Kotlin 多个catch块,try块可以有多个catch块。当我们不确定try块内是否会发生所有异常时,为潜在的异常设置多个catch块总是一个好的做法,并且在最后一个 catch 块中有父异常类来处理未指定的剩余异常通过catch块。
Kotlin 多个catch块的例子
在下面的示例中,我们有多个catch块,但是当发生异常时,它会查找该特定异常的处理程序。
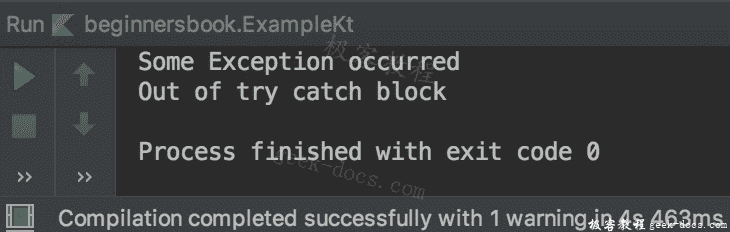
这里发生的异常是算术异常,但是前两个catch块没有处理算术异常,这就是为什么执行第三个catch块的代码。第三个块处理所有异常,因为它使用Exception类,它是所有异常类的父类。
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
try{
var num = 10/0
println(num)
}
catch(e: NumberFormatException){
println("Number format exception")
}
catch(e: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException){
println("Array index is out of range")
}
catch(e: Exception){
println("Some Exception occurred")
}
println("Out of try catch block")
}
输出:
多个catch块的另一个例子
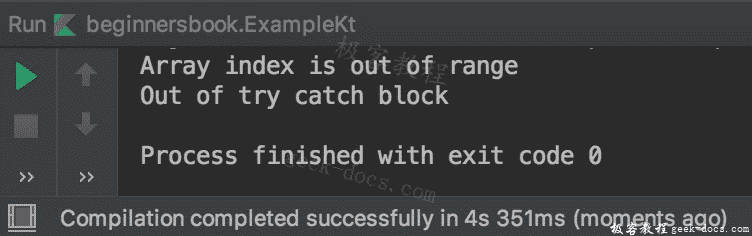
下面是多个catch块的另一个例子,这里发生了ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException,因为这个异常存在一个处理程序(catch块),执行处理程序内部的代码。
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
try{
val a = IntArray(5)
a[10] = 99
}
catch(e: ArithmeticException){
println("ArithmeticException occurred")
}
catch(e: NumberFormatException){
println("Number format exception")
}
catch(e: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException){
println("Array index is out of range")
}
catch(e: Exception){
println("Some error occurred")
}
println("Out of try catch block")
}
输出:
为什么在最后一个catch块中使用父Exception类是个好的做法
让我们采用我们上面的相同示例,但在此代码中,我们做了一个小改动。这里我们首先得到父Exception类的处理程序(catch块)。
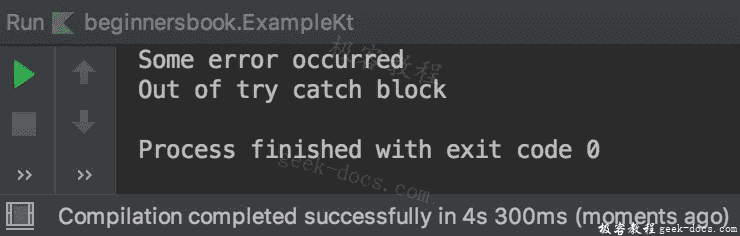
在代码中发生了ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException并且我们有这个特殊异常的处理程序,但是因为我们首先有一般的Exception类,它处理所有异常所以它被执行而不是处理ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException的catch块。
以顺序方式检查catch块,以便执行第一个catch块,实际上在任何异常的情况下,第一个catch将执行,这是一个糟糕的编程习惯,因为我们想要一个特定的消息而不是一般化的消息。因此,解决方案是在最后一个位置使用此默认处理程序,就像我们在上面的示例中所做的那样。
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
try{
val a = IntArray(5)
a[10] = 99
}
catch(e: Exception){
println("Some error occurred")
}
catch(e: ArithmeticException){
println("ArithmeticException occurred")
}
catch(e: NumberFormatException){
println("Number format exception")
}
catch(e: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException){
println("Array index is out of range")
}
println("Out of try catch block")
}
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程