Perl 分支 (if, if-else, Nested-if, if-elsif ladder, unless, unless-else, unless-elsif)
编程中的决策与现实生活中的决策类似。在编程中,当某些条件得到满足时,需要执行某个代码块。一种编程语言使用控制语句来控制基于某些条件的程序执行流程。这些语句被用来根据程序状态的变化使执行流前进和分支。
Perl中的决策语句:
- if
- If – else
- 嵌套 – if
- 如果 – elsif ladder
- unless
- unless–else
- Unless – elsif
if 语句
if 语句与其他编程语言相同。它用于执行基于条件的基本任务。它用于决定是否执行某个语句或语句块,即如果某个条件为真,则执行某个语句块,否则就不执行。
语法
if(condition)
{
# code to be executed
}
注意: 如果if语句没有使用大括号{ },那么在编译时就会出现错误。所以必须在if语句中使用大括号{ }。
流程图:
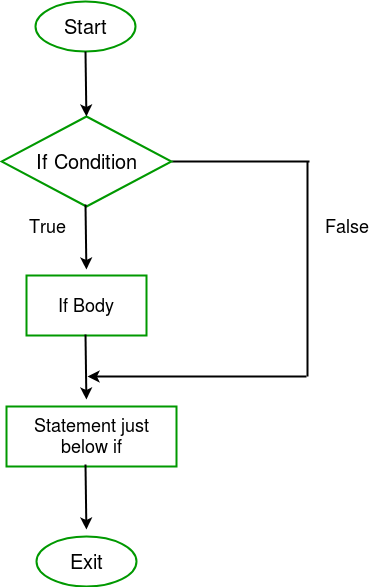
例子:
# Perl program to illustrate if statement
a = 10;
# if condition to check
# for even number
if(a % 2 == 0 )
{
printf "Even Number";
}
输出:
Even Number
if – else 语句
如果条件为真,if 语句会评估代码,但如果条件为假,else 语句就会出现。它告诉代码当if条件为假时该怎么做。
语法
if(condition)
{
# code if condition is true
}
else
{
# code if condition is false
}
流程图 :
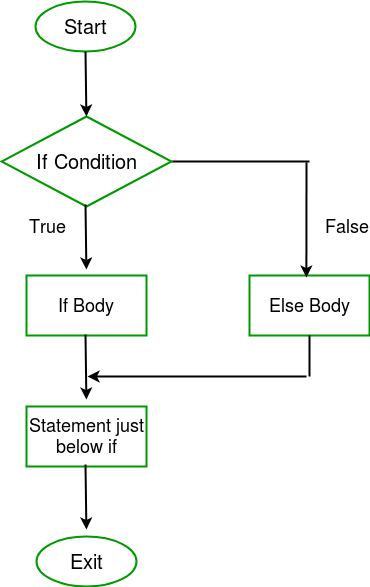
例子 :
# Perl program to illustrate
# if - else statement
a = 21;
# if condition to check
# for even number
if(a % 2 == 0 )
{
printf "Even Number";
}
else
{
printf "Odd Number\n";
}
输出:
Odd Number
嵌套–if 语句
在这种情况下,if 语句是另一个 if 或 else 语句的目标,if 语句的 内部 被称为嵌套 if。当一个以上的条件需要为真,并且其中一个条件是父条件的子条件时,可以使用嵌套if。
语法
if (condition1)
{
# Executes when condition1 is true
if (condition2)
{
# Executes when condition2 is true
}
}
流程图 :
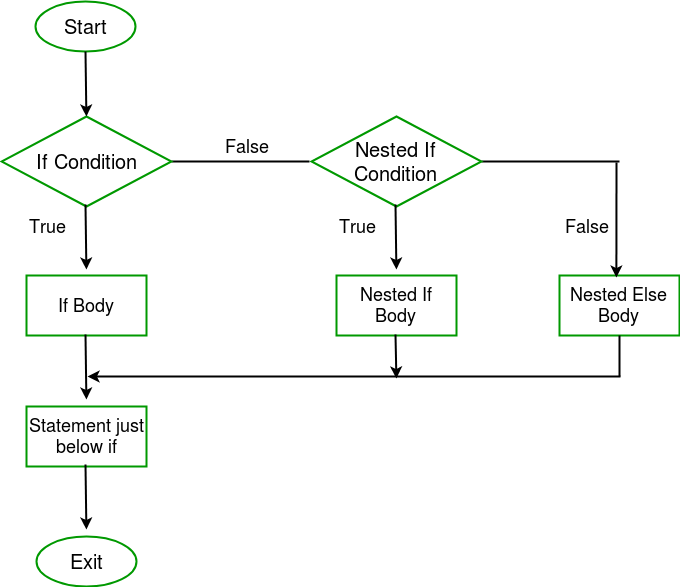
例子 :
# Perl program to illustrate
# Nested if statement
a = 10;
if(a % 2 ==0)
{
# Nested - if statement
# Will only be executed
# if above if statement
# is true
if($a % 5 == 0)
{
printf "Number is divisible by 2 and 5\n";
}
}
输出:
Number is divisible by 2 and 5
if- elsif – else 梯形语句
在这里,用户可以在多个选项中做出决定。if语句是自上而下执行的。只要控制if的条件之一为真,与之相关的语句就会被执行,梯形图的其他部分就会被绕过。如果没有一个条件为真,那么最后的else语句将被执行。
语法
if(condition1)
{
# code to be executed if condition1 is true
}
elsif(condition2)
{
# code to be executed if condition2 is true
}
elsif(condition3)
{
# code to be executed if condition3 is true
}
...
else
{
# code to be executed if all the conditions are false
}
流程图:
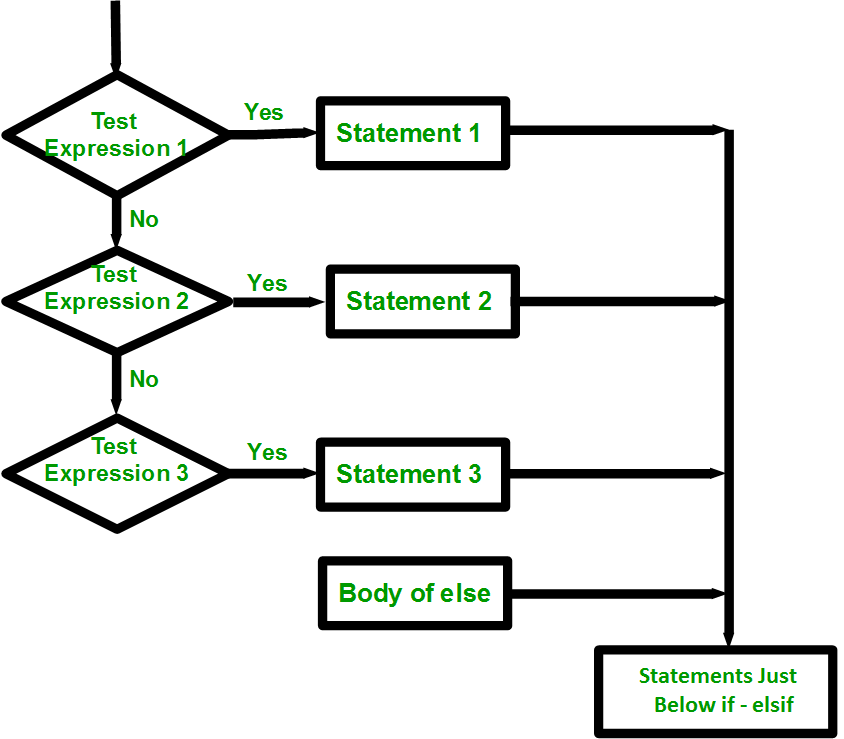
if-else-if
例子:
# Perl program to illustrate
# if - elseif ladder statement
i = 20;
if(i == 10)
{
printf "i is 10\n";
}
elsif(i == 15)
{
printf "i is 15\n";
}
elsif(i == 20)
{
printf "i is 20\n";
}
else
{
printf "i is not present\n";
}
输出:
i is 20
unless 语句
在这种情况下,如果条件是假的,那么语句将执行。 数字0、空字符串””、字符’0’、空列表()和undef 在布尔语境中都是 假的 ,其他值都是真的。
语法:
unless(boolean_expression)
{
# will execute if the given condition is false
}
流程图 :
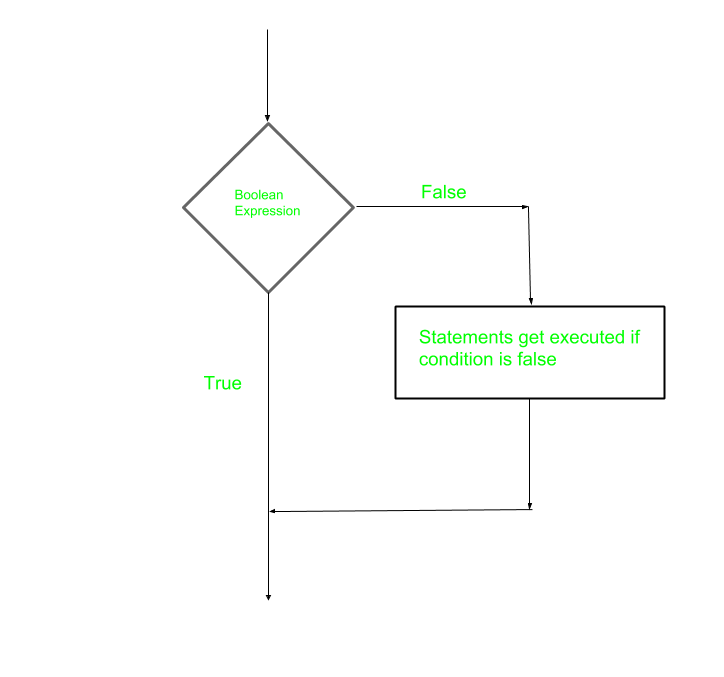
例子 :
# Perl program to illustrate
# unless statement
a = 10;
unless(a != 10)
{
# if condition is false then
# print the following
printf "a is not equal to 10\n";
}
输出:
a is not equal to 10
Unless-else 语句
Unless 语句后面可以有一个可选的else 语句,当布尔表达式为真时执行。
语法:
unless(boolean_expression)
{
# execute if the given condition is false
}
else
{
# execute if the given condition is true
}
流程图 :
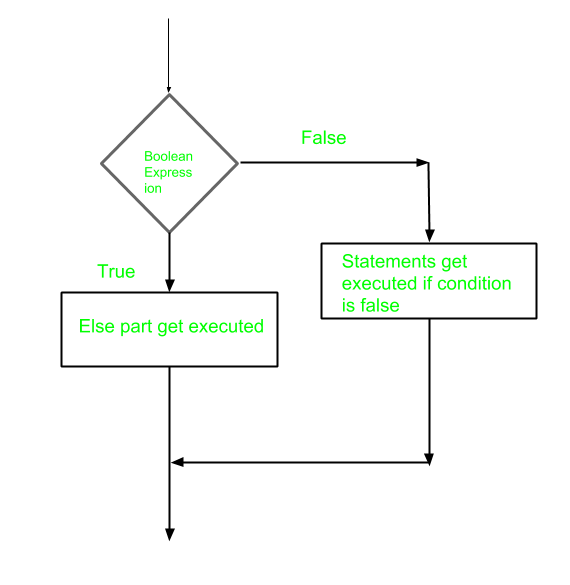
例子 :
# Perl program to illustrate
# unless - else statement
a = 10;
unless(a == 10)
{
# if condition is false then
# print the following
printf "a is not equal to 10\n";
}
else
{
# if condition is true then
# print the following
printf "a is equal to 10\n";
}
输出:
a is equal to 10
Unless – elsif 语句
Unless语句后面可以有一个可选的elsif…else语句,这对于使用单一的除非…elsif语句测试各种条件非常有用。
要记住的要点。
- Unless 语句可以有零到多个elsif,所有这些必须在else之前。
- 除非语句可以有零个或一个else,而且必须在任何elsif之后。
- 一旦一个elsif成功了,那么剩下的elsif或else都不会被测试。
语法:
unless(boolean_expression 1)
{
# Executes when the boolean expression 1 is false
}
elsif( boolean_expression 2)
{
# Executes when the boolean expression 2 is true
}
else
{
# Executes when the none of the above condition is met
}
流程图 :
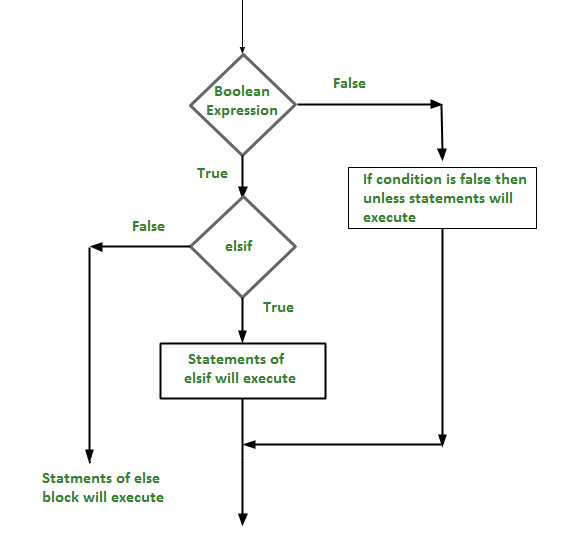
例子 :
# Perl program to illustrate
# unless - elsif statement
a = 50;
unless(a == 60)
{
# if condition is false
printf "a is not equal to 60\n";
}
elsif(a == 60)
{
# if condition is true
printf "a is equal to 60\n";
}
else
{
# if none of the condition matches
printf "The value of a isa\n";
}
输出
a is not equal to 60
输出:
a is not equal to 60
 极客教程
极客教程