Golang 数组
Golang或Go编程语言中的数组与其他编程语言很相似。在程序中,有时我们需要存储相同类型的数据集合,如学生的分数列表。这种类型的集合在程序中使用数组来存储。数组是一个固定长度的序列,用来存储内存中的同质元素。由于其固定长度,数组不像Go语言中的Slice那样流行。在一个数组中,你可以在其中存储零个或多个元素。数组中的元素是通过使用[]索引操作符以其零为基础的位置进行索引的,这意味着第一个元素的索引是array[0] ,最后一个元素的索引是array[len(array)-1] 。
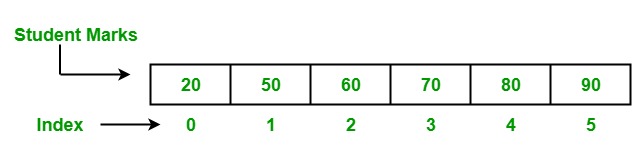
创建和访问数组
在Go语言中,数组的创建有两种不同的方式。
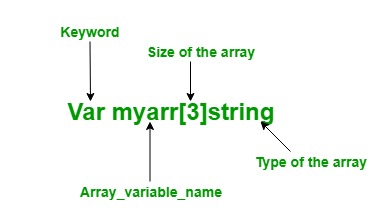
使用var关键字: 在Go语言中,使用var关键字创建一个具有名称、大小和元素的特定类型的数组。
语法
Var array_name[length]Type
重要的一点
在Go语言中,数组是可变的,因此你可以在赋值的左侧使用array[index]语法来设置给定索引处的数组元素。
Var array_name[index] = element
- 你可以通过使用索引值或使用for循环来访问数组的元素。
- 在Go语言中,数组类型是一维的。
- 数组的长度是固定的,不可改变的。
- 你可以在数组中存储重复的元素。
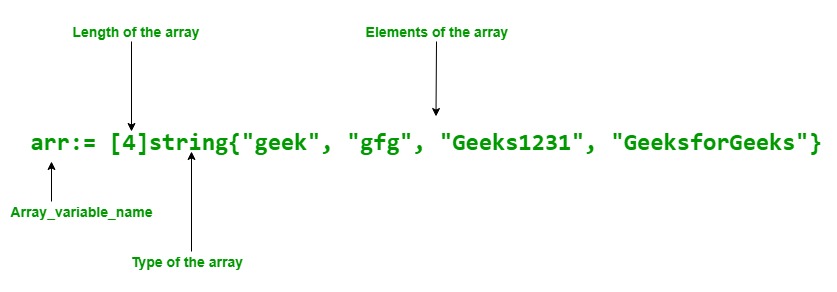
方法1: 使用shorthand声明。
在Go语言中,数组也可以使用shorthand声明。它比上面的声明更灵活。
语法
array_name:= [length]Type{item1, item2, item3,...itemN}
例子
// Go program to illustrate how to create
// an array using shorthand declaration
// and accessing the elements of the
// array using for loop
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// Shorthand declaration of array
arr:= [4]string{"geek", "gfg", "Geeks1231", "GeeksforGeeks"}
// Accessing the elements of
// the array Using for loop
fmt.Println("Elements of the array:")
for i:= 0; i < 3; i++{
fmt.Println(arr[i])
}
}
输出
Elements of the array:
geek
gfg
Geeks1231
多维数组
我们已经知道,数组是一维的,但是你可以创建一个多维数组。多维数组是同一类型的数组的数组。 在Go语言中,你可以使用以下语法创建一个多维数组。
Array_name[Length1][Length2]..[LengthN]Type
你可以使用Var关键字或使用shorthand声明来创建一个多维数组,如下面的例子所示。
注意: 在一个多维数组中,如果用户没有初始化某个单元的值,那么编译器会自动将其初始化为零。在Golang中没有未初始化的概念。
例子
// Go program to illustrate the
// concept of multi-dimension array
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// Creating and initializing
// 2-dimensional array
// Using shorthand declaration
// Here the (,) Comma is necessary
arr := [3][3]string{{"C #", "C", "Python"}, {"Java", "Scala", "Perl"},
{"C++", "Go", "HTML"}}
// Accessing the values of the
// array Using for loop
fmt.Println("Elements of Array 1")
for x := 0; x < 3; x++ {
for y := 0; y < 3; y++ {
fmt.Println(arr[x][y])
}
}
// Creating a 2-dimensional
// array using var keyword
// and initializing a multi
// -dimensional array using index
var arr1 [2][2]int
arr1[0][0] = 100
arr1[0][1] = 200
arr1[1][0] = 300
arr1[1][1] = 400
// Accessing the values of the array
fmt.Println("Elements of array 2")
for p := 0; p < 2; p++ {
for q := 0; q < 2; q++ {
fmt.Println(arr1[p][q])
}
}
}
输出
Elements of Array 1
C#
C
Python
Java
Scala
Perl
C++
Go
HTML
Elements of array 2
100
200
300
400
关于数组的重要观察
在一个数组中,如果一个数组没有明确地初始化,那么 这个数组的默认值是0 .
例子
// Go program to illustrate an array
package main
import "fmt"
func main()
{
// Creating an array of int type
// which stores, two elements
// Here, we do not initialize the
// array so the value of the array
// is zero
var myarr[2] int fmt.Println("Elements of the Array: ", myarr)
}
输出
Elements of the Array : [0 0]
在一个数组中,你可以 用len()方法找到数组的长度 ,如下所示。
例子
// Go program to illustrate how to find
// the length of the array
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// Creating array
// Using shorthand declaration
arr1:= [3]int{9,7,6}
arr2:= [...]int{9,7,6,4,5,3,2,4}
arr3:= [3]int{9,3,5}
// Finding the length of the
// array using len method
fmt.Println("Length of the array 1 is:", len(arr1))
fmt.Println("Length of the array 2 is:", len(arr2))
fmt.Println("Length of the array 3 is:", len(arr3))
}
输出
Length of the array 1 is: 3
Length of the array 2 is: 8
Length of the array 3 is: 3
在一个数组中, 如果省略号’…’在长度处可见,那么数组的长度就由初始化的元素决定。如下面的例子所示。
例子
// Go program to illustrate the
// concept of ellipsis in an array
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// Creating an array whose size is determined
// by the number of elements present in it
// Using ellipsis
myarray:= [...]string{"GFG", "gfg", "geeks",
"GeeksforGeeks", "GEEK"}
fmt.Println("Elements of the array: ", myarray)
// Length of the array
// is determine by
// Using len() method
fmt.Println("Length of the array is:", len(myarray))
}
输出
Elements of the array: [GFG gfg geeks GeeksforGeeks GEEK]
Length of the array is: 5
在一个数组中, 你可以在数组元素的范围内进行迭代。 如下面的例子所示:
例子
// Go program to illustrate
// how to iterate the array
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// Creating an array whose size
// is represented by the ellipsis
myarray:= [...]int{29, 79, 49, 39,
20, 49, 48, 49}
// Iterate array using for loop
for x:=0; x < len(myarray); x++{
fmt.Printf("%d\n", myarray[x])
}
}
输出
29
79
49
39
20
49
48
49
在Go语言中, 数组是值类型而不是引用类型。 所以当数组被分配到一个新的变量时,那么在新变量中的变化不会影响到原来的数组。正如下面的例子所示:
例子
// Go program to illustrate value type array
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// Creating an array whose size
// is represented by the ellipsis
my_array:= [...]int{100, 200, 300, 400, 500}
fmt.Println("Original array(Before):", my_array)
// Creating a new variable
// and initialize with my_array
new_array := my_array
fmt.Println("New array(before):", new_array)
// Change the value at index 0 to 500
new_array[0] = 500
fmt.Println("New array(After):", new_array)
fmt.Println("Original array(After):", my_array)
}
输出
Original array(Before): [100 200 300 400 500]
New array(before): [100 200 300 400 500]
New array(After): [500 200 300 400 500]
Original array(After): [100 200 300 400 500]
在一个数组中,如果数组的元素类型是可比的,那么数组的类型也是可比的。所以 我们可以直接用==操作符来比较两个数组。 如下面的例子所示。
例子
// Go program to illustrate
// how to compare two arrays
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// Arrays
arr1:= [3]int{9,7,6}
arr2:= [...]int{9,7,6}
arr3:= [3]int{9,5,3}
// Comparing arrays using == operator
fmt.Println(arr1==arr2)
fmt.Println(arr2==arr3)
fmt.Println(arr1==arr3)
// This will give and error because the
// type of arr1 and arr4 is a mismatch
/*
arr4:= [4]int{9,7,6}
fmt.Println(arr1==arr4)
*/
}
输出
true
false
false
 极客教程
极客教程