如何使用node.js将单个/多个图像上传到cloudinary
Cloudinary 是一个面向网站和移动应用程序的端到端图像和视频管理解决方案,涵盖从图像和视频上传、存储、操作、优化到发布的所有功能。
安装:
- 步骤1: 进入项目目录,并在终端中使用以下命令初始化项目。
npm init -y
- 步骤2: 使用以下命令安装所需的npm包。
npm install express multer cloudinary
- 步骤3: 在当前项目目录中创建两个文件,分别命名为 index.js 和 public/index.html ,如下所示。
项目结构:
index.html: 该文件包含两个表单,分别用于单个文件和多个文件上传。
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<body style="padding: 30px;">
<form method="POST" action="/profile-upload-single"
enctype="multipart/form-data">
<div>
<label>Upload profile picture</label>
<input type="file" name="profile-file" required/>
</div>
<div>
<input type="submit" value="Upload" />
</div>
</form>
<br><hr><br>
<form method="POST" action="/profile-upload-multiple"
enctype="multipart/form-data">
<div>
<label>Upload multiple profile picture</label>
<input type="file" name="profile-files" required multiple />
</div>
<div>
<input type="submit" value="Upload" />
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
index.js: 将 cloud_name 、 api_key 、 api_secret 替换为你的 cloudinary凭证 ,你可以在 cloudinary仪表盘 上找到。
index.js
// Requiring module
const express = require("express");
const multer = require("multer");
const port = 3000;
const app = express();
const cloudinary = require("cloudinary").v2;
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
const fs = require("fs");
// Creating uploads folder if not already present
// In "uploads" folder we will temporarily upload
// image before uploading to cloudinary
if (!fs.existsSync("./uploads")) {
fs.mkdirSync("./uploads");
}
// Multer setup
var storage = multer.diskStorage({
destination: function (req, file, cb) {
cb(null, "./uploads");
},
filename: function (req, file, cb) {
cb(null, file.originalname);
},
});
var upload = multer({ storage: storage });
// Body parser configuration
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.use(express.static(__dirname + "/public"));
app.use("/uploads", express.static("uploads"));
// Cloudinary configuration
cloudinary.config({
cloud_name: "YOUR_CLOUD_NAME",
api_key: "YOUR_API_NAME",
api_secret: "YOUR_API_SECRET",
});
async function uploadToCloudinary(locaFilePath) {
// locaFilePath: path of image which was just
// uploaded to "uploads" folder
var mainFolderName = "main";
// filePathOnCloudinary: path of image we want
// to set when it is uploaded to cloudinary
var filePathOnCloudinary =
mainFolderName + "/" + locaFilePath;
return cloudinary.uploader
.upload(locaFilePath, { public_id: filePathOnCloudinary })
.then((result) => {
// Image has been successfully uploaded on
// cloudinary So we dont need local image
// file anymore
// Remove file from local uploads folder
fs.unlinkSync(locaFilePath);
return {
message: "Success",
url: result.url,
};
})
.catch((error) => {
// Remove file from local uploads folder
fs.unlinkSync(locaFilePath);
return { message: "Fail" };
});
}
function buildSuccessMsg(urlList) {
// Building success msg to display on screen
var response = `<h1>
<a href="/">Click to go to Home page</a><br>
</h1><hr>`;
// Iterating over urls of images and creating basic
// html to render images on screen
for (var i = 0; i < urlList.length; i++) {
response += "File uploaded successfully.<br><br>";
response += `FILE URL: <a href="{urlList[i]}">
{urlList[i]}</a>.<br><br>`;
response += `<img src="{urlList[i]}" /><br><hr>`;
}
response += `<br>
<p>Now you can store this url in database or
// do anything with it based on use case.</p>
`;
return response;
}
app.post(
"/profile-upload-single",
upload.single("profile-file"),
async (req, res, next) => {
// req.file is the `profile-file` file
// req.body will hold the text fields,
// if there were any
// req.file.path will have path of image
// stored in uploads folder
var locaFilePath = req.file.path;
// Upload the local image to Cloudinary
// and get image url as response
var result = await uploadToCloudinary(locaFilePath);
// Generate html to display images on web page.
var response = buildSuccessMsg([result.url]);
return res.send(response);
}
);
app.post(
"/profile-upload-multiple",
upload.array("profile-files", 12),
async (req, res, next) => {
// req.files is array of `profile-files` files
// req.body will contain the text fields,
// if there were any
var imageUrlList = [];
for (var i = 0; i{port}!
\nClick http://localhost:3000/`);
});
运行程序的步骤:
node index.js
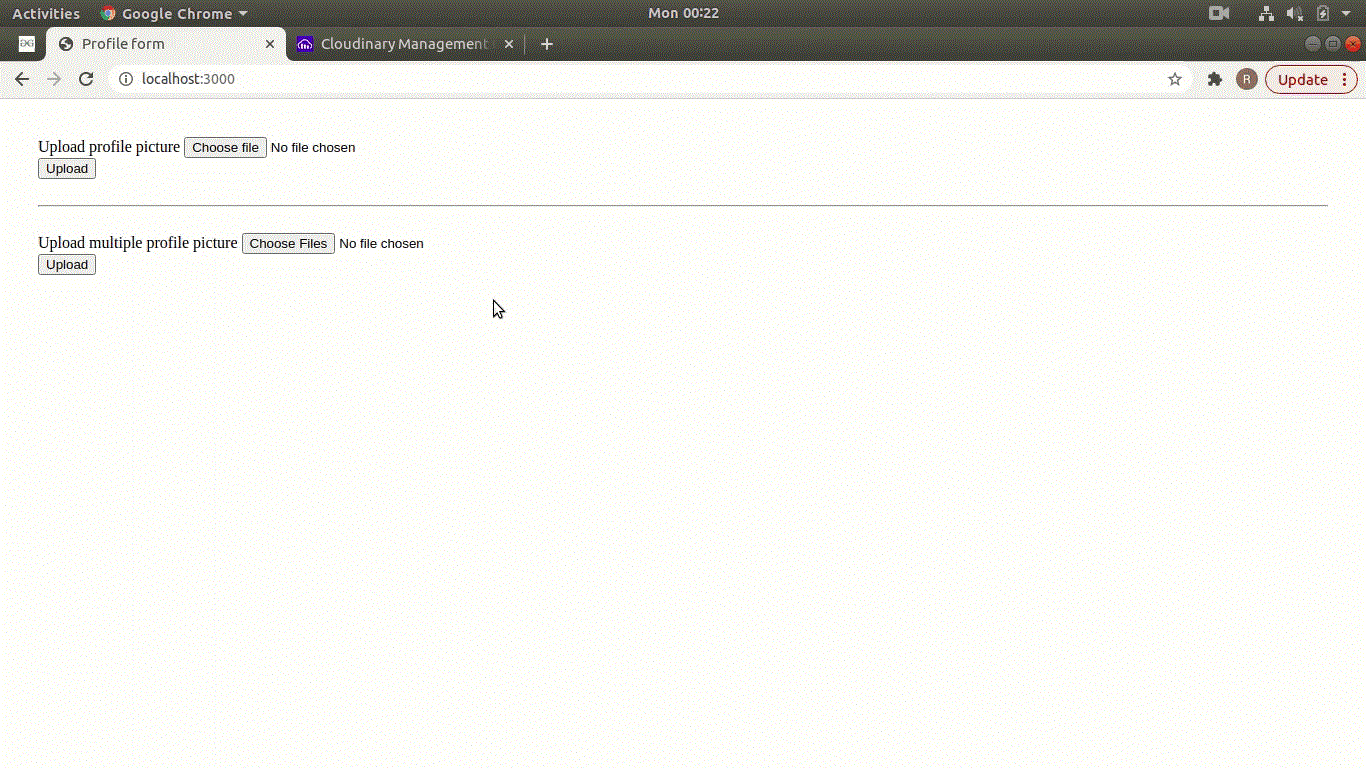
输出: 打开浏览器并访问 http://localhost:3000 。您现在可以看到下面显示的两个表单,即单个和多个图像上传。
参考资料: https://cloudinary.com/documentation/node_integration .
 极客教程
极客教程