如何在MERN应用程序中生成站点地图
在本文中,我们将讨论如何在MERN应用程序中生成站点地图。但在此之前,什么是站点地图以及我们为什么需要它?站点地图是一个列出网站上页面、视频和其他文件以及它们之间关系的文件。搜索引擎(例如Google、Duckduckgo、Bing等)使用该文件来帮助它们更高效地抓取您的站点。有关站点地图的更多信息,请点击此处。
生成静态站点地图: 如果您正在处理的网站有固定数量的URL,例如您的作品集,您可以使用任何在线工具生成sitemap.xml文件,并将该文件放置在src文件夹中。
步骤1: 访问https://www.xml-sitemaps.com/并生成sitemap.xml文件。
步骤2: 将文件移动到React应用程序的public文件夹中。
步骤3: 访问以下网址以验证更改: https://ahampriyanshu.com/sitemap.xml 。

步骤4: 最后,在你的 robots.txt 文件中,添加网站地图(sitemap)
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Sitemap: https://baseurl/sitemap.xml
生成动态网站地图: 到目前为止,我们已经讨论了如何创建一个包含静态URL的网站地图。但是如果URL的数量和现有URL的内容经常发生变化怎么办?假设我们正在创建一个GFG克隆版。因此,我们的网站地图应包含所有文章和重要页面的URL。
为此,我们将从后端发送一个网站地图文件,首先通过循环遍历我们数据库中的所有必需记录。之后,我们将手动添加其他重要页面的URL,例如关于、联系等。
步骤1: 为了演示目的,我们考虑了一个包含三个文件的基本项目。
app.js
const express = require("express"),
mongoose = require("mongoose"),
todoRouter = require("./routers/todoRouter"),
app = express();
app.use("/", todoRouter);
const port = 3000,
db = 'mongodb://localhost/todo';
mongoose
.connect(db)
.then(conn => {
console.log(`{db} connected`);
});
app.listen(port, () => console.log(
`Server listening on{port}`));
model.js
const mongoose = require("mongoose"),
todoSchema = new mongoose.Schema(
{
title: { type: String, unique: true },
},
{ timestamps: true }
);
module.exports = mongoose.model("Todo", todoSchema);
todoRouter.js
const express = require("express"),
router = express.Router();
/* Todo Controller functions */
module.exports = router;
步骤2: 安装“sitemap”包以流式传输站点地图缓冲区并写入其数据。
npm i sitemap
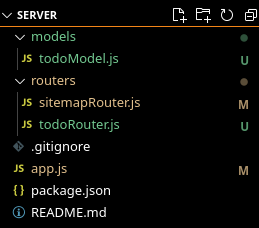
步骤3: 在你的路由文件夹中创建sitemapRouter.js文件。此时,你的文件夹结构可能如下所示。
步骤4: 导入所有所需的依赖项。
const express = require("express"),
{ SitemapStream, streamToPromise } = require('sitemap'),
Project = require("../models/projectModel"),
date = new Date().toISOString(),
zlib = require("zlib"),
router = express.Router();
步骤5: 为了缓存目的,声明一个对象并为给定的请求设置头部内容。
let sitemap;
router.get('/', async function (req, res) {
res.header('Content-Type', 'application/xml');
res.header('Content-Encoding', 'gzip');
// If we have a cached entry send it
if (sitemap) return res.send(sitemap)
});
module.exports = router;
步骤6: 现在我们将所有必要的URL写入我们的站点地图。
try {
// Fetching project records and mapping it
// the desired URL pattern
const data = await Project.find(),
projects = data.map(({ title }) => `/todo/${title}`),
// Base url of our site
smStream = new SitemapStream(
{ hostname: 'https://demosite.com/' }),
pipeline = smStream.pipe(zlib.createGzip());
// Write project URL to the stream
projects.forEach(
item => smStream.write({
url: item, lastmod: date, changefreq:
'daily', priority: 0.7
}));
// Manually add all the other important URLs
smStream.write({
url: '/about', lastmod: date, changefreq:
'monthly', priority: 0.9
})
smStream.write({
url: '/contact', lastmod: date, changefreq: 'monthly',
priority: 0.9
})
// Cache the response
streamToPromise(pipeline).then(sm => sitemap = sm);
smStream.end()
// Stream write the response
pipeline.pipe(res).on('error', e => { throw e });
} catch (err) {
console.error(err)
res.status(500).end()
}
步骤7: 最后, sitemapRouter.js 应该看起来像这样
const express = require("express"),
{ SitemapStream, streamToPromise } = require('sitemap'),
Todo = require("../models/todoModel"),
date = new Date().toISOString(),
zlib = require("zlib"),
router = express.Router();
let sitemap;
router.get('/', async function (req, res) {
res.header('Content-Type', 'application/xml');
res.header('Content-Encoding', 'gzip');
// If we have a cached entry send it
if (sitemap) return res.send(sitemap)
try {
// Fetching todo records and mapping
// it the desired URL pattern
const data = await Todo.find(),
todos = data.map(({ title }) => `/todo/${title}`),
// Base url of our site
smStream = new SitemapStream({
hostname: 'https://demosite.com/' }),
pipeline = smStream.pipe(zlib.createGzip());
// Write todo URL to the stream
todos.forEach(
item => smStream.write({
url: item, lastmod: date,
changefreq: 'daily', priority: 0.7
}));
// Manually add all the other important URLs
smStream.write({
url: '/about', lastmod: date,
changefreq: 'monthly', priority: 0.9
})
smStream.write({
url: '/contact', lastmod: date,
changefreq: 'monthly', priority: 0.9
})
// Cache the response
streamToPromise(pipeline).then(sm => sitemap = sm);
smStream.end()
// Stream write the response
pipeline.pipe(res).on('error', e => { throw e });
} catch (err) {
console.error(err)
res.status(500).end()
}
});
module.exports = router;
步骤8: 通过访问 {basename}/sitemap.xml 确认更改。
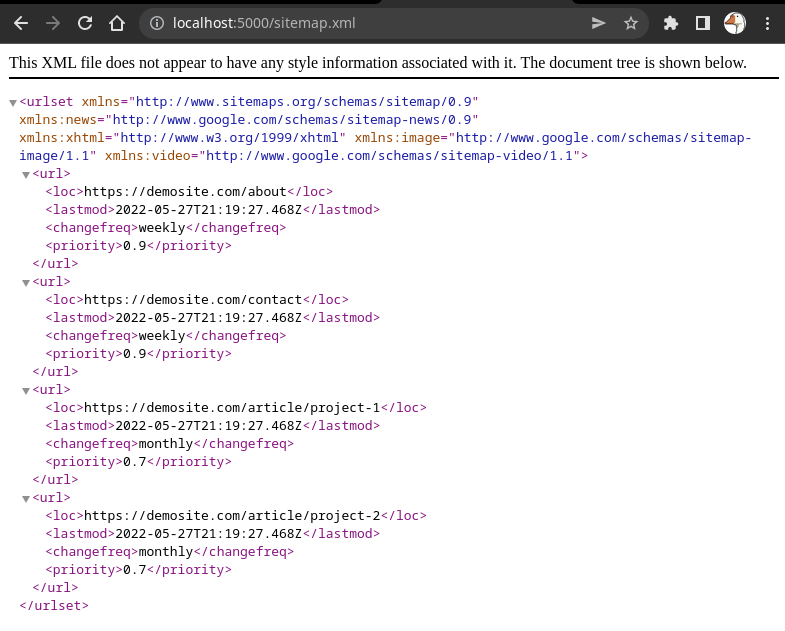
注意: 如果在按照上述步骤操作过程中遇到任何困难或错误,请查看 sitemapRouter.js 文件。
步骤9: 最后,将网站地图添加到您的 robots.txt 文件中。
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Sitemap: https://baseurl/sitemap.xml
 极客教程
极客教程