Java 非泛型与泛型集合
我们将在后面讨论两者的区别,首先让我们了解什么是泛型集合和非泛型集合,最重要的是处理好实现部分,因为在实现过程中,人们才能真正理解这个概念,因此,它们之间的区别。
泛型基本上是在编译时比在运行时出现的错误。泛型比非泛型有以下一些优点。
- 代码重用: 在泛型的帮助下,人们只需要写一次方法/类/接口,并将其用于任何类型,而在非泛型中,只要需要,就需要反复写代码。
- 类型安全: 泛型使错误在编译时出现,而不是在运行时出现(与其让你的代码在运行时失败,不如在编译时知道代码中的问题)。
例子: 创建一个存储学生姓名的ArrayList,如果程序员错误地添加了一个整数对象而不是字符串,编译器会允许它。但是,当这个数据从ArrayList中被检索时,对于非通用ArrayList来说,在运行时就会出现问题。
实现 。
例子1
// Java program to Demonstrate that Not Using Generics
// Can cause Run Time Exceptions
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an ArrayList
// Declaring object without any type specified
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
// Adding elements to the above object
// Custom input elements
al.add("Sachin");
al.add("Rahul");
// Compiler will allows this operation
al.add(10);
String s1 = (String)al.get(0);
String s2 = (String)al.get(1);
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Causes Runtime Exception
String s3 = (String)al.get(2);
}
// Catch block to handle the exceptions
catch (Exception e) {
// Display the exception
System.out.println("Exception: " + e);
}
}
}
输出
prog.java:19: warning: [unchecked] unchecked call to add(E) as a member of the raw type ArrayList
al.add("Sachin");
^
where E is a type-variable:
E extends Object declared in class ArrayList
prog.java:20: warning: [unchecked] unchecked call to add(E) as a member of the raw type ArrayList
al.add("Rahul");
^
where E is a type-variable:
E extends Object declared in class ArrayList
prog.java:23: warning: [unchecked] unchecked call to add(E) as a member of the raw type ArrayList
al.add(10);
^
where E is a type-variable:
E extends Object declared in class ArrayList
3 warnings
泛型是如何解决这个问题 的?
如果这个列表是泛型的,那么它将只接受字符串对象,而在其他情况下会抛出编译错误。
例子2
// Java Program to Illustrate Conversion of
// Runtime Exceptions into compile time errors
// Using generics
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an ArrayList
// Declaring object of string type
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<String>();
// Adding elements to the ArrayList
// Custom input elements
al.add("Sachin");
al.add("Rahul");
// Now compiler does not allow this operation
al.add(10);
String s1 = al.get(0);
String s2 = al.get(1);
String s3 = al.get(2);
}
}
输出
prog.java:24: error: incompatible types: int cannot be converted to String
al.add(10);
^
Note: Some messages have been simplified; recompile with -Xdiags:verbose to get full output
1 error
现在继续前进, 不需要单独的类型转换 。
如果不需要泛型,那么,在上面的例子中,每次从ArrayList中检索数据时,都需要进行类型转换。每次检索操作都要进行类型转换,这是一个很令人头痛的问题。如果已经知道列表中只有字符串数据,就可以避免这种情况。
例三
// Java program to Illustrate Type Casting is Needed
// Everytime in Non-Generic
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an ArrayList
// Declaring object without any type specified
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
// Adding elements to the above object
// using add() method
al.add("Sachin");
al.add("Rahul");
// For every retrieval,
// it needs to be casted to String for use
String s1 = (String)al.get(0);
String s2 = (String)al.get(1);
}
}
输出
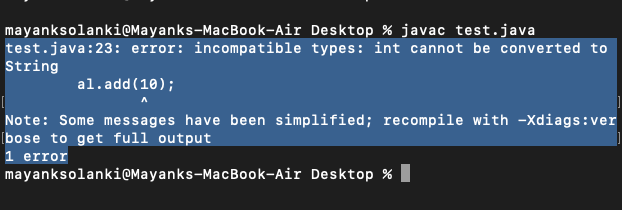
Geek , 现在你应该想知道泛型是如何解决这个问题 的?
如果这个列表是泛型的,那么它将只接受字符串对象,并且在检索时只返回字符串对象。因此就不需要单独的类型化。上面的说法是合理的
例四
// A Simple Java program to demonstrate that
// type casting is not needed in Generic
import java.util.*;
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an ArrayList
// Declaring object of type String
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<String>();
// Custom input elements
al.add("Sachin");
al.add("Rahul");
// Retrieval can be easily
// without the trouble of casting
String s1 = al.get(0);
String s2 = al.get(1);
// Print and display out the elements in objects
System.out.print(al);
}
}
输出
[Sachin, Rahul]
注意
在泛型的帮助下,人们可以实现算法 实现泛型算法,人们可以让它 在不同类型的对象上工作,同时它们也是类型安全的。
请记住,有一些要点将描述泛型和非泛型之间的区别,这些要点在下面的表格中列出,以便对它们有一个清晰的了解。
| 基础 | 非泛型集合 | 泛型集合 |
|---|---|---|
| 语法 | ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); | ArrayList |
| 类型安全 | 可以容纳任何类型的数据。因此不是类型安全的。 | 只能容纳定义的数据类型。因此是类型安全的。 |
| 类型转换 | 每次检索时都需要进行单独的类型转换。 | 不需要类型转换。 |
| 编译时检查 | 在运行时检查类型安全。 | 在编译时检查类型安全。 |
 极客教程
极客教程