Golang程序 计算立方体面积
在本教程中,我们将讨论在Golang编程中使用立方体的边来寻找立方体的表面积的方法。
但在编写代码之前,让我们先简单讨论一下立方体和它的面积。
立方体
一个立方体是一个有六个正方形面的三维图形。立方体的所有六个面都是正方形的形状。它的长、宽、高都相等。骰子是立方体的一个常见例子。
正方体的面积
正方体的六个面所包围的总面积被称为正方体的表面积。计算立方体的面积在我们想给立方体的表面上色或在它周围包上薄片的情况下是有好处的。
计算公式
正方体所有边的面积之和被定义为正方体的表面积。因此,这个公式可以写成边的平方的6倍。
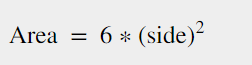
例子
- 边=5
立方体的面积 = 6 * (5)2 = 150
由于面积是通过边的平方乘以6来计算的,因此我们把6和(5)2 相乘,即6*25,得出150为立方体的面积。
- 边=10.5
立方体的面积=6 * (10.50)2 = 661.50
6和(10.50)2 相乘,即6*110.25,结果是661.50为立方体的面积。
在主函数中寻找立方体的面积
算法
第1步 --声明一个变量用于存储立方体的边–“边”。
第2步 --声明一个用于存储立方体面积的变量–“面积”,并将其初始化为0。
第3步–通过边的平方乘以6来计算面积,并将其存储在函数的’面积’变量中。
第4步 - 打印计算出的面积,即存储在变量’area’中的值。
例子
package main
// fmt package allows us to print formatted strings
// math package allows us to perform various mathematical
// operations
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
func main() {
fmt.Println("Program to find the area of a cube \n")
// declaring variable ‘side’ for storing the length of the cube
var side float64 = 5
// declaring variable ‘area’ for storing the area of the cube
var area float64 = 0
// calculating the area of the cube
area = 6 * math.Pow(side, 2)
// printing the results
fmt.Println("Dimension of the side : ", side)
fmt.Println("Therefore, Area of cube : ", area)
}
输出
Program to find the area of a cube
Dimension of the side : 5
Therefore, Area of cube : 150
代码的描述
- var side float64 = 5, var area float64 = 0 – 在这一行,我们声明了变量side和 area。由于side和 area的数据类型是float,这就是我们使用float64数据类型的原因。
-
area = 6 * math.Pow(side, 2)-我们使用公式求出立方体的面积-area = 6 * (side)2. math.Pow是一个数学函数,用于计算一个数字的幂。 -
fmt.Println(“Dimension of the side : “, side) – 打印立方体的边。
-
fmt.Println(“因此,立方体的面积 : “, area) – 打印计算出的立方体的面积。
因此,面积=6*(5)2
面积 = 6 * 25
面积=150
用不同的函数求出立方体的面积
算法
第1步 --声明一个变量来存储立方体的边–“边”。
第2步 --声明一个用于存储立方体面积的变量–“面积”,初始化为0。
第3步–通过边的平方乘以6来计算面积,并在函数calculateAreaOfCube()中把它存储在’面积’变量中。
第4步 - 通过在main()函数中调用calculateAreaOfCube()函数来打印计算出的面积,即存储在变量’area’中的值。
例子
package main
// fmt package allows us to print formatted strings
// math package allows us to perform various mathematical
// operations
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
func calculateAreaOfCube(side float64) float64 {
// declaring variable ‘area’ for storing the area of cube
var area float64 = 0
// calculating the area of the cube
area = 6 * math.Pow(side, 2)
return area
}
func main() {
// declaring variable ‘side’ for storing length of cube
var side float64 = 15
var area float64
fmt.Println("Program to find the area of a cube \n")
// calling function calculateAreaOfCube() for calculating
// the area of the cube
area = calculateAreaOfCube(side)
// printing the results
fmt.Println("Dimension of the side : ", side)
fmt.Println("Therefore, Area of cube : ", area)
}
输出
Program to find the area of a cube
Dimension of the side : 15
Therefore, Area of cube : 1350
代码的描述
- var side float64 = 5, var area float64 = 0 – 在这一行中,我们声明了变量side和 area。由于side和area的数据类型是float,我们使用了float64数据类型。
-
calculateAreaOfCube(side float64) float64 – 这是我们计算立方体面积的函数。该函数的参数是数据类型为float64的变量’side’,其返回类型也是float64。
-
area = 6 * math.Pow(side, 2)– 我们正在用这个公式计算立方体的面积–area = 6 * (side)2. math.pow是一个数学函数,用来计算一个数字的幂。 -
return area – 用于返回立方体的面积
-
area = calculateAreaOfCube(side) – 我们正在调用函数calculateAreaOfCube()并将计算值存储在’area’变量中。
-
fmt.Println(“Dimension of the side : “, side) – 打印立方体的侧面
-
fmt.Println(“Therefore, Area of cube : “, area) – 打印立方体的计算面积
总结
这就是关于用两种方法计算立方体的面积的全部内容。第二种方法在模块化和代码复用性方面要好得多。
 极客教程
极客教程