如何在C++中动态分配一个三维数组
在C/C++中,多维数组简单地说是指数组的数组。多维数组中的数据以表格形式存储(按行主序存储)。下面是声明 N维数组 的一般形式:
多维数组的语法:
data_type array_name[size1][size2]….[sizeN];
data_type: 数组中存储的数据类型。
这里的data_type是有效的C/C++数据类型。
array_name: 数组名
size1、size2、…、sizeN: 维度的大小
3-D数组是一个双重数组的数组:
3D数组的语法:
data_type array_name[x][y][z];
data_type:要存储的数据类型。有效的C/C++数据类型。
有关多维和三维数组的更多详细信息,请参阅C++中的多维数组文章。
问题: 给定一个三维数组,任务是使用C++中的new动态分配内存。
解答: 下面的方法使用两个有3行4列的二维数组,每个二维数组。其值如下:
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24
X= 2D数组的数量。
Y= 每个2D数组的行数。
Z= 每个2D数组的列数。
方法1: 使用单指针-在此方法中,分配大小为 x*y*z 的内存块,然后使用指针算术访问内存块。下面是相同的程序:
// C++ program to dynamically allocate
// the memory for 3D array in C++
// using new operator
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Dimensions of the 3D array
int x = 2, y = 3, z = 4;
int count = 0;
// Allocate memory blocks
// of size x*y*z
int* a = new int[x * y * z];
// Traverse the 3D array
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
// Assign values to the
// memory blocks created
*(a + i * y * z + j * z + k) = ++count;
}
}
}
// Traverse the 3D array again
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
// Print values of the
// memory blocks created
cout << *(a + i * y * z + j * z + k) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Deallocate memory
delete[] a;
return 0;
}
输出:
1 2 3 4
5 6 78
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24
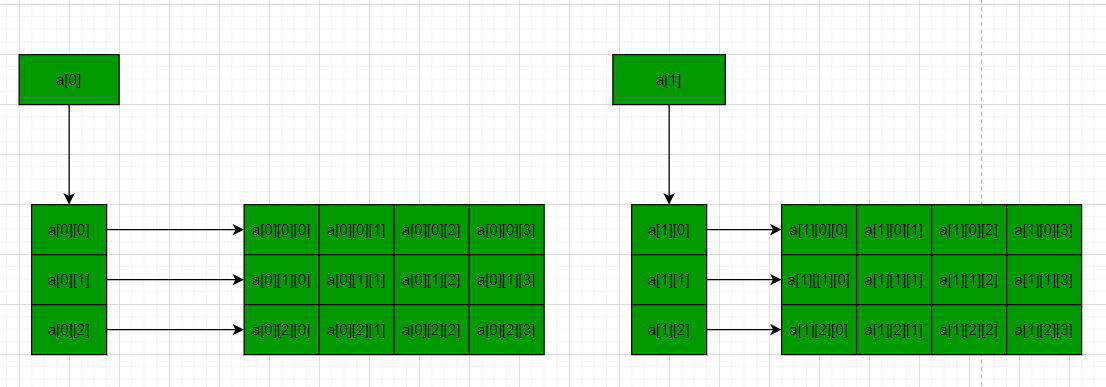
方法2: 使用三重指针-下面是说明该概念的图表:
以下是相同的程序:
// C++程序用new运算符为C++中的3D数组动态分配内存
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 驱动程序
int main()
{
// 3D数组的维度
int x = 2, y = 3, z = 4;
int count = 0;
// 分配大小为x的内存块,即2D数组的数量
int*** a = new int**[x];
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
// 为每个2D数组的行分配内存块
a[i] = new int*[y];
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
// 为每个2D数组的列分配内存块
a[i][j] = new int[z];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
// 将值分配给创建的内存块
a[i][j][k] = ++count;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < z; k++) {
// 打印创建的内存块的值
cout << a[i][j][k] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
// 释放内存
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++) {
delete[] a[i][j];
}
delete[] a[i];
}
delete[] a;
return 0;
}
输出:
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24
 极客教程
极客教程