Java LinkedHashSet例子
LinkedHashSet 是HashSet的一个有序版本,它在所有的元素中保持了一个双重链接的List。当需要维护迭代顺序时,可以使用这个类。当在HashSet中迭代时,顺序是不可预测的,而LinkedHashSet可以让我们按照元素插入的顺序来迭代。当使用迭代器在LinkedHashSet中循环时,元素将按照它们被插入的顺序返回。
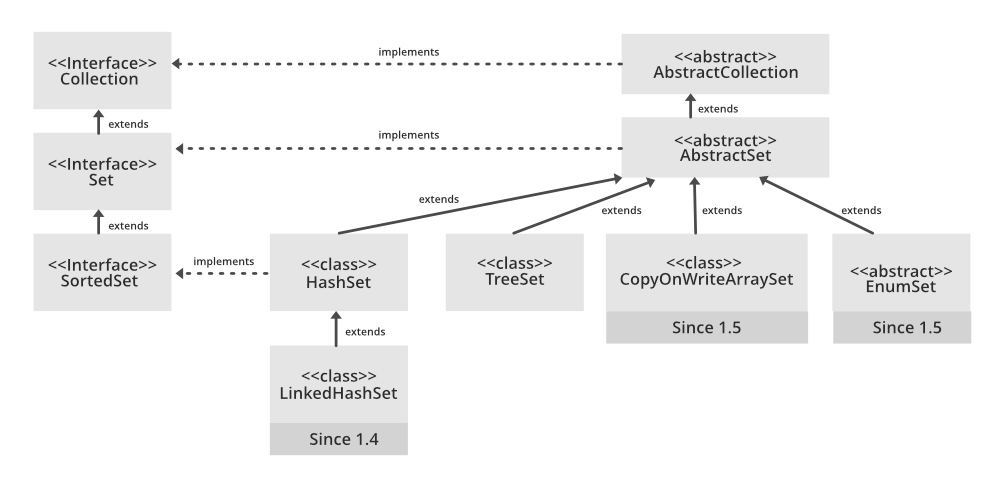
LinkedHashSet的层次结构如下 。
参数: 这个集合所维护的元素的类型
所有实现的接口如下所示。
Serializable
Cloneable,
Iterable
Collection
Set[E]
语法: 声明
public class LinkedHashSet<E> extends HashSet<E> implements Set<E>, Cloneable, Serializable
- 像HashSet一样只包含唯一的元素。它扩展了HashSet类并实现了Set接口。
- 保持插入的顺序。
LinkedHashSet类的构造函数
1.LinkedHashSet(): 这个构造函数用来创建一个默认的HashSet。
LinkedHashSet<E> hs = new LinkedHashSet<E>();
2.LinkedHashSet(Collection C): 用于用集合C的元素初始化HashSet。
LinkedHashSet<E> hs = new LinkedHashSet<E>(Collection c);
3.LinkedHashSet(int size): 用参数中提到的整数来初始化LinkedHashSet的大小。
LinkedHashSet<E> hs = new LinkedHashSet<E>(int size);
4.LinkedHashSet(int capacity, float fillRatio): 可以用来初始化LinkedHashSet的容量和填充率,也被称为LinkedHashSet的负载能力,参数中提到。当元素的数量超过哈希集的容量时,会与填充率相乘,从而扩大LinkedHashSet的容量。
LinkedHashSet<E> hs = new LinkedHashSet<E>(int capacity, int fillRatio);
例子
// Java Program to Illustrate LinkedHashSet
// Importing required classes
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
// Main class
// LinkedHashSetExample
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty LinkedHashSet of string type
LinkedHashSet<String> linkedset
= new LinkedHashSet<String>();
// Adding element to LinkedHashSet
// using add() method
linkedset.add("A");
linkedset.add("B");
linkedset.add("C");
linkedset.add("D");
// Note: This will not add new element
// as A already exists
linkedset.add("A");
linkedset.add("E");
// Getting size of LinkedHashSet
// using size() method
System.out.println("Size of LinkedHashSet = "
+ linkedset.size());
System.out.println("Original LinkedHashSet:"
+ linkedset);
// Removing existing entry from above Set
// using remove() method
System.out.println("Removing D from LinkedHashSet: "
+ linkedset.remove("D"));
// Removing existing entry from above Set
// that does not exist in Set
System.out.println(
"Trying to Remove Z which is not "
+ "present: " + linkedset.remove("Z"));
// Checking for element whether it is present inside
// Set or not using contains() method
System.out.println("Checking if A is present="
+ linkedset.contains("A"));
// Noew lastly printing the updated LinkedHashMap
System.out.println("Updated LinkedHashSet: "
+ linkedset);
}
}
输出
Size of LinkedHashSet = 5
Original LinkedHashSet:[A, B, C, D, E]
Removing D from LinkedHashSet: true
Trying to Remove Z which is not present: false
Checking if A is present=true
Updated LinkedHashSet: [A, B, C, E]
在LinkedHashSet类上执行各种操作
让我们看看如何在LinkedHashSet上执行一些常用的操作。
操作1: 添加元素
为了向LinkedHashSet添加一个元素,我们可以使用add()方法。这与HashSet不同,因为在HashSet中,插入顺序没有被保留,而在LinkedHashSet中被保留。
例子
// Java Program to Add Elements to LinkedHashSet
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// AddingElementsToLinkedHashSet
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet<String> hs = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
// Adding elements to above Set
// using add() method
// Note: Insertion order is maintained
hs.add("Geek");
hs.add("For");
hs.add("Geeks");
// Printing elements of Set
System.out.println("LinkedHashSet : " + hs);
}
}
输出
LinkedHashSet : [Geek, For, Geeks]
操作2: 删除元素
可以使用remove()方法从LinkedHashSet中删除数值。
例子
// Java program to Remove Elements from LinkedHashSet
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// RemoveElementsFromLinkedHashSet
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty LinekdhashSet of string type
LinkedHashSet<String> hs
= new LinkedHashSet<String>();
// Adding elements to above Set
// using add() method
hs.add("Geek");
hs.add("For");
hs.add("Geeks");
hs.add("A");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("Z");
// Printing all above elements to the console
System.out.println("Initial HashSet " + hs);
// Removing the element from above Set
hs.remove("B");
// Again removing the element
System.out.println("After removing element " + hs);
// Returning false if the element is not present
System.out.println(hs.remove("AC"));
}
}
输出
Initial HashSet [Geek, For, Geeks, A, B, Z]
After removing element [Geek, For, Geeks, A, Z]
false
操作3: 通过LinkedHashSet进行迭代
使用iterator()方法遍历LinkedHashSet中的元素。最著名的方法是使用增强的for循环。
例子
// Java Program to Illustrate Iterating over LinkedHashSet
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// IteratingLinkedHashSet
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate an object of Set
// Since LinkedHashSet implements Set
// Set points to LinkedHashSet
Set<String> hs = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
// Adding elements to above Set
// using add() method
hs.add("Geek");
hs.add("For");
hs.add("Geeks");
hs.add("A");
hs.add("B");
hs.add("Z");
// Iterating though the LinkedHashSet
// using iterators
Iterator itr = hs.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext())
System.out.print(itr.next() + ", ");
// New line
System.out.println();
// Using enhanced for loop for iteration
for (String s : hs)
System.out.print(s + ", ");
System.out.println();
}
}
输出
Geek, For, Geeks, A, B, Z,
Geek, For, Geeks, A, B, Z,
LinkedHashSet的方法
这里, E 是存储元素的类型。
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Spliterator() | 在这个集合中的元素上创建一个晚期绑定的、故障快速的Spliterator。 |
java.util.AbstractSet类中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| equals(Object o) | 将指定的对象与这个集合进行比较,看是否相等。 |
| hashCode() | 返回这个集合的哈希代码值。 |
| removeAll(Collection c) | 从这个集合中删除所有包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 |
java.util.AbstractCollection类中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| addAll(Collection c) | 将指定集合中的所有元素添加到这个集合中(可选操作)。 containsAll(Collection c) |
如果这个集合包含了指定集合中的所有元素,返回true。 |
| retainAll(Collection<?> c) | 只保留本集合中包含在指定集合中的元素(可选操作)。 |
| toArray() | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组。 |
| toArray(T[] a) | 返回一个包含此集合中所有元素的数组;返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型。 |
| toString() | 返回这个集合的字符串表示。 |
java.util.Collection接口中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| parallelStream() | 返回一个以该集合为源的可能的并行流。 |
| removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) | 删除这个集合中满足给定谓词的所有元素。 |
| stream() | 返回一个以该集合为源的顺序流。 |
java.util.HashSet类中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | 将指定的元素添加到这个集合中,如果它还没有存在的话。 |
| clear() | 删除这个集合中的所有元素。 |
| clone() | 返回这个HashSet实例的一个浅层拷贝:元素本身并没有被克隆。 |
| contains(Object o) | 如果这个集合包含指定的元素,返回true。 |
| isEmpty() | 如果这个集合不包含任何元素,则返回true。 |
| iterator() | 返回这个集合中的元素的迭代器。 |
| remove(Object o) | 如果指定的元素存在的话,从这个集合中删除它。 |
| size() | 返回这个集合中元素的数量(它的cardinality)。 |
java.lang.Iterable接口中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) | 对Iterable中的每个元素执行给定的动作,直到所有元素都被处理完或者该动作抛出一个异常。 |
接口java.util.Set中声明的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| add(element) | 这个方法用于将一个特定的元素添加到集合中。只有当指定的元素还没有出现在集合中时,该函数才会添加该元素,否则,如果该元素已经出现在集合中,该函数会返回False。 |
| addAll(Collection c) | 这个方法用于将所述集合中的所有元素追加到现有的集合中。这些元素是随机添加的,不遵循任何特定的顺序。 |
| clear() | 这个方法用来从集合中删除所有的元素,但不是删除集合。该集合的引用仍然存在。 |
| contains(element) | 这个方法用来检查一个特定的元素是否存在于集合中。 |
| containsAll(Collection c) | 这个方法用来检查集合是否包含了存在于给定集合中的所有元素。如果集合包含所有的元素,该方法返回true,如果有任何元素丢失,则返回false。 |
| hashCode() | 这个方法用来获取这个Set实例的hashCode值。它返回一个整数,这个整数就是这个Set实例的hashCode值。 |
| isEmpty() | 该方法用于检查该集合是否为空。 |
| iterator() | 这个方法用来返回集合的迭代器。集合中的元素将以随机顺序返回。 |
| remove(element) | 这个方法用来从集合中删除给定的元素。如果指定的元素存在于集合中,该方法返回True,否则返回False。 |
| removeAll(collection) | 该方法用于从集合中删除所有存在于集合中的元素。如果这个集合因调用而改变,该方法返回真。 |
| retainAll(collection) | 这个方法用于保留集合中的所有元素,这些元素在给定的集合中被提及。如果这个集合在调用后发生了变化,该方法将返回true。 |
| size() | 这个方法用来获取集合的大小。它返回一个整数值,表示元素的数量。 |
| toArray() | 这个方法用来形成一个与集合相同元素的数组。 |
| toArray(T[] a) | 返回一个包含这个集合中所有元素的数组;返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型。 |
下面是 LinkedHashMap 和LinkedHashSet 的 区别 。
| 类别 | LinkedHashMap | LinkedHashSet |
|---|---|---|
| 操作 | 用来存储键值对。 | 用来存储事物的集合 |
| 重复的 | 采取唯一的和不重复的键,但可以采取重复的值 | 存储没有重复的元素 |
| 执行 | HashMap | HashSet |
| 例子 | Map<String, Integer> lhm = new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>(); | Set |
注意: 在LinkedHashmap和LinkedHashset中保持插入顺序有额外的相关成本,无论是在花费额外的CPU周期还是需要更多的内存方面。如果你不需要保持插入顺序,建议使用更轻量级的HashSet和HashMap来代替。
 极客教程
极客教程