Java SortedSet接口及实例
java.util包中的SortedSet接口扩展了集合框架中的Set接口。它是一个实现数学集合的接口。这个接口包含了从Set接口继承的方法,并增加了一个功能,即把所有的元素以分类的方式存储在这个接口中。
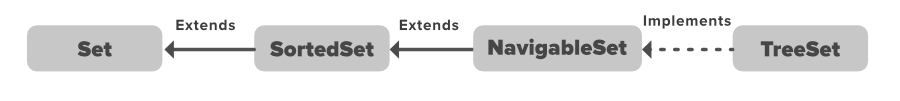
在上图中,可导航的集合扩展了排序的集合接口。由于集合并不保留插入顺序,可导航集合接口提供了在集合中导航的实现。实现可导航集合的类是TreeSet,它是自平衡树的一个实现。因此,这个接口为我们提供了一种在这个树中导航的方法。
声明: SortedSet接口被声明为。
public interface SortedSet extends Set
一个排序集的例子
// Java program to demonstrate the
// Sorted Set
import java.util.*;
class SortedSetExample{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<String> ts
= new TreeSet<String>();
// Adding elements into the TreeSet
// using add()
ts.add("India");
ts.add("Australia");
ts.add("South Africa");
// Adding the duplicate
// element
ts.add("India");
// Displaying the TreeSet
System.out.println(ts);
// Removing items from TreeSet
// using remove()
ts.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("Set after removing "
+ "Australia:" + ts);
// Iterating over Tree set items
System.out.println("Iterating over set:");
Iterator<String> i = ts.iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
}
}
输出。
[Australia, India, South Africa]
Set after removing Australia:[India, South Africa]
Iterating over set:
India
South Africa
注意: SortedSet中的所有元素都必须实现Comparable接口(或者被指定的比较器接受),并且所有这些元素必须是相互可比的。相互可比较只是意味着两个对象相互接受对方作为其compareTo方法的参数。
创建SortedSet对象
由于SortedSet是一个接口,所以不能创建SortedSet类型的对象。我们总是需要一个扩展这个列表的类来创建一个对象。而且,在Java 1.5引入泛型之后,我们可以限制可以存储在SortedSet中的对象的类型。这个类型安全的集合可以定义为。
// Obj是要存储在SortedSet中的对象的类型
SortedSet<Obj> set = new TreeSet<Obj> ();
在SortedSet上执行各种操作
由于SortedSet是一个接口,它只能与实现这个接口的类一起使用。TreeSet就是实现了SortedSet接口的类。现在,让我们看看如何在TreeSet上执行一些常用的操作。
1.添加元素: 为了向排序集添加一个元素,我们可以使用add()方法。然而,插入顺序在TreeSet中没有被保留。在内部,每一个元素的值都是按照升序进行比较和排序的。我们需要注意的是,重复的元素是不允许的,所有重复的元素都会被忽略。而且,排序集也不接受空值。
// Java code to demonstrate
// the working of SortedSet
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<String> ts
= new TreeSet<String>();
// Elements are added using add() method
ts.add("A");
ts.add("B");
ts.add("C");
ts.add("A");
System.out.println(ts);
}
}
输出。
[A, B, C]
2.访问元素: 在添加元素后,如果我们希望访问这些元素,我们可以使用内置的方法,如contains()、first()、last()等。
// Java code to demonstrate
// the working of SortedSet
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<String> ts
= new TreeSet<String>();
// Elements are added using add() method
ts.add("A");
ts.add("B");
ts.add("C");
ts.add("A");
System.out.println("Sorted Set is " + ts);
String check = "D";
// Check if the above string exists in
// the SortedSet or not
System.out.println("Contains " + check
+ " " + ts.contains(check));
// Print the first element in
// the SortedSet
System.out.println("First Value " + ts.first());
// Print the last element in
// the SortedSet
System.out.println("Last Value " + ts.last());
}
}
输出。
Sorted Set is [A, B, C]
Contains D false
First Value A
Last Value C
3.删除数值: 可以使用remove()方法将数值从排序集中删除。
// Java code to demonstrate
// the working of SortedSet
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<String> ts
= new TreeSet<String>();
// Elements are added using add() method
ts.add("A");
ts.add("B");
ts.add("C");
ts.add("B");
ts.add("D");
ts.add("E");
System.out.println("Initial TreeSet " + ts);
// Removing the element b
ts.remove("B");
System.out.println("After removing element " + ts);
}
}
输出。
Initial TreeSet [A, B, C, D, E]
After removing element [A, C, D, E]
4.遍历排序集: 有多种方法来遍历排序集。最著名的方法是使用增强的for循环。
// Java code to demonstrate
// the working of SortedSet
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<String> ts
= new TreeSet<String>();
// Elements are added using add() method
ts.add("C");
ts.add("D");
ts.add("E");
ts.add("A");
ts.add("B");
ts.add("Z");
// Iterating though the SortedSet
for (String value : ts)
System.out.print(value
+ ", ");
System.out.println();
}
}
输出。
A, B, C, D, E, Z,
实现SortedSet接口的类是TreeSet
TreeSet: 在集合框架中实现的TreeSet类是对SortedSet接口的实现,SortedSet扩展Set接口。它的行为就像一个简单的集合,不同的是它以排序的形式存储元素。TreeSet使用树形数据结构进行存储。对象是以排序后的升序存储的。但是我们可以使用TreeSet.descendingIterator()方法以降序进行迭代。让我们看看如何使用这个类来创建一个sortedset对象。
// Java program to demonstrate the
// creation of SortedSet object using
// the TreeSet class
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<String> ts
= new TreeSet<String>();
// Adding elements into the TreeSet
// using add()
ts.add("India");
ts.add("Australia");
ts.add("South Africa");
// Adding the duplicate
// element
ts.add("India");
// Displaying the TreeSet
System.out.println(ts);
// Removing items from TreeSet
// using remove()
ts.remove("Australia");
System.out.println("Set after removing "
+ "Australia:" + ts);
// Iterating over Tree set items
System.out.println("Iterating over set:");
Iterator<String> i = ts.iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
System.out.println(i.next());
}
}
输出。
[Australia, India, South Africa]
Set after removing Australia:[India, South Africa]
Iterating over set:
India
South Africa
SortedSet接口的方法
以下是SortedSet接口中的方法。这里,*代表这些方法是Set接口的一部分。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
*add(element) |
这个方法用来添加一个特定的元素到集合中。只有当指定的元素还没有出现在集合中时,该函数才会添加该元素,否则,如果该元素已经出现在集合中,该函数会返回False。 |
*addAll(collection) |
这个方法用于将所述集合中的所有元素追加到现有的集合中。这些元素是随机添加的,不遵循任何特定的顺序。 |
*clear() |
这个方法用来从集合中删除所有的元素,但不是删除集合。该集合的引用仍然存在。 |
comparator() |
这个方法返回用于对这个集合中的元素进行排序的比较器,如果这个集合使用其元素的自然排序,则返回空。 |
*contains(element) |
这个方法用来检查一个特定的元素是否存在于这个集合中。 |
*containsAll(collection) |
这个方法用来检查集合是否包含了存在于给定集合中的所有元素。如果集合包含所有的元素,该方法返回true;如果有任何元素丢失,则返回false。 |
first() |
该方法返回该集合中存在的第一个(最低)元素。 |
hashCode() |
这个方法用来获取这个Set实例的hashCode值。它返回一个整数值,这就是这个Set实例的hashCode值。 |
headSet(element) |
该方法返回排序后的集合中小于该元素的元素。 |
*isEmpty() |
该方法用于检查一个排序集是否为空。 |
last() |
该方法返回集合中存在的最后(最高)元素。 |
*remove(element) |
该方法用于从集合中删除给定的元素。如果指定的元素存在于集合中,该方法返回True,否则它返回False。 |
*removeAll(collection) |
该方法用于从集合中删除所有存在于集合中的元素。如果这个集合因调用而改变,该方法返回真。 |
*retainAll(collection) |
这个方法用于保留集合中的所有元素,这些元素在给定的集合中被提及。如果这个集合在调用后发生了变化,该方法将返回true。 |
*size() |
这个方法用来获取集合的大小。它返回一个整数值,表示元素的数量。 |
subSet(element1, element2) |
这个方法返回一个包含元素1和元素2之间的元素的排序子集。 |
tailSet(element) |
该方法返回大于或等于元素的元素,这些元素存在于排序的集合中。 |
*toArray() |
这个方法用来形成一个与Set的元素相同的数组。 |
 极客教程
极客教程