Java 字符流与字节流
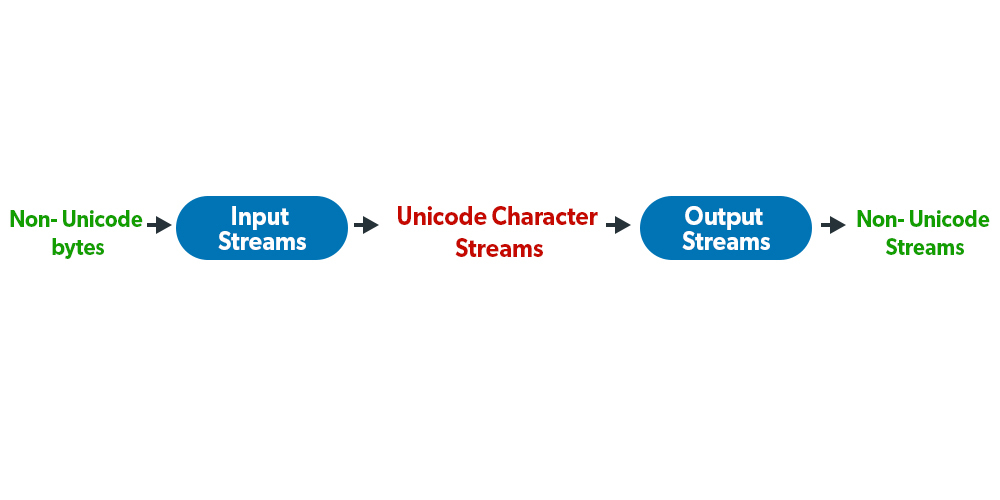
一个 流是 一个数据序列。 I/O流 ,指的是一个流,它不可能是一个按顺序访问文件的方法。I/O流指的是一个输入源或输出目的地,代表不同类型的来源,例如:磁盘文件。java.io包提供的类允许你在Unicode字符流和非Unicode文本的字节流之间转换。
- 输入流: 从源头读取数据。
- 输出流: 将数据写到目的地。
什么时候使用字符流而不是字节流 ?
在Java中,字符是使用Unicode惯例存储的。当我们想处理文本文件时,字符流很有用。这些文本文件可以被逐个处理。字符大小通常为16位。
什么时候使用字节流而不是字符流?
面向字节的读取是逐个字节进行的。 字节流适用于处理原始数据,如二进制文件。
在使用和处理上述任何一种流时,关键点如下 。
- 字符流的名称通常以Reader/Writer结尾,字节流的名称以InputStream/OutputStream结尾。
- 示例代码中使用的流是未缓冲的流,效率较低。为了提高效率,我们通常将它们与缓冲的读/写器一起使用。我们很快就会讨论使用BufferedReader/BufferedWriter(用于字符流)和BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream(用于字节流)类。
- 如果不再使用流,我们总是建议关闭它。这可以确保如果发生任何错误,流不会受到影响。
- 上述代码可能无法在在线编译器中运行,因为文件可能不存在。
字符流
在Java中,字符是使用Unicode惯例存储的。字符流自动允许我们按字符读/写数据。例如,FileReader和FileWriter是字符流,用于从源头读取和写入目的地。
例子
// Java Program illustrate Reading
// a File in Human Readable
// Format Using FileReader Class
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// Initially assigning null as we have not read
// anything
FileReader sourceStream = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Reading from file
sourceStream = new FileReader(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.rtf");
// Reading sourcefile and writing content to
// target file character by character.
int temp;
// If there is content inside file
// than read
while ((temp = sourceStream.read()) != -1)
System.out.println((char)temp);
// Display message for successful execution of program
System.out.print("Program successfully executed");
}
// finally block that executes for sure
// where we are closing file connections
// to avoid memory leakage
finally {
// Closing stream as no longer in use
if (sourceStream != null)
sourceStream.close();
}
}
}
输出: 将内容逐字写入目标文件中
Program successfully executed
字节流
字节流逐个处理数据(8位)。例如,FileInputStream用于从源头读取数据,FileOutputStream用于向目的地写入数据。
例子
// Java Program Illustrate ByteStream Class to
// Copy Contents of One File to Another File
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// Initially assigning null ot objects for
// reading and writing to file
FileInputStream sourceStream = null;
FileOutputStream targetStream = null;
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Passing the files via local directory
sourceStream = new FileInputStream(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.rtf");
targetStream = new FileOutputStream(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/democopy.rtf");
// Reading source file and writing content to
// target file byte by byte
int temp;
// If there is content inside file
// than read
while ((temp = sourceStream.read()) != -1)
targetStream.write((byte)temp);
// Display message for successful execution of program
System.out.print("Program successfully executed");
}
// finally block that executes for sure
// where we are closing file connections
// to avoid memory leakage
finally {
if (sourceStream != null)
sourceStream.close();
if (targetStream != null)
targetStream.close();
}
}
}
输出
Program successfully executed
 极客教程
极客教程