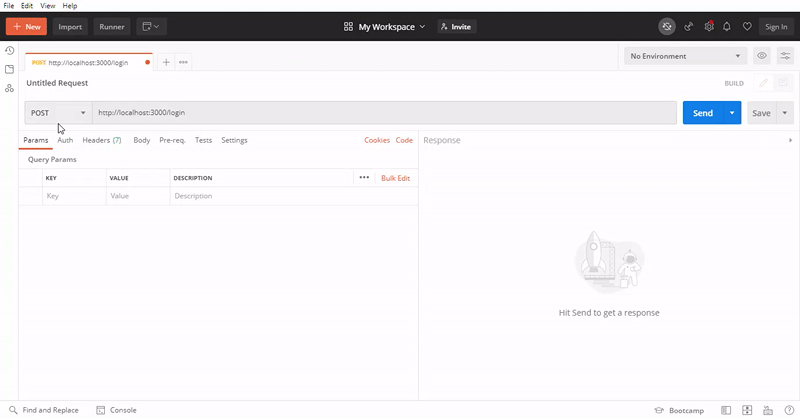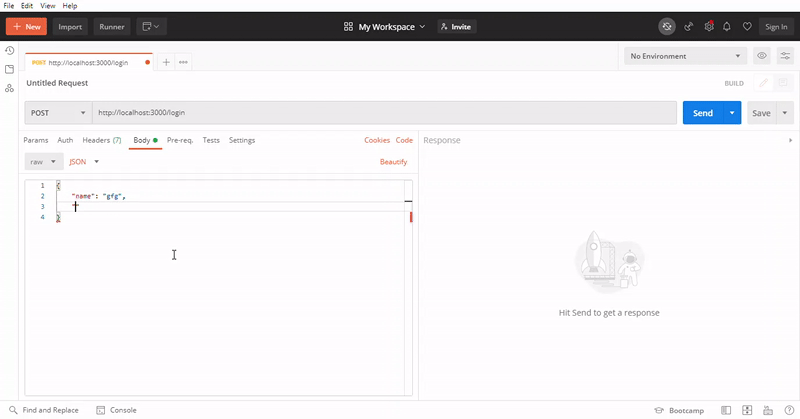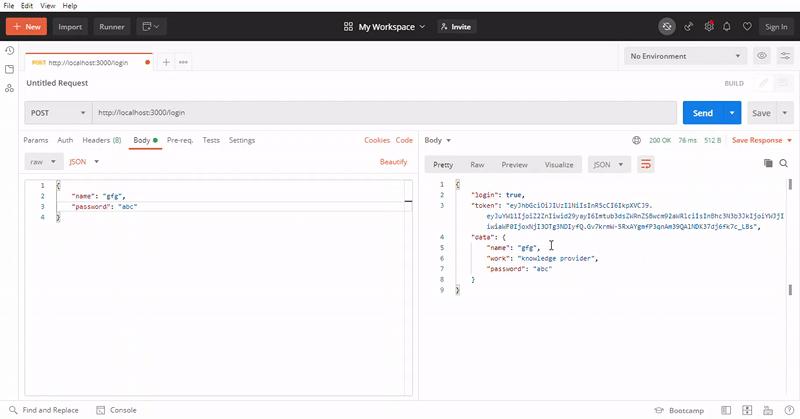
使用本地地址,在/login路径上进行POST请求并以JSON格式发送相应的数据,最后,您将获得一个JSON响应,其中包含登录状态和令牌或对象的数据。使用令牌对API端点进行身份验证,并再次使用本地地址,在 ‘/auth’ 路由上进行GET请求,并发送相应的令牌数据。
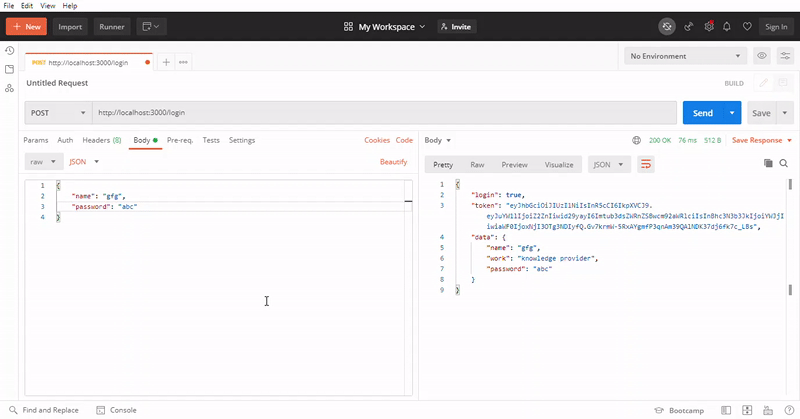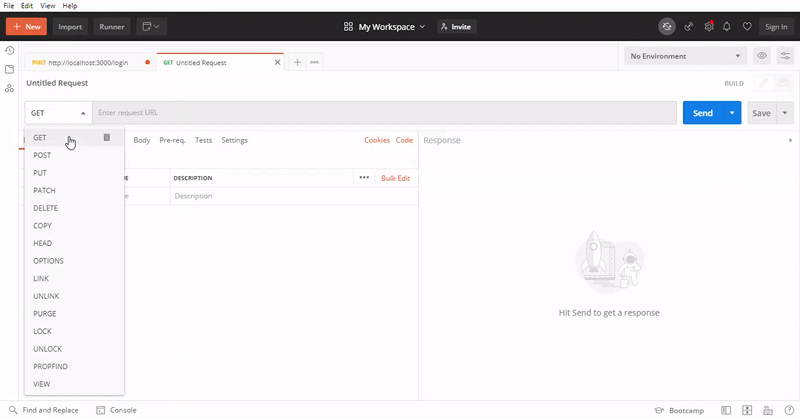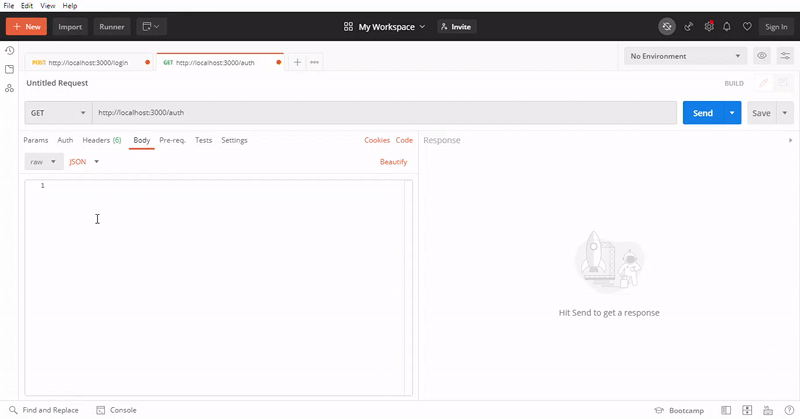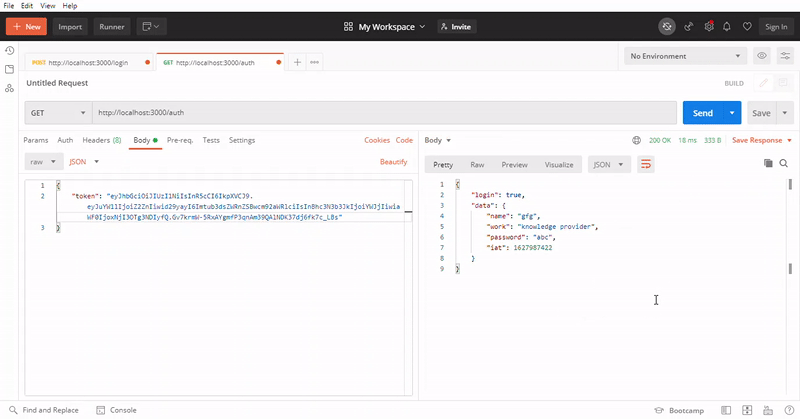
验证之后,您将获得在令牌中存储的正确数据对象。
 极客教程
极客教程