C++程序 将数组左旋d个元素
给定大小为 N 的整数数组 arr[] 和整数,任务是将数组元素向 左 旋转 d 个位置。
例子:
输入:
arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7},d = 2
输出: 3 4 5 6 7 1 2
输入: arr[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2},d=2
输出: 5 6 7 1 2 3 4
方法1(使用临时数组): 这个问题可以使用下面的思路来解决:
将元素向左旋转 d 个位置后,第一个 d 个元素会成为数组的最后 d 个元素。
- 首先将原数组第 d 个到第 N-1 个元素的值存储到临时数组中。
- 然后将原数组的前 d 个元素的值存储到临时数组中。
- 将临时数组中的元素复制回原数组中。
说明:
假设给定数组为 arr[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] , d = 2 。
第一步:
=> 将第2个元素到最后的元素存储到临时数组中。
=> temp[] = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
第二步:
=> 现在将原始数组的前2个元素存储到temp[]数组中。
=> temp[] = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2]
第三步:
=> 将temp[]数组的元素复制回原始数组中。
=> arr[] = temp[] 所以 arr[] = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2]
按照以下步骤解决给定问题。
- 初始化一个与原始数组长度相同的临时数组( temp[n] )
- 初始化一个整数( k )来跟踪当前索引
- 将位置为 d 到 n-1 的元素存储到临时数组中
- 现在,将原始数组的前 0 到 d-1 个元素存储到临时数组中。
- 最后,将临时数组复制回原始数组。
下面是上述方法的实现:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// 旋转数组的函数
void Rotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
// 保存旋转后的数组版本
int temp[n];
// 记录 temp[] 的当前索引
int k = 0;
// 将数组 arr[] 的前 n-d 个元素存储到 temp[] 的前面
for (int i = d; i < n; i++) {
temp[k] = arr[i];
k++;
}
// 将数组 arr[] 的前 d 个元素存储到 temp[] 的后面
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) {
temp[k] = arr[i];
k++;
}
// 复制 temp[] 中的元素到数组 arr[],得到最终旋转后的数组
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = temp[i];
}
}
// 打印数组元素的函数
void PrintTheArray(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
}
// 主函数
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int d = 2;
// 调用函数
Rotate(arr, d, N);
PrintTheArray(arr, N);
return 0;
}
输出
3 4 5 6 7 1 2
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅空间复杂度: O(N)
方法 2(逐个旋转): 这个问题可以使用以下思路解决:
- 在每次迭代时,将数组向左循环移动一个位置(即,第一个元素变为最后一个元素)。
- 执行此操作 d 次,将元素向左旋转 d 个位置。
举例:
让我们取 arr[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7] 、 d = 2 为例。
第一步:
=> 向左旋转一个位置。
=> arr[] = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1}
第二步:
=> 再次向左旋转一个位置。
=> arr[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2}
旋转了 2 次。
所以数组变为 arr[] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2}
具体步骤如下:
- 将数组向左循环移动一个位置。具体步骤如下:
- 将数组的第一个元素存储到一个临时变量中。
- 将原始数组中的其余元素向左移动一个位置。
- 更新数组的最后一个索引为临时变量的值。
- 按照所需的左旋转次数重复上述步骤。
下面是实现上述思路的代码:
// C++ program to rotate an array by
// d elements
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/*Function to left rotate arr[] of size n by d*/
void Rotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
int p = 1;
while (p <= d) {
int last = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
}
arr[n - 1] = last;
p++;
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int d = 2;
// Function calling
Rotate(arr, d, N);
printArray(arr, N);
return 0;
}
输出
3 4 5 6 7 1 2
时间复杂度: O(N*d)
辅助空间: O(1)
方法 3 (Juggling算法): 这是方法 2 的扩展。
不是一个一个移动,而是将数组分成不同的集合,其中集合的数量等于N和d的最大公约数(假设为X,因此距离X个位置的元素是集合的一部分),并将元素在集合内向左旋转1个位置。
- 计算长度和要移动的距离之间的最大公约数。
- 元素仅在集合内移动。
- 我们从temp = arr [0]开始,不断将arr [I + d]移动到arr [I],最后将temp存储到正确的位置。
按照下面的示例进行更好的理解。
案例:
以下是每个步骤的外观:
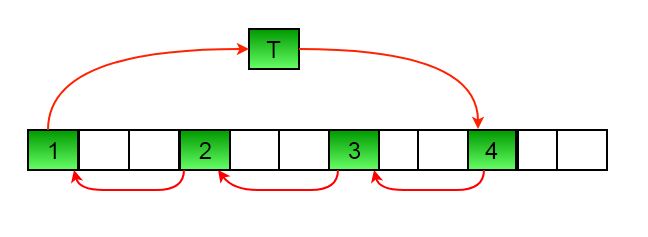
让 arr[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14} 和 d = 10
第一步:
=> 第一组是 {0, 5, 10}.
=> 将此集合按循环顺序左旋d个位置
=> arr [0] = arr [0 + 10]
=> arr [10] = arr [(10 + 10)% 15]
=> arr [5] = arr [0]
=>该集合变为 {10,0,5}
=> 数组 arr[] = {10, 1, 2, 3, 4, 0, 6, 7, 8, 9, 5, 11, 12, 13, 14}
第二步:
=> 第二组是 {1, 6, 11}.
=> 将此集合按循环顺序左旋d个位置
=>该集合变为 {11, 1, 6}
=>数组 arr [] = {10, 11, 2, 3, 4, 0, 1, 7, 8, 9, 5, 6, 12, 13, 14}
第三步:
=> 第二组是 {2, 7, 12}.
=> 将此集合按循环顺序左旋d个位置
=>该集合变为 {12, 2, 7}
=> 数组 arr[] = {10, 11, 12, 3, 4, 0, 1, 2, 8, 9, 5, 6, 7, 13, 14}
第四步:
=> 第二组是 {3, 8, 13}.
=> 将此集合按循环顺序左旋d个位置
=>该集合变为 {13, 3, 8}
=> 数组 arr[] = {10, 11, 12, 13, 4, 0, 1, 2, 3, 9, 5, 6, 7, 8, 14}
第五步:
=> 第二组是 {4, 9, 14}.
=> 将此集合按循环顺序左旋d个位置
=>该集合变为 {14, 4, 9}
=> 数组 arr[] = {10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
按照以下步骤解决给定的问题。
- 执行 d%n 以使 d 的值保持在数组范围内,其中 d 是数组旋转的次数,而 N 是数组的大小。
- 计算 GCD(N,d) 以将数组分成集合。
- 从0到GCD获得的值运行for循环。
- 在临时变量中存储 arr [i] 的值( i 的值表示 集合编号 )。
- 运行while循环以根据集更新值。
- 退出while循环后,将 arr [j] 的值分配为临时变量的值( j 的值表示第 **i th ** 集的最后一个元素)。
以下是上述方法的实现:
// C++ program to rotate an array by
// d elements
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/*Function to get gcd of a and b*/
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
else
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
/*Function to left rotate arr[] of size n by d*/
void leftRotate(int arr[], int d, int n)
{
/* To handle if d >= n */
d = d % n;
int g_c_d = gcd(d, n);
for (int i = 0; i < g_c_d; i++) {
/* move i-th values of blocks */
int temp = arr[i];
int j = i;
while (1) {
int k = j + d;
if (k >= n)
k = k - n;
if (k == i)
break;
arr[j] = arr[k];
j = k;
}
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function calling
leftRotate(arr, 2, n);
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
输出:
3 4 5 6 7 1 2
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)
方法4:使用Collections模块
Python模块有一个名为“collections”的模块,它提供各种数据结构。其中之一是“deque“。
deque也称为双向队列。模块还提供不同的内置方法之一是“rotate”。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
int main() {
deque<int> dq {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
int d = 2;
// Rotate the deque left by d elements
for(int i=0; i<d; i++) {
int temp = dq.front();
dq.pop_front();
dq.push_back(temp);
}
// Print the rotated deque
for(auto it=dq.begin(); it!=dq.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
return 0;
}
输出:
deque([3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2])
时间复杂度: 代码的时间复杂度为O(d * n),其中d是旋转次数,n是deque大小。
辅助空间为O(n),其中n是deque的大小。
 极客教程
极客教程