C++程序 寻找链表长度
编写一个函数来计算给定单链表中的节点数。
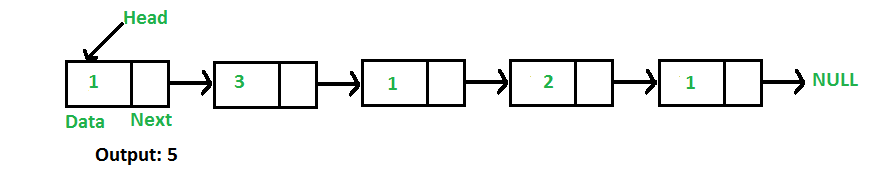
例如,该函数应该为连接列表1->3->1->2->1返回5。
迭代解决方案:
1)将计数初始化为0
2)将节点指针current =head初始化。
3)只要当前不为NULL,就执行以下操作
a)当前= current -> next
b) count ++;
4)返回计数
以下是实现上述算法以查找给定单链表中节点计数的迭代实现。
// 迭代C ++程序以查找链表中的节点长度
//或计数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//链接列表节点
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
/*给定参考(指向指针)
列表的头和一个int, push
在列表的前面推一个新节点。*/
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
//分配节点
Node* new_node =new Node();
//放入数据
new_node->data = new_data;
//链接新节点的旧列表
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
//将头移动到
//新节点
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
//按链接列表计算节点数
int getCount(Node* head)
{
//初始化计数
int count = 0;
//初始化当前
Node* current = head;
while (current != NULL)
{
count ++;
current = current->next;
}
返回计数;
}
//驱动程序
int main()
{
//从空列表开始
Node* head = NULL;
//使用push()构建列表
// 1->2->1->3->1
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
//检查计数函数
cout << "节点数为" <<
getCount(head);
返回0;
}
//此代码由rathbhupendra提供```
输出:
节点数为5
时间复杂度: O(n),其中n表示给定链表的长度。
辅助空间: O(1),不需要额外的空间,因此它是常数。
递归解决方案:
int getCount(head)
1)如果头为NULL,则返回0。
2)否则返回1 + getCount(head->next)
以下是实现上述算法以查找给定单链表中节点计数的递归实现。
// 使用递归方法计算单链表的长度或节点数的C++程序
// 见到英文不要慌,后面有中文翻译哦。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// 单链表的节点
class Node
{
public:
int data; //数据域
Node* next; //指针域
};
/* 在单链表的头节点前插入新节点
@head_ref: 指向头节点指针的指针
@new_data: 待插入节点的数据
*/
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// 创造新节点
Node* new_node = new Node();
// 插入数据
new_node->data = new_data;
// 对新节点的链表进行链接
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// 将head指向新节点
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// 利用递归方法计算单链表的节点数
int getCount(Node* head)
{
// 基本情况
if (head == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
// 计算当前节点加余下链接的节点数
else
{
return 1 + getCount(head->next);
}
}
// 主函数
int main()
{
// 初始化空的单链表
Node* head = NULL;
// 使用push函数构建单链表
// 1->2->1->3->1
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
// 输出节点数
cout << "单链表的节点数是 " <<
getCount(head);
return 0;
}
// 代码由 rajsanghavi9 提供```
输出:
单链表的节点数是 5
时间复杂度: O(n),其中n表示单链表的长度。
空间复杂度: O(n),其中n表示单链表的长度。
 极客教程
极客教程