在 Java ResourceBundle教程中,我们展示了如何在 Java 中使用ResourceBundle。
硬编码特定于语言环境的数据不是要走的路。 诸如消息或标签之类的值应放在单独的文件中。 这样,我们可以处理多个语言环境,而不必为每个语言环境编写不同的代码。 对于翻译人员来说,这也很方便,因为它们仅处理可翻译的文本,而不查看编程代码。
Java ResourceBundle
资源包是 Java 属性文件,其中包含特定于语言环境的数据。 通过使代码与语言环境无关,这是使 Java 应用国际化的一种方式。
资源包捆绑到具有相同基本名称的族中。 例如,如果我们有一个words基本名称,则words_sk与斯洛伐克语的语言环境匹配。 如果不支持特定的语言环境,则使用默认资源束。
资源包还支持方言。 例如words_es_AR用于阿根廷使用的西班牙语,而玻利维亚使用words_es_BO。
ResourceBundle是一个抽象类,具有两个子类:PropertyResourceBundle和ListResourceBundle。 PropertyResourceBundle从属性文件加载数据。 属性文件是包含可翻译文本的纯文本文件。 属性文件不是 Java 源代码的一部分,它们只能包含 String 值。 ListResourceBundle通过方便的列表管理资源; 它从类文件中获取数据。 我们可以将任何特定于语言环境的对象存储在ListResourceBundle中。
为了获得适当的ResourceBundle,我们调用ResourceBundle.getBundle()方法。 这是一种寻找ListResourceBundle的工厂方法,如果找不到,将寻找PropertyResourceBundle。 如果找不到资源束,则抛出MissingResourceException。
Java PropertyResourceBundle示例
在第一个应用中,我们创建一个简单的 Java 应用,该应用使用三个资源包:默认的英语,德语和斯洛伐克语。
Figure: NetBeans project structure
我们创建三个属性文件,并将它们放置在resources目录中。
words.properties
w1 = Earth
w2 = ocean
这是默认属性文件。 它通常是英语。 文件中有两个词。
words_de.properties
w1 = Erde
w2 = ozean
words_de.properties文件包含德语单词。
words_sk.properties
w1 = Zem
w2 = oceán
words_de.properties文件包含斯洛伐克语单词。
ResourceBundleEx.java
package com.zetcode;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class ResourceBundleEx {
static public void main(String[] args) {
Locale[] locales = {
Locale.GERMAN,
new Locale("sk", "SK"),
Locale.ENGLISH
};
System.out.println("w1:");
for (Locale locale : locales) {
getWord(locale, "w1");
}
System.out.println("w2:");
for (Locale locale : locales) {
getWord(locale, "w2");
}
}
static void getWord(Locale curLoc, String key) {
ResourceBundle words
= ResourceBundle.getBundle("resources/words", curLoc);
String value = words.getString(key);
System.out.printf("Locale: %s, Value: %s %n", curLoc.toString(), value);
}
}
在代码示例中,我们打印了三个资源包中使用的所有单词。
Locale[] locales = {
Locale.GERMAN,
new Locale("sk", "SK"),
Locale.ENGLISH
};
在示例中,我们有三种语言环境:德语,斯洛伐克语和英语。
for (Locale locale : locales) {
getWord(locale, "w1");
}
我们遍历语言环境并打印带有w1键标记的单词。
ResourceBundle words
= ResourceBundle.getBundle("resources/words", curLoc);
使用ResourceBundle.getBundle()方法,可以获得当前使用的语言环境的捆绑软件。 由于我们尚未创建ListResourceBundle,因此该方法使用PropertyResourceBundle,从而从属性文件加载数据。
String value = words.getString(key);
System.out.printf("Locale: %s, Value: %s %n", curLoc.toString(), value);
我们获取值并打印语言环境名称,键和值。
w1:
Locale: de, Value: Erde
Locale: sk_SK, Value: Zem
Locale: en, Value: Earth
w2:
Locale: de, Value: ozean
Locale: sk_SK, Value: oceán
Locale: en, Value: ocean
这是示例的输出。
Java ListResourceBundle示例
在以下应用中,我们使用ListResourceBundle。
Figure: NetBeans project structure II
我们为斯洛伐克语和捷克语创建语言环境资源。
MyResources_sk.java
package com.zetcode.myres;
import java.util.ListResourceBundle;
public class MyResources_sk extends ListResourceBundle {
@Override
protected Object[][] getContents() {
return resources;
}
private final Object[][] resources = {
{ "Capital", "Bratislava" },
{ "Area", 49035 },
{ "Currency", "EUR" },
};
}
在这里,我们为斯洛伐克语实现了ListResourceBundle的实现。 我们必须重写getContents()方法。 该方法返回键/值对的数组。
MyResources_cs_CZ.java
package com.zetcode.myres;
import java.util.ListResourceBundle;
public class MyResources_cs_CZ extends ListResourceBundle {
@Override
protected Object[][] getContents() {
return resources;
}
private final Object[][] resources = {
{ "Capital", "Praha" },
{ "Area", 78866 },
{ "Currency", "CZK" },
};
}
这是捷克语的实现。
ResourceBundleEx2.java
package com.zetcode;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class ResourceBundleEx2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Locale sk_loc = new Locale("sk", "SK");
ResourceBundle bundle =
ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.zetcode.myres.MyResources", sk_loc);
System.out.println("Capital: " + bundle.getObject("Capital"));
System.out.println("Area: " + bundle.getObject("Area"));
System.out.println("Currency: " + bundle.getObject("Currency"));
System.out.println();
Locale cz_loc = new Locale("cs", "CZ");
ResourceBundle bundle2 =
ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.zetcode.myres.MyResources", cz_loc);
System.out.println("Capital: " + bundle2.getObject("Capital"));
System.out.println("Area: " + bundle2.getObject("Area"));
System.out.println("Currency: " + bundle2.getObject("Currency"));
}
}
该示例打印了斯洛伐克和捷克共和国的一些地理数据。
Locale sk_loc = new Locale("sk", "SK");
ResourceBundle bundle =
ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.zetcode.myres.MyResources", sk_loc);
使用ResourceBundle.getBundle()方法,我们从com.zetcode.myres.MyResources_sk.class创建资源束。
Capital: Bratislava
Area: 49035
Currency: EUR
Capital: Praha
Area: 78866
Currency: CZK
This is the output of the example.
Swing 应用
在第三个示例中,我们使用 Java Swing 创建了一个简单的 GUI 应用。 该示例可以动态更改 UI 的语言。 该示例使用ListResourceBundle类。
源代码和图像可在作者的 Github 存储库中获得。
MyResources_sk.java
package com.zetcode.myres;
import java.util.ListResourceBundle;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
public class MyResources_sk extends ListResourceBundle {
@Override
protected Object[][] getContents() {
return resources;
}
private final Object[][] resources = {
{"name", "Slovensko"},
{"lang_menu", "Jazyk"},
{"lang_sk", "Slovenčina"},
{"lang_hu", "Maďarčina"},
{"flag", new ImageIcon("src/resources/slovakia.png")},
{"description", "Slovensko je vnútrozemský štát v strednej Európe."}
};
}
这些是斯洛伐克语的资源。 我们有五个字符串和一个ImageIcon。
MyResources_hu.java
package com.zetcode.myres;
import java.util.ListResourceBundle;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
public class MyResources_hu extends ListResourceBundle {
@Override
protected Object[][] getContents() {
return resources;
}
private final Object[][] resources = {
{"name", "Magyarország"},
{"lang_menu", "Nyelv"},
{"lang_sk", "Szlovák"},
{"lang_hu", "Magyar"},
{"flag", new ImageIcon("src/resources/hungary.png")},
{"description", "Magyarország közép-európai ország "
+ "a Kárpát-medencében."}
};
}
这些是匈牙利语的资源。
ResourceBundleEx3.java
package com.zetcode;
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import javax.swing.ButtonGroup;
import javax.swing.GroupLayout;
import javax.swing.Icon;
import javax.swing.JComponent;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JMenu;
import javax.swing.JMenuBar;
import javax.swing.JRadioButtonMenuItem;
import javax.swing.LayoutStyle;
/*
* Java ResourceBundle tutorial
*
* This program uses a ResourceBundle in a
* Java Swing application.
*
* Author: Jan Bodnar
* Website: zetcode.com
* Last modified: August 2016
*/
public class ResourceBundleEx3 extends JFrame {
private ResourceBundle bundle;
private JLabel flag;
private JLabel lbl;
private JMenu langMenu;
private JRadioButtonMenuItem skMenuItem;
private JRadioButtonMenuItem huMenuItem;
public ResourceBundleEx3() {
initUI();
}
private void initUI() {
createMenuBar();
flag = new JLabel();
lbl = new JLabel();
updateLanguage(new Locale("sk", "SK"));
createLayout(lbl, flag);
pack();
setTitle(bundle.getString("name"));
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
private void updateLanguage(Locale locale) {
bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.zetcode.myres.MyResources", locale);
langMenu.setText(bundle.getString("lang_menu"));
skMenuItem.setText(bundle.getString("lang_sk"));
huMenuItem.setText(bundle.getString("lang_hu"));
flag.setIcon((Icon) bundle.getObject("flag"));
lbl.setText(bundle.getString("description"));
setTitle(bundle.getString("name"));
pack();
}
private void createMenuBar() {
JMenuBar menubar = new JMenuBar();
langMenu = new JMenu();
langMenu.setMnemonic(KeyEvent.VK_F);
ButtonGroup btnGroup = new ButtonGroup();
skMenuItem = new JRadioButtonMenuItem("Slovak", true);
btnGroup.add(skMenuItem);
skMenuItem.addActionListener((ActionEvent e) -> {
updateLanguage(new Locale("sk", "SK"));
});
langMenu.add(skMenuItem);
huMenuItem = new JRadioButtonMenuItem("Hungarian");
btnGroup.add(huMenuItem);
huMenuItem.addActionListener((ActionEvent e) -> {
updateLanguage(new Locale("hu", "HU"));
});
langMenu.add(huMenuItem);
menubar.add(langMenu);
setJMenuBar(menubar);
}
private void createLayout(JComponent... arg) {
Container pane = getContentPane();
GroupLayout gl = new GroupLayout(pane);
pane.setLayout(gl);
gl.setAutoCreateContainerGaps(true);
gl.setHorizontalGroup(gl.createParallelGroup()
.addComponent(arg[0])
.addComponent(arg[1])
);
gl.setVerticalGroup(gl.createSequentialGroup()
.addComponent(arg[0])
.addPreferredGap(LayoutStyle.ComponentPlacement.RELATED)
.addComponent(arg[1])
);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
ResourceBundleEx3 ex = new ResourceBundleEx3();
ex.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
我们有一个菜单栏,其中的菜单包含两个单选按钮菜单项。 选择单选按钮菜单项会更改应用用户界面的语言。
private void updateLanguage(Locale locale) {
bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.zetcode.myres.MyResources", locale);
langMenu.setText(bundle.getString("lang_menu"));
skMenuItem.setText(bundle.getString("lang_sk"));
huMenuItem.setText(bundle.getString("lang_hu"));
flag.setIcon((Icon) bundle.getObject("flag"));
lbl.setText(bundle.getString("description"));
setTitle(bundle.getString("name"));
pack();
}
当我们选择单选按钮菜单项时,将调用updateLanguage()方法。 它根据给定的语言环境创建一个新的ResourceBundle,并更新菜单,单选菜单项,图像图标,说明和框架标题。
skMenuItem.addActionListener((ActionEvent e) -> {
updateLanguage(new Locale("sk", "SK"));
});
选择斯洛伐克单选按钮菜单项,我们调用updateLanguage()方法并传递斯洛伐克语言环境作为参数。
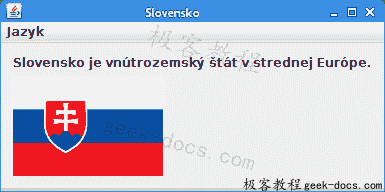
Figure: Swing application
Spring Boot 应用
在下一个示例中,我们在 Spring Boot 应用中使用资源包。 Spring 是流行的 Java 应用框架。 Spring Boot 是一种新的解决方案,可以轻松创建基于生产级别的独立 Spring 应用。
Figure: NetBeans project structure of a Spring Boot application
同样,我们创建三个属性文件,并将它们放置在src/main/resources/messages目录中。
words.properties
w1 = Earth
w2 = ocean
这是默认属性文件。
words_de.properties
w1 = Erde
w2 = ozean
The words_de.properties file contains words in German language.
words_sk.properties
w1 = Zem
w2 = oceán
The words_de.properties file contains words in Slovak language.
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.zetcode</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootMessagesEx</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.4.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath />
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<name>SpringBootMessagesEx</name>
</project>
pom.xml文件包含 Spring Boot 框架的依赖项。
Application.java
package com.zetcode;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
@Bean
public ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource() {
ResourceBundleMessageSource source = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
source.setBasenames("messages/words");
source.setUseCodeAsDefaultMessage(true);
return source;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
Application是主要的应用类。 我们设置了 Spring Boot 程序。
@Bean
public ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource() {
ResourceBundleMessageSource source = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
source.setBasenames("messages/words");
source.setUseCodeAsDefaultMessage(true);
return source;
}
使用@Bean注解,我们生成了一个ResourceBundleMessageSource bean,该 bean 由 Spring 容器管理。 ResourceBundleMessageSource是一种MessageSource实现,它使用指定的基本名称访问资源束。 此类依赖于基础 JDK 的ResourceBundle实现。
MyRunner.java
package com.zetcode;
import java.util.Locale;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private MessageSource messageSource;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(messageSource.getMessage("w1",
null, Locale.GERMAN));
System.out.println(messageSource.getMessage("w1",
null, Locale.ENGLISH));
System.out.println(messageSource.getMessage("w2",
null, new Locale("sk", "SK")));
}
}
MyRunner是 Spring Boot 应用的命令行运行程序。
@Autowired
private MessageSource messageSource;
我们将MessageSource注入到该字段中。
System.out.println(messageSource.getMessage("w1",
null, Locale.GERMAN));
我们使用getMessage()方法在德语语言环境中得到单词 w1。
...
Erde
Earth
oceán
...
这是应用的输出。
在本教程中,我们介绍了 Java ResourceBundle。 我们创建了两个 Java 控制台应用,一个 Swing 应用和一个 Spring Boot 应用。
 极客教程
极客教程