什么是Mongoose中的SchemaType
Mongoose是一个用于MongoDB的对象数据建模(ODM)库,并且它提供了丰富的Schema类型来定义存储在MongoDB集合中的文档的结构和数据类型。
SchemaType用于定义模式中特定字段的数据类型和验证规则。
语法:
const mySchema = new mongoose.Schema({
myField: {
type: MySchemaType,
required: Boolean,
default: Any,
unique: Boolean,
min: Number,
max: Number,
enum: Array,
validate: Function
}
});
参数:
- type: 此参数用于指定字段的数据类型。例如,字符串、数字、日期等。
- required: 此参数用于指定字段是否必需。如果设置为true,如果文档中缺少该字段,Mongoose将抛出验证错误。
- default: 此参数用于为字段设置默认值。如果字段未提供值,Mongoose将使用默认值。
- unique: 此参数用于指定字段值是否应在集合中的所有文档中是唯一的。如果设置为true,如果具有相同字段值的文档已经存在,Mongoose将抛出验证错误。
- min/max: 这些参数用于为数字字段(如数字和日期)设置最小和最大值。如果字段的值超出指定范围,Mongoose将抛出验证错误。
- enum: 此参数用于指定字段的允许值列表。如果字段的值不是允许值之一,Mongoose将抛出验证错误。
- validate: 此参数用于指定字段的自定义验证函数。此函数应将字段的值作为其参数,并返回true表示该值有效,否则返回false。Mongoose在验证过程中调用此函数。
安装mongoose模块:
步骤1: 您可以使用以下命令安装此软件包。
npm install mongoose
步骤2: 安装了mongoose模块之后,你可以在命令提示符中使用以下命令检查你的mongoose版本。
npm version mongoose
步骤3: 之后,你只需要创建一个文件夹并添加一个文件,例如index.js。要运行此文件,需要运行以下命令。
node index.js
项目结构: 项目结构将如下所示:
示例1: 在这个示例中,我们为一个名为”book”的文档定义了一个Mongoose模式,其中包含书籍的标题、作者、页数、出版日期、可用性和流派等字段。我们为每个字段设置了不同的参数,如required、min、default、enum等。
然后我们使用该模式创建一个Mongoose模型,并使用它创建一个新的文档对象book,并为每个字段赋值。然后,我们调用save()方法将文档保存到数据库中。
Index.js
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
mongoose.set("strictQuery", true);
mongoose
.connect("mongodb://localhost:27017/geeksforgeeks", {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
})
.then(() => console.log("Connected to MongoDB"))
.catch((err) =>
console.error("Error connecting to MongoDB:", err));
// Define a Mongoose schema
const bookSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
author: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
pageCount: {
type: Number,
min: 1,
required: true,
},
publishedDate: {
type: Date,
default: Date.now,
},
isAvailable: {
type: Boolean,
default: true,
},
genres: {
type: [String],
enum: [
"Fiction",
"Non-Fiction",
"Biography",
"History",
"Science Fiction",
"Comedy",
],
},
});
// Create a Mongoose model using the schema
const Book = mongoose.model("Book", bookSchema);
// Create a new document using the model
const book = new Book({
title: "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
author: "Douglas Adams",
pageCount: 215,
isAvailable: false,
genres: ["Science Fiction", "Comedy"],
});
// Save the document to the database
book.save(function (err, savedBook) {
if (err) {
console.log("Error saving book:", err);
} else {
console.log("Book saved successfully:", savedBook);
}
});
使用以下命令运行index.js文件:
node index.js
输出:
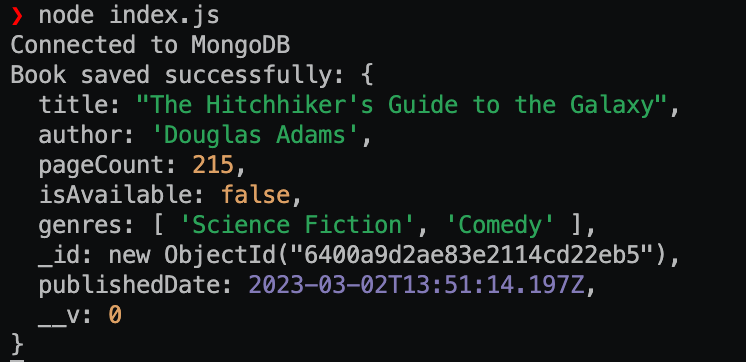
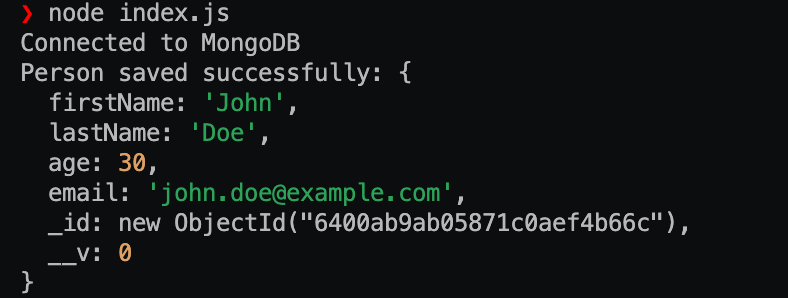
示例2: 在这个示例中,我们连接到一个MongoDB数据库并定义一个Mongoose模式来表示一个”person”文档。该模式包括名字、姓氏、年龄和电子邮件字段。
然后,我们使用该模式创建一个Mongoose模型,并根据每个字段的值创建一个新的文档对象person。最后,我们调用save()方法将文档保存到数据库中。
Index.js
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
mongoose.set("strictQuery", true);
mongoose
.connect("mongodb://localhost:27017/geeksforgeeks", {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
})
.then(() => console.log("Connected to MongoDB"))
.catch((err) =>
console.error("Error connecting to MongoDB:", err));
// Define a Mongoose schema
const personSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
firstName: String,
lastName: String,
age: Number,
email: String,
});
// Create a Mongoose model using the schema
const Person = mongoose.model("Person", personSchema);
// Create a new document using the model
const person = new Person({
firstName: "John",
lastName: "Doe",
age: 30,
email: "john.doe@example.com",
});
// Save the document to the database
person.save(function (err, savedPerson) {
if (err) {
console.log("Error saving person:", err);
} else {
console.log("Person saved successfully:", savedPerson);
}
});
使用以下命令运行 index.js 文件:
node index.js
输出:
参考: https://mongoosejs.com/docs/schematypes.html
 极客教程
极客教程