如何将MongoDB连接到ReactJS
在创建全栈应用程序和带有数据库的Web应用程序时,将MongoDB与React连接起来是一项重要任务。一种被广泛使用的NoSQL数据库MongoDB提供了一种可扩展和适应性强的存储和检索数据的方式。在使用ReactJS创建Web应用程序时,您可能需要与MongoDB数据库建立连接以获取和修改数据。
连接MongoDB与ReactJS的方法
为了与MongoDB进行交互,我们首先必须在服务器端建立与其的连接。然后,从ReactJS客户端,我们必须通过API来与MongoDB进行通信。让我们将过程分为两个主要步骤:建立服务器端连接和使用ReactJS客户端进行API调用。
先决条件
- React JS
- Node JS
- Mongo DB
连接MongoDB与React JS的步骤
创建React应用
按照以下步骤构建一个React应用:
步骤1: 使用以下命令创建一个React应用
npx create-react-app foldername
步骤2: 一旦完成,使用以下命令将目录更改为新创建的应用程序
cd foldername
运行该应用的步骤: 输入以下命令来运行应用程序。
npm start
使用NodeJS进行后端设置
设置NodeJs用于与前端集成的后端:
步骤1: 使用以下命令在根目录中创建一个文件夹
mkdir backend
步骤2: 一旦完成,使用以下命令将目录更改为新建的名为“backend”的文件夹
cd backend
步骤3: 运行以下命令创建配置文件
npm init -y
步骤4: 现在使用以下命令安装mongoose MongoDB。
npm i express mongoose mongodb cors
步骤5: 创建一个名为 index.js 的文件
touch index.js
运行应用程序的步骤: 输入以下命令来运行应用程序。
nodemon index.js
应用程序结构
前端服务器的依赖列表。
{
"name": "mongosetup",
"version": "0.1.0",
"private": true,
"dependencies": {
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.17.0",
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
"react": "^18.2.0",
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
}
}
后端服务器的依赖列表。
"dependencies": {
"cors": "^2.8.5",
"express": "^4.18.2",
"mongodb": "^6.1.0",
"mongoose": "^7.6.1"
}
示例: 在后端的backend/index.js文件中导入并配置mongo,并在react的App.js组件中创建一个表单,将mongo与前端链接起来
// Code for mongoose config in backend
// Filename - backend/index.js
// To connect with your mongoDB database
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/', {
dbName: 'yourDB-name',
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
}, err => err ? console.log(err) :
console.log('Connected to yourDB-name database'));
// Schema for users of app
const UserSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
email: {
type: String,
required: true,
unique: true,
},
date: {
type: Date,
default: Date.now,
},
});
const User = mongoose.model('users', UserSchema);
User.createIndexes();
// For backend and express
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const cors = require("cors");
console.log("App listen at port 5000");
app.use(express.json());
app.use(cors());
app.get("/", (req, resp) => {
resp.send("App is Working");
// You can check backend is working or not by
// entering http://loacalhost:5000
// If you see App is working means
// backend working properly
});
app.post("/register", async (req, resp) => {
try {
const user = new User(req.body);
let result = await user.save();
result = result.toObject();
if (result) {
delete result.password;
resp.send(req.body);
console.log(result);
} else {
console.log("User already register");
}
} catch (e) {
resp.send("Something Went Wrong");
}
});
app.listen(5000);
// Frontend code
// Filename - App.js
// Filename - App.js
import { useState } from 'react'
function App() {
const [name, setName] = useState("");
const [email, setEmail] = useState("");
const handleOnSubmit = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
let result = await fetch(
'http://localhost:5000/register', {
method: "post",
body: JSON.stringify({ name, email }),
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
})
result = await result.json();
console.warn(result);
if (result) {
alert("Data saved succesfully");
setEmail("");
setName("");
}
}
return (
<>
<h1>This is React WebApp </h1>
<form action="">
<input type="text" placeholder="name"
value={name} onChange={(e) => setName(e.target.value)} />
<input type="email" placeholder="email"
value={email} onChange={(e) => setEmail(e.target.value)} />
<button type="submit"
onClick={handleOnSubmit}>submit</button>
</form>
</>
);
}
export default App;
运行应用程序的步骤:
步骤1: 在项目目录中输入以下命令来运行应用程序。
npm start
步骤2: 在后端目录中使用以下命令来运行后端服务器
nodemon index.js
输出: 此输出将会在浏览器上的https://localhost:3000/可见,并且在Mongo数据库中。
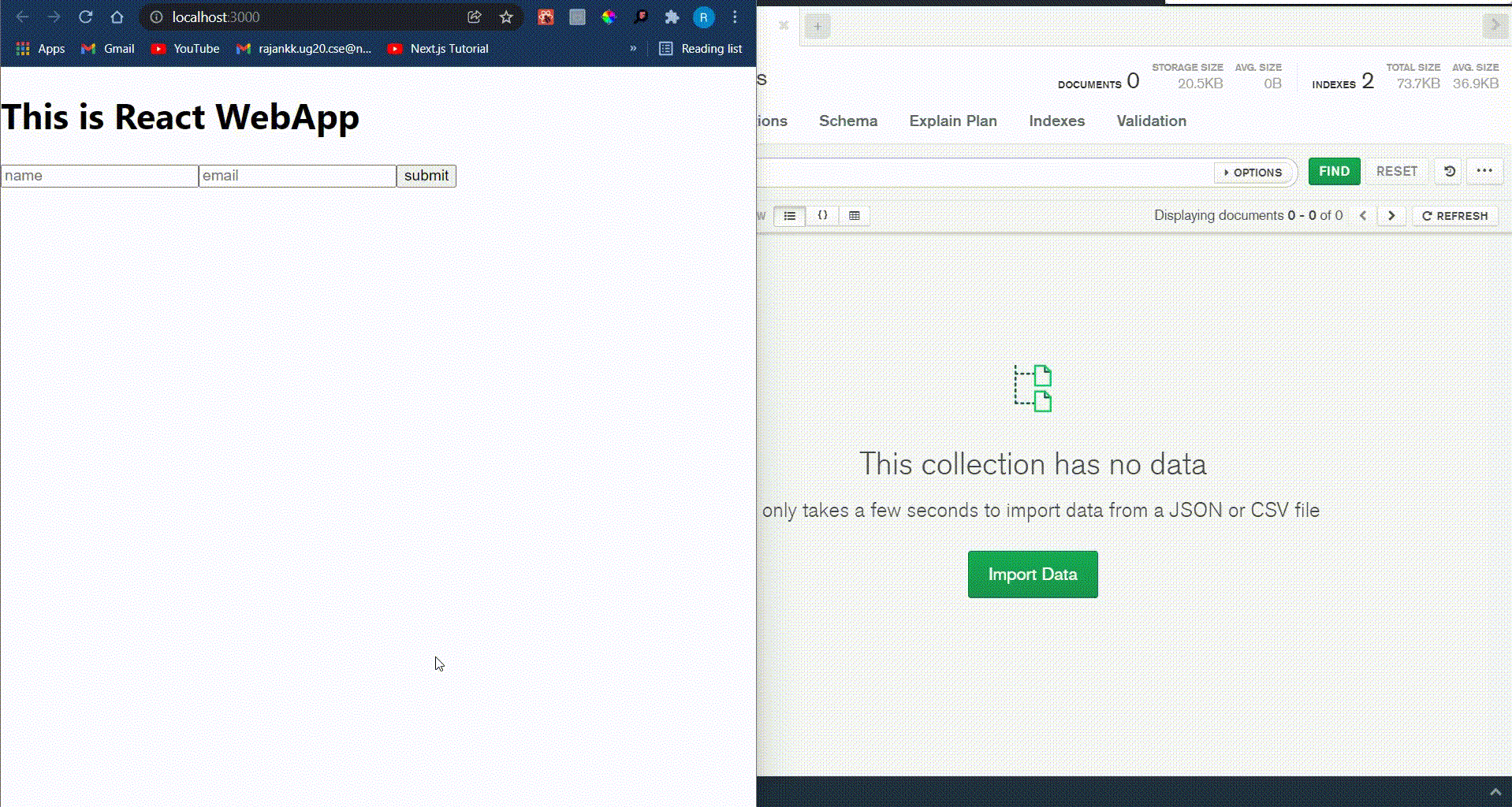
我们将React应用程序与MongoDB数据库连接起来。我们通过运行在3000端口上的React应用程序从用户那里获取两个输入,即姓名和电子邮件,然后我们调用由express和NodeJs创建的API,并将数据发送到MongoDB数据库中。
 极客教程
极客教程