Golang 条件语句
编程中的决策与现实生活中的决策类似。在决策中,当给定的条件得到满足时,就执行一段代码。有时这些也被称为控制流语句。Golang使用控制语句来控制基于某些条件的程序的执行流程。这些语句用于根据程序状态的变化使执行流前进和分支。
Go编程的决策语句有:
如果语句
这是最简单的决策语句。它用于决定是否执行某个语句或语句块,即如果某个条件为 真,则执行某个语句块,否则不执行。
语法:
if condition {
// Statements to execute if
// condition is true
}
流程图:
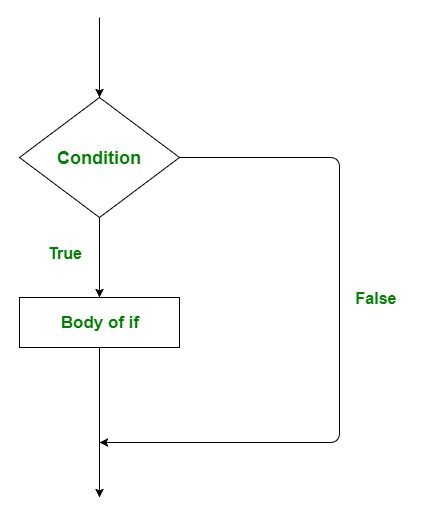
示例:
// Go program to illustrate the
// use of if statement
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// taking a local variable
var v int = 700
// using if statement for
// checking the condition
if v < 1000 {
// print the following if
// condition evaluates to true
fmt.Printf("v is less than 1000\n")
}
fmt.Printf("Value of v is : %d\n", v)
}
输出:
v is less than 1000
value of v is : 700
if…else 语句
仅仅是if语句就告诉我们,如果一个条件为真,它将执行一个语句块,如果条件为假,它将不执行。但是,如果我们想在条件为假的情况下做其他事情,该怎么办呢?这时就会出现else语句。我们可以将else语句与if语句一起使用,在条件为假时执行一个代码块。
语法:
if condition {
// Executes this block if
// condition is true
} else {
// Executes this block if
// condition is false
}
流程图:
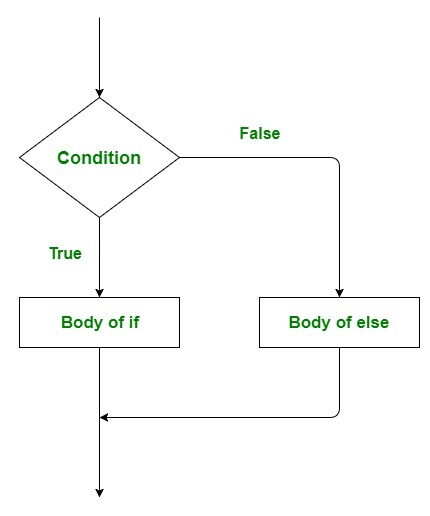
示例:
// Go program to illustrate the
// use of if...else statement
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// taking a local variable
var v int = 1200
// using if statement for
// checking the condition
if v < 1000 {
// print the following if
// condition evaluates to true
fmt.Printf("v is less than 1000\n")
} else {
// print the following if
// condition evaluates to true
fmt.Printf("v is greater than 1000\n")
}
}
输出:
v is greater than 1000
嵌套的if语句
在Go语言中,嵌套的if是一个if语句,它是另一个if或else的目标。嵌套的if语句是指在一个if语句中包含一个if语句。是的,Golang允许我们在if语句中嵌套if语句。也就是说,我们可以把一个if语句放在另一个if语句中。
语法:
if condition1 {
// Executes when condition1 is true
if condition2 {
// Executes when condition2 is true
}
}
流程图:
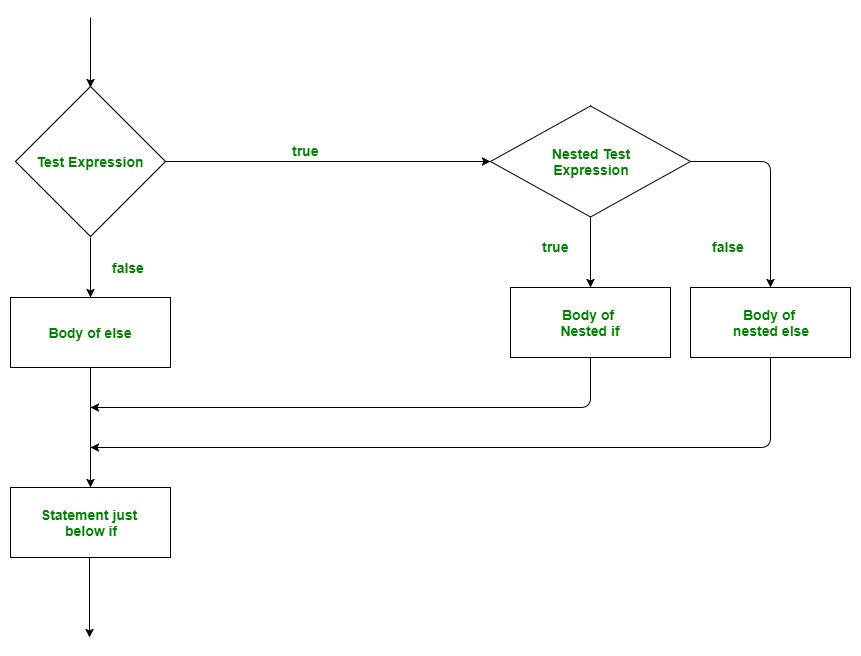
示例:
// Go program to illustrate the
// use of nested if statement
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// taking two local variable
var v1 int = 400
var v2 int = 700
// using if statement
if( v1 == 400 ) {
// if condition is true then
// check the following
if( v2 == 700 ) {
// if condition is true
// then display the following
fmt.Printf("Value of v1 is 400 and v2 is 700\n" );
}
}
}
输出:
Value of v1 is 400 and v2 is 700
if…else…if 梯子
在这里,用户可以在多个选项中做出决定。if语句是自上而下执行的。只要控制if的一个条件为真,与该if相关的语句就会被执行,而梯子的其他部分就会被绕过。如果没有一个条件为真,那么最后的else语句将被执行。
要点:
- if语句可以有零个或一个else,它必须在任何else if语句之后。
- if语句可以有零到多个else if,它必须在else之前。
- 如果一个else if成功了,其余的else if或else都不会被测试。
语法:
if condition_1 {
// this block will execute
// when condition_1 is true
} else if condition_2 {
// this block will execute
// when condition2 is true
}
.
.
. else {
// this block will execute when none
// of the condition is true
}
流程图:
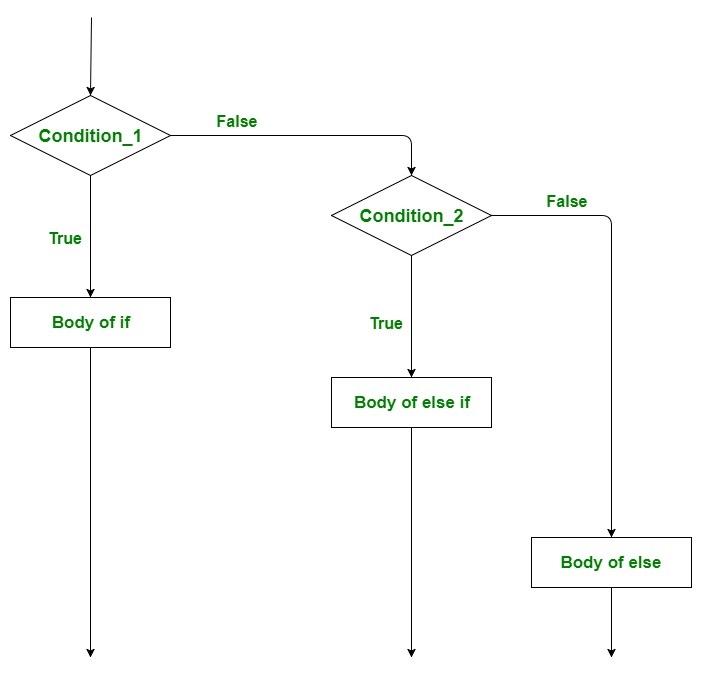
示例:
// Go program to illustrate the
// use of if..else..if ladder
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// taking a local variable
var v1 int = 700
// checking the condition
if v1 == 100 {
// if condition is true then
// display the following */
fmt.Printf("Value of v1 is 100\n")
} else if v1 == 200 {
fmt.Printf("Value of a is 20\n")
} else if v1 == 300 {
fmt.Printf("Value of a is 300\n")
} else {
// if none of the conditions is true
fmt.Printf("None of the values is matching\n")
}
}
输出:
None of the values is matching
 极客教程
极客教程