Perl 文件处理简介
在Perl中,一个FileHandle将一个名字与一个外部文件联系起来,这个名字可以一直使用到程序结束或FileHandle被关闭为止。简而言之,FileHandle就像一个连接,可以用来修改一个外部文件的内容,并给这个连接(FileHandle)起了一个名字,以便更快访问和方便。
Perl中的三个基本FileHandle是STDIN、STDOUT和STDERR,它们分别代表标准输入、标准输出和标准错误设备。
文件处理通常是通过open函数完成的。
语法:open(FileHandle, Mode, FileName)
参数。
- FileHandle-文件的引用,可以在程序中使用,也可以在程序关闭前使用。
- Mode–要打开文件的模式。
- FileName- 要打开的文件的名称。
另外,Mode和FileName可以结合在一起,形成一个单一的打开表达式。
语法:open(FileHandle, Expression);
参数:
- FileHandle- 对文件的引用,可以在程序中使用,也可以在程序结束前使用。
- Expression–模式和 FileName 结合在一起。
使用close函数关闭FileHandle。
语法:close(FileHandle);
参数
- FileHandle- 要关闭的 FileHandle。
使用FileHandle从文件中读取和写入文件
从FileHandle中读取文件可以通过print函数完成。
语法:print(<FileHandle>);
参数。
- FileHandle- 以读取模式或类似模式打开的文件柄。
写入文件也可以通过print函数完成。
语法:打印 FileHandle 字符串
参数:
- FileHandle- 在写模式或类似模式下打开的文件柄。
- String- 要插入文件中的字符串。
文件处理的不同模式
| 模式 | 解释 |
|---|---|
< |
只读模式 |
> |
创建文件(如果需要),清除文件的内容并写入文件 |
>> |
创建文件(如有必要),添加到文件中 |
+< |
读取和写入,但不创建 |
+> |
创建文件(如果需要),清除,读和写 |
+>> |
创建文件(如有必要),读取和添加 |
例子:
考虑一个包含 “Welcome to GeeksForGeeks!!!”字符串的Hello.txt文件。
- **Mode = “ <” **
这是只读模式。该模式用于从文件中逐行读取内容。
#!/usr/bin/perl
# Opening a File in Read-only mode
open(r, "<", "Hello.txt");
# Printing content of the File
print(<r>);
# Closing the File
close(r);
输出:

- **Mode = “ >” **
这是只写模式。一旦以这种模式打开文件,文件的原始内容就会被清除。如果没有找到的话,它会创建一个同名的新文件。
#!/usr/bin/perl
# Opening File Hello.txt in Read mode
open(r, "<", "Hello.txt");
# Printing the existing content of the file
print("Existing Content of Hello.txt: " . <r>);
# Opening File in Write mode
open(w, ">", "Hello.txt");
# Set r to the beginning of Hello.txt
seek r, 0, 0;
print "\nWriting to File...";
# Writing to Hello.txt using print
print w "Content of this file is changed";
# Closing the FileHandle
close(w);
# Set r to the beginning of Hello.txt
seek r, 0, 0;
# Print the current contents of Hello.txt
print("\nUpdated Content of Hello.txt: ".<r>);
# Close the FileHandle
close(r);
输出:
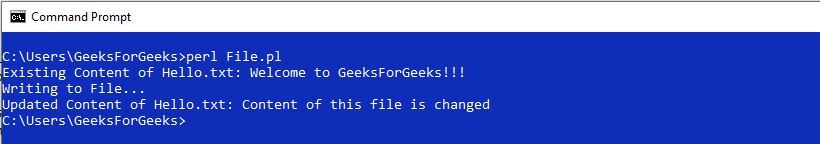
- **Mode=” >>” **
这是追加模式。当文件以这种模式打开时,文件的原始内容不会被清除。这种模式不能用来覆盖,因为字符串总是附在结尾处。如果没有找到的话,它会创建一个同名的新文件。
#!/usr/bin/perl
# Opening File Hello.txt in Read mode
open(r, "<", "Hello.txt");
# Printing the existing content of the file
print("Existing Content of Hello.txt: " . <r>);
# Opening the File in Append mode
open(A, ">>", "Hello.txt");
# Set r to the beginning of Hello.txt
seek r, 0, 0;
print "\nAppending to File...";
# Appending to Hello.txt using print
print A " Hello Geeks!!!";
# close the FileHandle
close(A);
# Set r to the beginning of Hello.txt
seek r, 0, 0;
# Print the current contents of Hello.txt
print("\nUpdated Content of Hello.txt: ".<r>);
# Close the FileHandle
close(r);
输出:
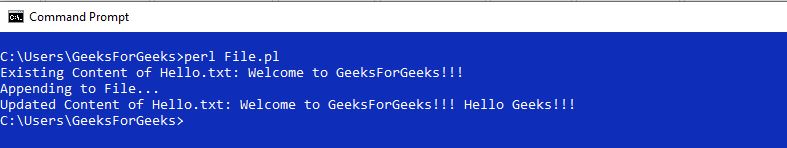
- **Mode = “+ <“ **
这是读写模式。这可以用来覆盖文件中现有的字符串。它不能创建一个新的文件。
#!/usr/bin/perl
# Open Hello.txt in Read-Write Mode
open(rw, "+<", "Hello.txt");
# Print original contents of the File.
# rw is set to the end.
print("Existing Content of Hello.txt: ".<rw>);
# The string is attached at the end
# of the original contents of the file.
print rw "Added using Read-Write Mode.";
# Set rw to the beginning of the File for reading.
seek rw, 0, 0;
# Printing the Updated content of the File
print("\nUpdated contents of Hello.txt: ".<rw>);
# Close the FileHandle
close(rw);
输出:
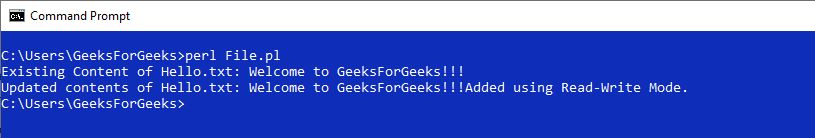
- **Mode = “+ >” **
这是读写模式。+<和 +>之间的区别是,+>可以创建一个新的文件,如果没有找到与之同名的文件,但 +<不能。
#!/usr/bin/perl
# Opening File Hello.txt in Read mode
open(r, "<", "Hello.txt");
# Printing the existing content of the file
print("Existing Content of Hello.txt: " . <r>);
# Closing the File
close(r);
# Open Hello.txt in Read-Write Mode
open(rw, "+>", "Hello.txt");
# Original contents of the File
# are cleared when the File is opened
print("\nContents of Hello.txt gets cleared...");
# The string is written to the File
print rw "Hello!!! This is updated file.";
# Set rw to the beginning of the File for reading.
seek rw, 0, 0;
print("\nUpdated Content of Hello.txt: " .<rw>);
# Closing the File
close(rw);
输出:
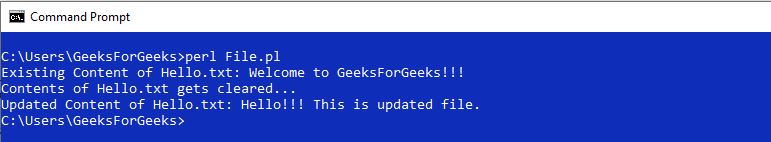
- **Mode = “+ >>” **
这是Read-Append模式。这可以用来从一个文件中读取,也可以用来追加到一个文件中。如果没有找到一个新的文件,将创建一个同名的文件。
# Open Hello.txt in Read-Append Mode
open(ra, "+>>", "Hello.txt");
# Set ra to the beginning of the File for reading.
seek ra, 0, 0;
# Original content of the File
# is NOT cleared when the File is opened
print("Existing Content of the File: " . <ra>);
print "\nAppending to the File....";
# The string is appended to the File
print ra "Added using Read-Append Mode";
# Set ra to the beginning of the File for reading.
seek ra, 0, 0;
# Printing the updated content
print("\nUpdated content of the File: " . <ra>);
# Closing the File
close(rw);
输出:
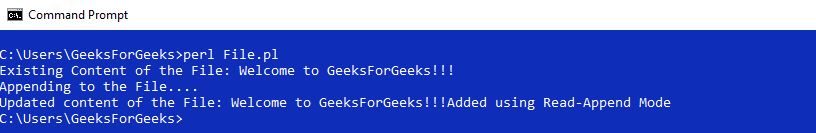
重定向输出
输出可以通过选择功能从控制台重定向到一个文件中。
语法: select FileHandle;
参数:
- FileHandle – 要选择的文件的FileHandle。
步骤:
- 打开一个要写的FileHandle,即”>”、”>”、”+<“、”+>”或 “+>>”。
- 使用select函数选择FileHandle。
现在,任何使用打印函数打印的东西都会被重定向到该文件。
例子
# Open a FileHandle in Write Mode.
open(File, ">", "Hello.txt");
# This sets File as the default FileHandle
select File;
# Writes to File
print("This goes to the File.");
# Writes to File
print File "\nThis goes to the File too.";
# This sets STDOUT as default FileHandle
select STDOUT;
print("This goes to the console.");
# Close the FileHandle.
close(File);
控制台中的输出:

Hello.txt的内容:
原始文件:

更新文件:

 极客教程
极客教程