Python os.lchown()
Python os模块中的所有函数在文件名和路径无效或不可访问,或其他具有正确类型但操作系统不接受的参数时都会引发OSError。
Python中的os.lchown()方法用于将指定文件路径的所有者和组id更改为指定的数字所有者id (UID)和组id (GID)。该方法不遵循符号链接,相当于os.chown(path, uid, gid, follow_symlinks = False)方法。
注意:os.lchown()方法只在UNIX平台上可用,而且此方法的功能通常只对超级用户或特权用户可用。
语法:os.lchown(pth, uid, gid)
参数:
path:一个类似路径的对象,表示要设置所有权的文件路径。
uid:一个整数值,表示要为文件设置的所有者id。
gid:一个整数值,表示要为文件设置的组id。
返回类型:此方法不返回任何值。
示例1
使用os.lchown()方法
# Python program to explain os.lchown() method
# importing os module
import os
# File path
path = "./file.txt"
# Print the current owner id
# and group id of the file
# os.stat() method will return a
# 'stat_result’ object of
# ‘os.stat_result’ class whose
# 'st_uid' and 'st_gid' attributes
# will represent owner id and group id
# of the file respectively
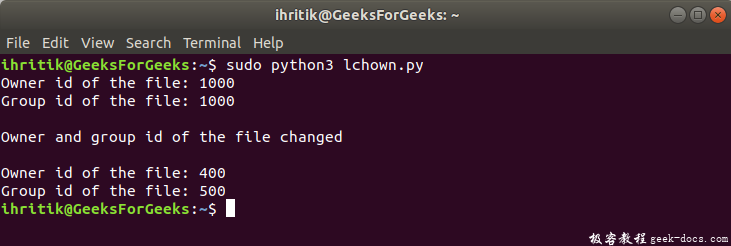
print("Owner id of the file:", os.stat(path).st_uid)
print("Group id of the file:", os.stat(path).st_gid)
# Change the owner id and
# the group id of the file
# using os.lchown() method
uid = 400
gid = 500
os.lchown(path, uid, gid)
print("\nOwner and group id of the file changed")
# Print the owner id
# and group id of the file
print("\nOwner id of the file:", os.stat(path).st_uid)
print("Group id of the file:", os.stat(path).st_gid)
输出:
示例2
使用os.lchown()方法设置任意一个id,其他id保持不变。
# Python program to explain os.lchown() method
# importing os module
import os
# File path
path = "./file.txt"
# Print the current owner id
# and group id of the file
# os.stat() method will return a
# 'stat_result’ object of
# ‘os.stat_result’ class whose
# 'st_uid' and 'st_gid' attributes
# will represent owner id and group id
# of the file respectively
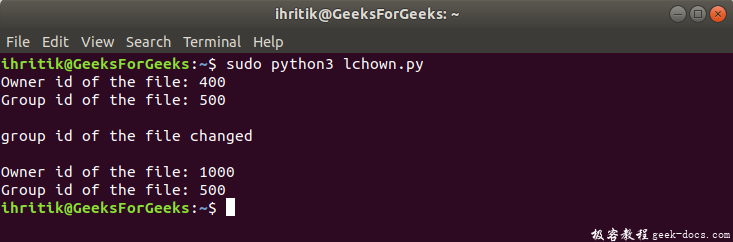
print("Owner id of the file:", os.stat(path).st_uid)
print("Group id of the file:", os.stat(path).st_gid)
# Change only group id of
# the file and leave
# owner id unchanged
# set id as -1 to leave
# it unchanged
uid = 1000
gid = -1
os.lchown(path, uid, gid)
print("\ngroup id of the file changed")
# Print the owner id
# and group id of the file
print("\nOwner id of the file:", os.stat(path).st_uid)
print("Group id of the file:", os.stat(path).st_gid)
输出:
示例3
如果指定的路径是符号链接
# Python program to explain os.lchown() method
# importing os module
import os
# File path
path = "./file.txt"
# Creating a symlink
# of the above path
# using os.symlink() method
symlink = "file(symlink).txt"
os.symlink(path, symlink)
# Print the current owner id
# and group id of the file
# as well as the symlink pointing
# to the above specified file path
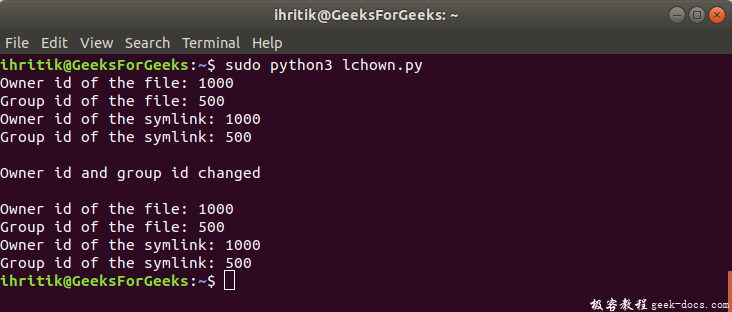
print("Owner id of the file:", os.stat(path).st_uid)
print("Group id of the file:", os.stat(path).st_gid)
print("Owner id of the symlink:", os.stat(symlink).st_uid)
print("Group id of the symlink:", os.stat(symlink).st_gid)
# Change the ownership
# of the symlink pointing
# to the above file 'file.txt'
uid = 600
gid = 700
os.lchown(symlink, uid, gid)
print("\nOwner id and group id changed")
# Print the owner id
# and group id of the file
# as well as the symlink pointing
# to the above specified file path
print("\nOwner id of the file:", os.stat(path).st_uid)
print("Group id of the file:", os.stat(path).st_gid)
print("Owner id of the symlink:", os.stat(symlink).st_uid)
print("Group id of the symlink:", os.stat(symlink).st_gid)
# As os.lchown() method
# does not follow symlinks
# so, we can not change the
# owner and group id
# through a symlink
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程